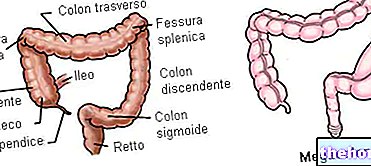
"to indicate an" alteration of intestinal motility characterized bySecretory (eg induced by microscopic colitis, abuse of stimulating laxatives, tumors) Functional (e.g. favored by irritable bowel syndrome) In chronic osmotic diarrhea there is a considerable retention of water in the colon, caused by a reduced absorption of some substances.
In the secretory variant, diarrhea is the result of reduced water absorption. Furthermore, chronic secretory diarrhea is distinguished by the exaggerated volume of fecal material emitted (> 1 l / day) and by the urgent need to go to the bathroom even at night.
Functional diarrhea is caused by a "hypermotility of intestinal transit. Chronic greasy diarrhea (from malabsorption) This type of chronic diarrhea is distinguished by the excessive formation of intestinal gas, steatorrhea and by a marked reduction in body weight. Chronic inflammatory (or exudative) diarrhea Chronic inflammatory diarrhea is distinguished by the presence of blood and pus in the stool and by an increase in the levels of calprotectin (marker of neutrophil activity: an increase in this protein indicates inflammatory disease of the digestive tract)
Liquid or semi-solid stools Urgent need to go to the bathroom Bowel sounds Feeling of bloating in the abdomen
Satellite symptoms that suggest the presence of chronic diarrhea Hypothesis on the causes and type of chronic diarrhea Chronic irritable bowel syndrome diarrhea Chronic celiac disease diarrhea Chronic celiac disease diarrhea Chronic diarrhea from infections or tumors Chronic diarrhea from inflammatory colon diseases Chronic hyperthyroid diarrhea Chronic diarrhea due to microscopic colitis: the hypothesis is almost certain when the aforementioned symptoms occur in the elderly, especially if they take anti-inflammatory drugs Chronic infectious / inflammatory diarrhea Chronic Crohn's disease diarrhea / ulcerative colitis Chronic irritable bowel syndrome diarrhea Chronic diarrhea from malabsorption syndrome Chronic diarrhea due to infectious colitis (almost certain hypothesis in case of recent travel / camping or contact with infected subjects) Chronic psychological diarrhea
, dehydration, malnutrition, hypotension, tachycardia.
We also remind you that extremely aggressive conical diarrhea can lead to patient death from dehydration and metabolic acidosis.
Tags:
human-health food allergy stomach-health
- a number of daily evacuations greater than / equal to 3, with the emission of liquid or semi-solid stools (diarrhea),

that persists
- for at least three or four consecutive weeks
In the secretory variant, diarrhea is the result of reduced water absorption. Furthermore, chronic secretory diarrhea is distinguished by the exaggerated volume of fecal material emitted (> 1 l / day) and by the urgent need to go to the bathroom even at night.
Functional diarrhea is caused by a "hypermotility of intestinal transit.
- Infectious (e.g. caused by giardiasis)
- Non-infectious (eg induced by celiac disease, amyloidosis, administration of some drugs such as orlistat and acarbose)
- Infectious: caused for example by bacteria such as Clostridium difficile, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex, tuberculosis
- Non-infectious: induced by ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, lymphomas, tumors
Clearly, according to the cause of origin, the clinical picture of the patient suffering from chronic diarrhea is enriched by more complex symptoms.
Based on the "satellite" symptoms that accompany the classic clinical picture of chronic diarrhea, it is possible to hypothesize about the triggering cause:
- Chronic diarrhea alternating with periods of constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal pain relieved after evacuation
- Noticeable abdominal swelling
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
- Diarrhea with mucus (symptom that occurs in 25% of bowel movements)
- The evacuations often recur after meals and almost always during the day
- Accentuation of symptoms in the presence of anxiety, stress and tension
- Abdominal cramps
- Abdominal pain
- Flatulence
- Weight loss
- Steatorrhea (excessive fat in the stool)
- Herpetiform dermatitis
- Skin rash (with blisters and itching)
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Weight loss
- Lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes)
- Episcleritis: inflammation of the superficial layers of the ocular sclera (white part of the eye)
- Exophthalmos (prominent eyes)
- Feeling of heat, hyper-sweating
- Nocturnal diarrhea
- Watery secretory diarrhea
- Pain on palpation of the abdomen
- Anal fistulas
- Blood in the stool
- Weight loss, anemia and fever (possible symptoms)
- Immediate stimulation of defecation after meals
- Oily stools
- Vomiting, nausea
- Fever
- Severe abdominal pain
- Anxiety
- Tension, fear, stress
We also remind you that extremely aggressive conical diarrhea can lead to patient death from dehydration and metabolic acidosis.
Other articles on "Chronic Diarrhea: Types, Symptoms and Complications"
- Chronic diarrhea
- Diarrhea
- Diarrhea: causes and treatment
- Dysentery
- Traveler's Diarrhea
- Chronic diarrhea: Diagnosis, Treatment, Diet
- Diet and diarrhea
- Nutrition and diarrhea
- Diarrhea and Antibiotics
- Probotics and Diarrhea
- Drugs That Cause Diarrhea
- Diarrhea - Drugs for the treatment of Diarrhea
- Herbal Teas Against Diarrhea