
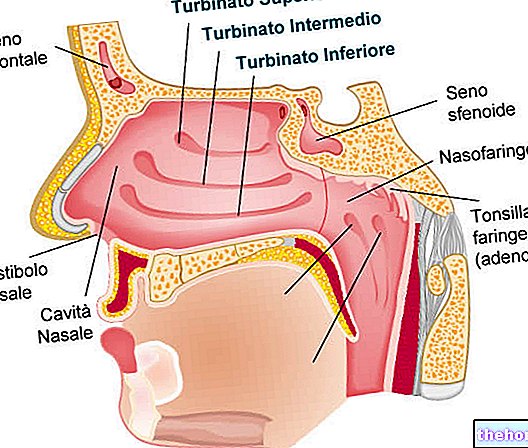
Hypertrophic tonsils tend to appear enlarged, red and, in some cases, they can touch each other.
The inflammation underlying the increase in tonsillar volume is often attributable to infections: being located in the oropharynx, where they participate in the immune defense of the upper airways, these organs are easily in contact with bacteria and viruses. Tonsillar hypertrophy and inflammation are disorders that occur mainly in children, but can also affect adults.
In addition to swelling, hypertrophic tonsils involve pain when swallowing (dysphagia) and sore throat and whitish or purulent plaques on their surface. It is also not uncommon for general malaise, fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, bad breath to appear. and ear pain.
A "careful clinical evaluation by the otolaryngologist allows to identify the causes and establish suitable therapeutic strategies. If the hypertrophic tonsils are the cause of severe respiratory limitations or recurrent infections resistant to drug treatment, the indication is given to their removal (tonsillectomy).
.
It should be noted that hypertrophic tonsils may depend on constitutional factors, therefore they are not always caused by an underlying pathology.



.jpg)





















