Although the color of the stool is heavily influenced by eating habits, a possible chromatic anomaly may also be due to morbid conditions. For this reason, if the alteration is not attributable to particular dietary changes or is accompanied by other symptoms - such as diarrhea, constipation , weakness, abdominal pain or dizziness - it is important to report this promptly to your doctor.
, derived from the breakdown of red blood cells. This is metabolized by the intestinal bacterial flora into stercobilin, which gives the faeces the typical brown color. Bilirubin in turn derives from a precursor, called biliverdin, also present in the bile and sometimes in the faeces, to which it gives a green color. This situation occurs when intestinal transit is so fast as to cause an "incomplete transformation of biliverdin. in bilirubin and derivatives. Green stools are therefore a typical expression of diarrhea and of the conditions of a pathological and non-pathological nature (eg abuse of laxatives) that cause it. Some antibiotic treatments or iron-based supplements can also give the same inconvenience.
The green color of the faeces can be linked to the conspicuous intake of foods rich in chlorophyll, contained above all in spinach, rocket, parsley, green beans and green leafy vegetables in general.
, recognizable because they are characterized by yellow-orange shades (carrots, pumpkins, apricots, mangoes, sweet potatoes, etc.). Even the abuse of supplements that contain this antioxidant pigment, the intake of medicines based on rifampin (an antimicobacterial) or foods with dyes of a similar shade, can cause the evacuation of orange stools. , or an intestinal polyp with a tendency to evolve into a cancerous form.
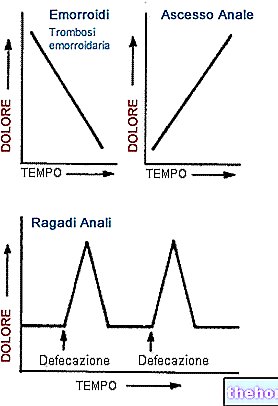
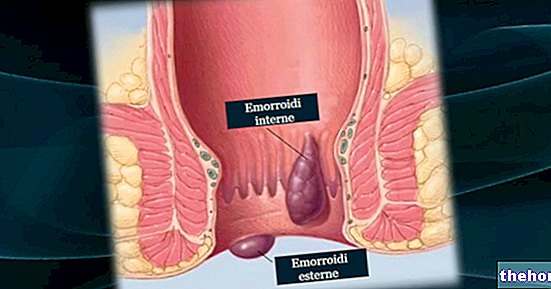
The red color of the stool can be uniform or altered by bright red filaments or spots, which can also be seen on the toilet paper or on the walls of the toilet; this condition occurs when the bleeding affects the last part of the intestine (proctitis, diverticulitis, hemorrhoids, anal fissures, polyps or tumors of the rectum).
If the stools are dark red, the bleeding is more likely to come from the upper parts of the digestive tract (esophagus, stomach and duodenum).
, potatoes or tapioca. The ingestion of antacids (based on aluminum hydroxide) or barium used as a contrast method for x-rays of the digestive tract, can give the fecal mass a chalky white color.
In the initial part we said that the color of the stool is mainly due to the presence of bilirubin and its metabolites. It follows that a "faecal hypochromia is often due to the non-arrival of bile in the intestine, for example due to the presence of gallbladder stones or, more rarely, to a tumor of the bile duct or pancreas. White colored stools can also signal a number of serious liver disorders involving blockage of the bile ducts, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer.
Shiny, greasy and pale colored stools are typical of steatorrhea (excessive presence of fat in the excrement, generally caused by intestinal malabsorption as occurs in celiac disease).