Generality
There are many varieties of edible algae and, in some ways, they possess sufficiently similar nutritional characteristics (with the due differences related to the specific case).

Below we will list the most widely cultivated edible algae (in aquaculture), processed, preserved and sold on the PLANETARY market.
What are algae?
First of all, we specify that algae (Algae), although they are autotrophic organisms that produce oxygen (many of them, but not all, using chlorophyll photosynthesis), they are NOT real plants (otherwise defined embryophytes). Algae can be unicellular or multicellular and do not possess a tissue complexity comparable to that of the other category mentioned above, even if both constitute the clade (group) of green plants.
Obviously, from a food point of view, algae are not all the same; some can be eaten and are harmless for the organism, while others represent a risk for human health and other forms of aquatic and sub-aquatic life; some inedible algae are highly harmful because they are responsible for the release of polluting toxins, even deadly.
Most common edible algae
Let's proceed to the alphabetical list of the most common edible algae species (with some derivatives):
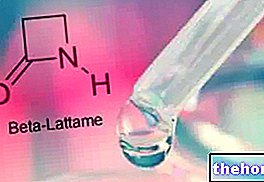
- Agar agar seaweed: agar agar, although known by the Japanese term of kanten, Is NOT a "real algae, but a polysaccharide based on D-galactose, obtained by processing some RED algae (Gelidum, Gracilaria, Gelidiella, Pterocladia and Sphaerococcus). The" agar agar is widely used as an additive in the " food industry (E406) for its gelling function, greater than the others (even if with less solubility, see for example: recipes with agar agar). Being almost totally NOT digestible, agar agar is non-caloric and slightly laxative. it is a derivative of edible algae very rich in mineral salts. Its use is simple and requires a short and mild cooking with subsequent solidification at room temperature (about 60 ").
- Arame or Aramu seaweed: in Latin Eisenia bicyclis or Eicklonia bicyclis, it is also called "sea oak". It is a group of edible BROWN algae that grow spontaneously in the temperate waters of the Pacific Ocean and are cultivated both in the Japanese area and on the South Korean coasts; it has the shape of two flattened ovals, is both single and branched, and grows up to one meter in height. Arame is an edible seaweed object of numerous studies due to its alleged beneficial effects on the organism (antibiotic action on Staphylococci aureo); it is marketed in dry form and, once found in water, has a firm consistency and a taste sweetish. Arame is very rich in mineral salts and equivalent retinol, it is characterized by the presence of: a glucose polysaccharide (with β 1,3 and β 1,6 bonds) called laminated; l "eisenin-tripeptide, with immunological functions; the lignan-estrogens; and many other molecules.
- Blue Algae: BLUE or blue-green algae are unicellular organisms also known by the name of cyanobacteria (Cyanophitya). The blue algae are NOT all edible and some of them can be highly toxic (cyanotoxins: anatoxin, aplysiatoxin, cylindrospermosin, domoic acid, microcystin LR, nodularin R, neosaxitoxin and saxitoxin). On the other hand, edible blue algae contain numerous biological substances of nutritional interest: polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), essential amino acids, pigments and antioxidants, vitamins and minerals. Blue algae have been studied for their theoretical ability to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production by inhibiting NF-kB from macrophages and splenocytes. Some researchers argue that consuming edible blue algae could also reduce the risk of: age-related cataracts and macular degeneration, as well as mitigating some NON-alcohol related liver diseases (such as steato-hepatitis) and ameliorating Parkinson's disease. The sulphate polysaccharides contained in them are immunomodulating, antitumor, antithrombotic, anticoagulant, anti-mutagen, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic and antiviral (against HIV, herpes, and hepatitis).
- Brown algae: group of plants that includes numerous edible species, of which a classic example is the aforementioned Arame. Brown algae belong to the class of Phaeophyceae, they are all multicellular and live exclusively in salt water; are known for their high content of chlorophyll, retinol equivalents, pigments (xanthophyllins, such as astaxanthin), minerals and laminated. Brunettes are edible algae that contain excellent quantities of alginates, which are substances used with high frequency by the food industry, in particular in the production of ice cream (E401 in which they prevent the crystallization of ice). Alginic acid is also a recommended food supplement. in low-calorie diet therapy, as it should reduce the sense of appetite and modulate the absorption of fats and sugars.
- Carragheen seaweed: Latin name Chondrus crispus, also known as moss of Ireland or lichens; it is a RED alga that grows on the low coastal waters of the Atlantic ocean (east and west), where it reaches 15-30cm in height. Like the other red algae that make up the agar agar, also Carraghen is an edible alga with thickening properties used as a gelling additive (E407-E407b); however, compared to the latter, the Chondrus crispus produces a less dense gelatin. On the market it is already cleaned and dried, while if harvested by hand it needs a thorough cleaning of marine residues. It contains considerable quantities of polysaccharides called carrageenan, from which the relative thickening and modulating power of intestinal absorption derives; some researchers argue that Carragheen may be useful in the treatment of diarrhea and urinary and respiratory tract infections.
- Condro crispo seaweed: see above, Carraghen edible seaweed
- Darusu seaweed: Latin name Palmaria palmata, is a small edible RED alga that reaches 15-30cm in height and grows on the shallow rocky bottoms of the North Atlantic Ocean. Darusu is a VERY USED alga in the MACROBIOTIC diet as a food yin; it is eaten both raw and cooked (in soups) but only after having been carefully washed and cleaned. Darusu is one of the edible algae that contains the greatest amount of ascorbic acid, iron, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, iodine and lysine; the protein intake is quite high.
- Dulse seaweed: see above, Darusu edible seaweed
CONTINUE: Other edible algae "