Hematoma: causes
In addition to trauma and contusions, hematoma can also be caused by other factors: impaired coagulation (thrombocytopenia, haemophilia), surgical wounds, leukemia, anticoagulant therapy (heparin, dicumarol, etc.).
Hematoma: symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of the hematoma differ according to the severity of the trauma suffered. The pain varies from mild (superficial hematomas) to acute / intense (severe / deep trauma). A mild to medium-sized hematoma fades its color from red to blue, and from purple to yellow Superficial hematomas self-resolve in a short time.
Hematoma: classification
SUBCUTANEOUS HEMATOMES are classified into: petechiae, purpura and ecchymosis
The most frequent HEMATOMAS OF THE BRAIN are: cephalohematoma, epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hematoma, subgaleal hematoma.
Among the OTHER TYPES of hematoma, we mention: otohematoma, perianal hematoma, surgical wound hematoma, sub-nail hematoma.
Hematoma: cure
The treatment of the hematoma depends on the severity of the damage suffered. Superficial hematomas tend to self-resolve within a few days: the application of ice is recommended to speed up healing. Deep hematomas must be evacuated by surgery. The hematoma sub ungueale should be treated with perforation of the nail: the blood drains from the hole and the hematoma is reabsorbed.
, more or less abundant, located outside the blood vessels. The blood, released from the circulatory system after trauma or contusions, is concentrated in a tissue or in a cavity of the organism, thus originating a hematoma.
The term hematoma comes from the Greek: the root "hemat- "refers to" blood ", while the suffix -oma (from soma) means "body".
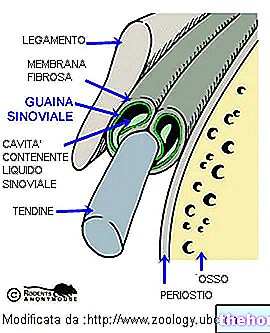
Hematomas can develop in any area of the body: inside a muscle, under the surface of the skin, in the head or brain, in the ear, in the anal region or under the nail.
The "hematoma proper must" be distinguished from ecchymosis and hemangioma:
- ecchymosis (or bruise): it is a kind of minor hematoma, characterized by the spread of blood under the skin (blood transfer is limited)
- hemangioma: is an abnormal accumulation of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs. It is precisely a form of cancer in which blood vessels proliferate in the endothelium.
But why does a hematoma form? What are the main symptoms? What types of hematoma are there? What are the treatments? In the course of the discussion, we will give an answer to these questions.
. The blood coming from the injured subcutaneous capillaries pours into the underlying tissue, where it remains imprisoned; finding no outlet, the blood causes a typical red spot on the skin, or a hematoma.The triggering causes of the hematoma are many:
- Impaired coagulation: some defects in the blood coagulation capacity - such as thrombocytopenia or haemophilia - can favor the formation of hematomas. In such circumstances, small pseudo-hematomas (better to say bruising) can occur even after minor trauma. The same symptom is found in patients taking antithrombotic drugs, such as coumadin.
- Surgery: hematoma is one of the most common complications that occur after some surgeries. A hypertensive patient, undergoing surgery, is more exposed to the risk of hematomas.
- Lesion of blood vessels already altered by pathological diseases, such as aneurysms, infections and neoplasms
- Leukemia
- Anticoagulant therapy: administration of heparin or dicumarol
- Trauma, bruises, blows: after the rupture of a blood vessel, the blood collects in the injured tissue or organ, becomes denser and causes a hematoma.
The hematoma can involve any structure of the body; the severity of the lesion depends on the type of trauma, the size of the hematoma and, above all, the anatomical site in which it occurs.
Often, it is sufficient to hit against an object to break the capillaries and originate a small hematoma: it is easy to understand that, in such situations, the hematoma certainly does not constitute a medical emergency. In other circumstances, a serious contusion can cause deep and extensive damage, therefore the hemorrhage created takes on a completely different meaning from the previous situation.
Key concepts
The severity of the hematoma depends on:
- Size of the damaged blood vessel
- Extent of the trauma
- Characteristics of the tissue in which the hematoma is formed
- Efficiency of the coagulation capacity
The elderly develop bruises more easily than the young: in fact, as the age advances, the blood vessels become more fragile and thin, therefore more exposed to the risk of rupture.
/ TENSION of the affected area and FEELING OF HEAT. Mild hematomas of this type resolve themselves in a short time, without the need for intervention.Typical of "superficial" hematomas is the variation of the color scheme. Initially, the bruise appears reddish; after a couple of days, the hematoma takes on a bluish / purplish color, sometimes black. After about a week, the hematoma becomes greenish-yellow and, after a couple of weeks, disappears completely.
The change in the color of the hematoma is due to the transformation of the heme (prosthetic group of hemoglobime) into bilirubin, the yellow-orange bile pigment derived from the catabolism of red blood cells
Some hematomas can even go unnoticed: this is the case of the classic "home accidents", in which the "collision with an object can cause a micro-hematoma (therefore a rupture of the small blood vessels), which may not be felt.
Different and more delicate speech for serious trauma: for example, a cerebral hematoma, which involves complex and imposing symptoms, requires urgent and immediate intervention.
To understand the severity of a hematoma, we distinguish two cases:
- The hematoma resolves spontaneously: typical condition of small hematomas, involving capillaries or small caliber vessels. The blood accumulated in the tissue coagulates and is slowly reabsorbed.
- The hematoma increases in volume: when the hematoma involves large blood vessels (eg arteries), the bleeding tends to persist, and the lesion is unable to self-resolve. spontaneous haemostasis, therefore the hematoma increases in volume. In these cases, medical intervention is necessary to remedy possible and catastrophic consequences.