Proctoscopy is a diagnostic method aimed at endoscopic observation of the anal canal (anoscopy) and of the rectal canal (rectoscopy). For this purpose, a special instrument is used, known as a rectoscope or proctoscope, introduced after lubrication through the anal opening; it is basically a metal tube equipped with a support at the apex and a possible magnifying glass to better observe the examined region. A similar instrument, but of shorter length, is used for the study of the anal canal only (anoscopy) .
To allow an "adequate visualization of the rectal walls during proctoscopy, it is good that these are adequately clean. In this regard, precise instructions are given to the patient by the same digestive endoscopy center; generally, the day before the examination is asked to practice an enema with a liter of warm water or with a special preparation that can be purchased at the pharmacy; the same operation must be performed a few hours before the appointment. On the other hand, no particular dietary rules are required, nor the use of laxatives (not recommended).
To facilitate the examination of the rectal walls, the patient is asked to undress from the waist down and kneel on the table, tilting the trunk forward and arching the back in order to facilitate the rectal exploration (genu-pectoral position shown in the center of the figure); alternatively, they may be asked to adopt the left side stance (known as the Sims stance). Although this is an awkward position, it is important that it be held by trying to remain still. The insertion of the proctoscope is preceded by a visual examination of the anal opening and by manual exploration of the anus and rectum (the doctor inserts the tip of the right index finger appropriately lubricated into the anal canal). At the end of this examination, the rectoscope is then gently introduced after careful lubrication. After having reached the desired depth and having removed the obturator, the instrument is made to come out slowly and gently, making circular movements, to have a direct view of the rectal and anal walls. In the eventuality, inside the central canal they can other instruments to be inserted, in order to take a small tissue sample (biopsy) to be examined later in the laboratory. Often, moreover, air is blown to stretch the walls of the rectum and make them easier to explore.

The operation is not normally painful, at most annoying; however, in certain conditions the examination is performed under local anesthesia.
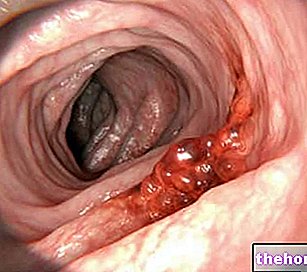
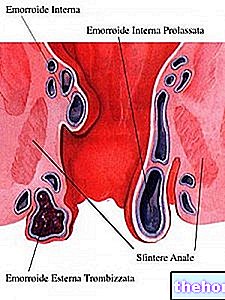
There are numerous pathologies that can be objectified by proctoscopy, which is diagnosed in the presence of rectal bleeding, hemorrhoids, anal or rectal polyps, carcinoma of the anal canal or rectum, anal fistulae, wounds and trauma of this region. Rectoscopy also has potential therapeutic applications, mainly aimed at the resection of polyps or tumors and the treatment of hemorrhoids (for example to perform injections of sclerosing substances or for selective cryotherapy operations).
The results of the proctoscopy are available instantly, but in the case of biopsies the report is delivered after a few days.
Today, the traditional procedure illustrated in the article is slowly retiring in favor of the so-called digital videoproctoscopy, in which the aid of a micro-camera allows you to view enlarged images on the special screen and record them on magnetic support, with the possibility of viewing them at different speed and compare them with the results of future or previous rectoscopic examinations.