Edited by Dr. Massimo Bonazzelli
Synonyms
The recumbent bench press with dumbells exercise is also known as the Dumbell declined bench press, Declined bench press with dumbells.
Type of Exercise
Dumbbell bench press is a multi-joint exercise / accessory
Variants
- Barbell Recumbent Bench Press
- Parallel stretches
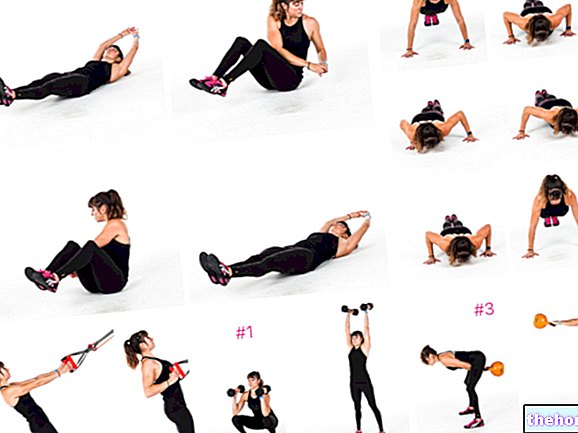
Recumbent Dumbbell Bench Press: Execution
The starting position sees the athlete sitting on a bench reclined between 10 ° and 30 °, with his back in his position of strength, legs apart and feet firmly resting on the ground behind the knees or better still locked in the special stops, when present. The elbows are flexed, the wrists straight and the shoulders are adducted and oriented so that the elbow, wrist and dumbbell are in exactly the same vertical plane perpendicular to the floor (not the bench) from a side view. The dumbbells are held at the same height as the lower part of the sternum or the upper part of the abdomen with a grip that can be prone or neutral; the latter is more correct and particularly recommended when the dumbbells are bulky and heavy, which therefore, if held with a prone grip, would force the athlete to keep the elbows less flexed than it would take to have the forearms perpendicular to the ground from a frontal view, resulting in unnecessary effort on the part of the elbow flexors to hold the handlebars and reduction of the descent movement. The execution consists of pushing the dumbbells up on the vertical plane they were on before starting, thus trying to draw a straight line segment and not a curve. During the push, the shoulders flex in the sagittal plane and adduce in the longitudinal plane, while the elbows extend and the shoulder blades begin to abduct and rotate downward in the last third of movement. The execution ends with full extension. elbows and just before the arms come to be perpendicular to the ground.
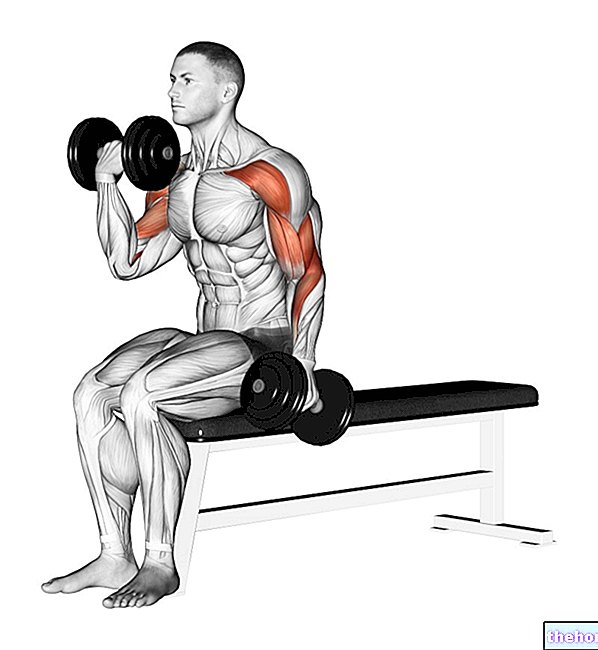
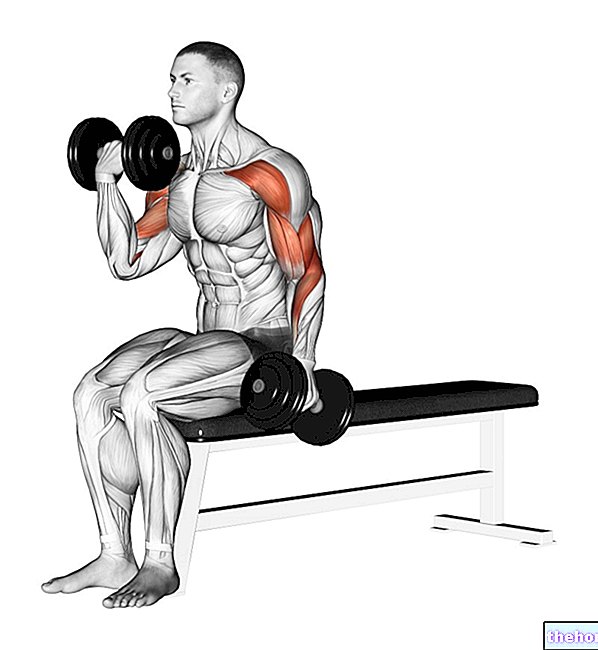
Muscles involved in the exercise Recumbent bench press with dumbbells
Group 0
- Big breastplate
- Anterior deltoid
- Coracobrachialis
- Brachial biceps (weak)
Shoulder flexion
Group 1
- Great dorsal
- Big round
Shoulder adduction
Group 2
- Brachial triceps
- Anconeus
Elbow extension
Group 3
- Large thoracic dentate
- Small breastplate
Scapular abduction
Group 4
- Scapula elevator
- Rhomboid
Lower scapular rotation
Function of the stabilizing muscles: Stability of the shoulder, shoulder blade, elbow, grip, torso, hip, knee, ankle and foot