A clinical feature of diabetes is hyperglycemia, resulting from the aforementioned changes in insulin.
Currently, the medical-scientific community recognizes the existence of 3 major types of diabetes mellitus, which are: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes; once upon a time, the classification of diabetes was broader and less simple to consult.
The presence of diabetes in the world population has increased over the last 30-40 years: consider that, while in 1980 there were 108 million patients, in 2014 the number of people with diabetes reached 422 million.

- macroangiopathy (a particularly severe and early form of atherosclerosis)
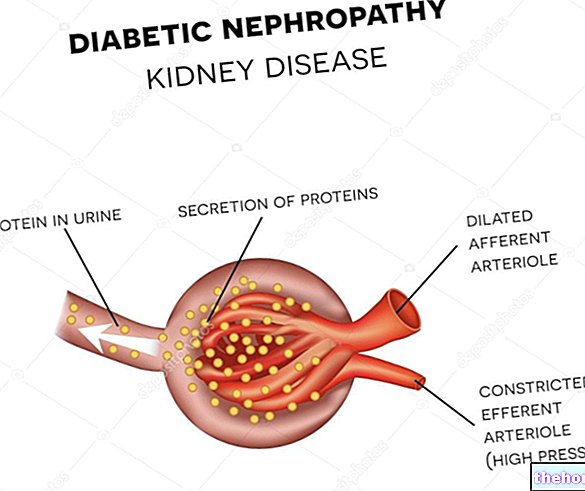
- microangiopathy (an "alteration of the blood circulation inside the small arterial vessels, manifested above all in the retina, kidney and nerves).
While microangiopathy is specific to the disease in question, macroangiopathy is not.
, also defined with the acronym NIDDM or diabetes of adulthood or maturity;- pancreatic diseases (chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer),
- endocrine diseases responsible for an "excessive secretion of counter-regulatory hormones" insulin (Cushing's syndrome, acromegaly, pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism, glucagonoma, somatostatinoma and aldosteronoma)
- the use of drugs that induce hyperglycemia (glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, interferon, pentamidine and adrenergic agonists)
- the intake of toxic substances;
- abnormalities of insulin or its receptor;
- specific genetic anomalies.
THE "NEW" CLASSIFICATION
Internationally recognized, the classification of diabetes mellitus drawn up in 1997 by the WHO and the ADA is decidedly simpler than the previous one. In fact, it divides diabetes into three main types:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus. This includes almost all immune-mediated forms of diabetes; in these circumstances, the underlying cause is a malfunction of the immune system, which, recognizing the pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans as foreign, attacks and destroys them.
Since the immune system is involved, type 1 diabetes mellitus is fully included among the autoimmune diseases. - Type 2 diabetes mellitus. This includes all forms of diabetes due to
- a deficiency in insulin secretion by the pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans,
- resistance of the body's tissues to the action of insulin (a condition known as insulin resistance).
- Gestational diabetes. As "was in the old classification, this includes forms of diabetes secondary to pregnancy. Generally, it is a transient phenomenon.
It should be noted that the types "type 1 diabetes" and "type 2 diabetes" also include the forms of diabetes associated with: viral infections (ex: rubella, cytomegalovirus), genetic syndromes (Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Turner syndrome, Friedreich ataxia, Laurence-Moon syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, Prader-Willi syndrome, Huntington's chorea etc.) and genetic defects of hereditary nature borne by the pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans (known as MODY, i.e. Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young).

.jpg)