, first of all involves the structural modification of the peptides called denaturation of proteins. Specifically, by protein denaturation we mean the physical distortion of the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins, which occurs through the breaking of stabilizing bonds (such as disulfide bridges).

Denaturation is a positive aspect, indeed, it is the fundamental objective for which it is important to cook proteins which, through this process, lose their original biological function and tend to coagulate, aggregate and lose solubility.
Denaturation begins at temperatures of around 60-70 ° C and is facilitated by acid pH (<7) and / or coagulating-digestive enzymes.
, such as egg or milk, consequently the release of hydrogen sulphide or hydrogen sulphide or dihydrogen sulphide (H2S) occurs as a consequence of the breaking of the disulfide bridges.
H2S is a toxic compound that acts negatively on the cells of all tissues (except red blood cells) since it inhibits mitochondrial respiration; obviously, by simply cooking food, the release of H2S is minimal and is extremely important. reduced ... but for disclosure correctness, it should still be remembered.
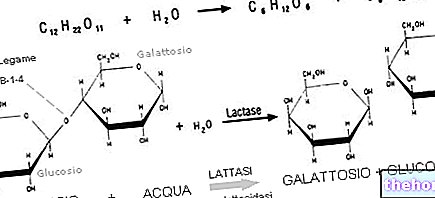
and involves the differentiation into smaller amino acid chains that are more easily attacked by digestive juices.and, at times, (in the presence of oxygen) it determines the oxidation of the radical group (R). The most sensitive amino acids are: sulphured: cysteine, cystine, methionine (which, as anticipated, can release hydrogen sulfide) and those heterocyclics: tryptophan, tyrosine and histidine (tryptophan, in cooking> 200 ° C, can convert into polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons).
.
Maillard mechanism: 1) condensation of the NH2 group of an amino acid with a carbohydrate and consequent production of a base of Shiff; 2) transformation of the base of Shiff in a product of Amadori; 3) transmutation of the product of Amadori in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons - which by cooking give the food a brown color and a "cooked" flavor - but also in intermediate compounds such as "hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) or le melanoidins.
NB. From a nutritional point of view, the Maillard reaction involves the partial loss of the amino acid lysine and a reduction in the digestibility of melanoidins as it is indigestible.
or high flame grilling. Finally, it should be remembered that cooking protein foods par excellence (fish and meat) is essential to prevent food poisoning of various kinds; in this regard see the articles: raw fish and raw meat. As for eggs and legumes, which are also rich in proteins, cooking is important to inactivate antinutrients that could harm the body.