Depending on the etiology, the burning sensation can occur suddenly or gradually, over the course of weeks or months, and can be associated with other symptoms, such as itching, erythema, tenderness, vaginal or urethral discharge.
The evaluation of this symptom - fundamental to establish the correct therapy directed to the triggering cause - must be performed by the gynecologist and usually includes anamnesis, physical examination and analysis of vaginal or urethral secretions. adequate treatment of the pathological condition underlying the intimate burning reduces the risk of possible complications.
. Intimate burning can affect people of any age.
Clearly, the extent of this problem varies according to the underlying cause and the individual factors that contribute to determining its appearance (eg. Irritative reactions, hormonal alterations and other situations that contribute to modifying the physiological balance of the genitals). Often, the burning sensation intimate is associated with other symptoms and signs such as pain, discharge, redness and itching.
. In some cases, the disorder has trivial reasons, while in other circumstances it may indicate a more serious problem, such as, for example, a sexually transmitted disease.In women, the main causes of intimate burning are:
- VAGINITIS
In the female sex, intimate burning is often related to vaginitis, ie inflammation of the vagina.
The conditions that can favor the inflammatory process are different and, first of all, they include:
- Local pH increase (secondary, for example, to menstrual blood or sperm in post-coitus);
- Alteration of the microbial flora (reduction of lactobacilli due to poor personal hygiene or to the use of drugs, such as antibiotics or corticosteroids).
These situations predispose to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and make the vaginal mucosa more vulnerable to infectious attacks. The agents responsible for vaginitis and the resulting intimate burning are: fungi (such as Candida albicans), bacteria (Gardnerella vaginalis, streptococci, staphylococci etc.), protozoa (eg. Trichomonas vaginalis) and, more rarely, viruses (eg herpes simplex).
Vaginitis from which intimate burning arises can also be caused by physical causes, such as:
- Abrasions due to "inadequate lubrication during sexual intercourse;
- Rubbing from clothing that is too tight, especially if made with synthetic materials;
- Prolonged contact with a foreign body (e.g. tampons, toilet paper residues or grains of sand).
Vaginitis can also result from irritation of the genital mucous membranes or allergic reactions to specific substances.
Other causes of intimate burning include:
- HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS
In both men and women, intimate burning can arise as a result of substances capable of inducing irritation of the genital area or hypersensitivity reactions (or allergies). The disturbance can derive, for example, from the excessive use of intimate detergents and vaginal douches or from the residues of fabric softeners and laundry detergents on the linen. In susceptible people, the risk of suffering from intimate burning can also depend on: deodorants, creams depilatories, soaps, bubble baths and perfumed toilet paper.
Occasionally, the irritation and burning sensation can be a consequence of the use of latex condoms or lubricants.
Vaginal creams, spermicides, contraceptive vaginal rings, diaphragms or intrauterine devices also fall into the category of potential sensitizing agents.
- BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
Normally, in women of reproductive age, lactobacilli are the predominant constituents of the vaginal microbial flora. Colonization by these bacteria is normally protective, as it maintains the vaginal pH at normal values (between 3.8 and 4.2) and prevents the excessive growth of pathogenic microorganisms. However, in the presence of situations that can alter the vaginal ecosystem, the genitals can be vulnerable.
Bacterial vaginosis is a very common genital infection characterized by vaginal dysmicrobism which causes an increase in pathogenic bacteria. Often, its presence is signaled by itching, intimate burning and increased vaginal discharge (homogeneous white-greyish secretions, characterized by bad odor). If neglected, bacterial vaginosis can cause gynecological complications, as well as favoring the transmission of venereal diseases that can be spread through sexual intercourse.
- SEXUAL TRANSMISSION DISEASE
In both men and women, intimate burning is often one of the first signs of a sexually transmitted infection, such as: genital herpes, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and chlamydia. Sharp warts (cockscombs) and syphilis can also cause this manifestation.
- HORMONAL IMBALANCES (menopause, pregnancy and drug therapies)
In women of reproductive age, the high levels of estrogen maintain the thickness of the vaginal mucosa, strengthening local defenses. On reaching menopause, however, the physiological decrease in the production of these hormones causes the thinning of the walls of the vagina and can lead to problems such as dryness, itching and intimate burning (atrophic vaginitis).
The reduction of estrogen and the resulting intimate burning can also represent the side effect of some drugs or some particular treatments, such as surgical removal of the ovaries, pelvic irradiation and chemotherapy.
The onset of intimate burning can also occur due to hormonal alterations typical of the post-partum period or breastfeeding.
- OTHER POSSIBLE CAUSES in men and women
Intimate burning can be caused by a number of other disorders involving the external genitalia and urinary tract, including:
- Repeated episodes of cystitis;
- Parasitosis, including scabies or pediculosis of the pubis;
- Neurological lesions (eg Tarlov cyst, post-traumatic outcomes of the pudendal nerve, etc.);
- Micro-trauma induced by scratching due to local itching, abrasions due to inadequate lubrication during sexual intercourse and rubbing from clothing that is too tight.

In men, moreover, intimate burning can be indicative of the following pathological conditions:
- Urethritis;
- Prostatitis;
- Balanitis;
- Prostate stones.
Intimate burning can also depend on states of immunosuppression and systemic diseases, such as diabetes. In some cases, this manifestation can be associated with dermatological diseases (including dermatitis, lichen sclerosus and psoriasis) and disorders of a psychosomatic or psychiatric nature (such as stress, anxiety and depression).
or the glans, can be particularly annoying.The disorder can manifest itself as a burning sensation, of varying severity, in the genital area:
- During urination;
- With contact (e.g. pressure or rubbing);
- After sexual intercourse;
- Without any kind of solicitation.
Depending on the cause, the burning sensation may or may not be accompanied by other local and sometimes general symptoms (eg fever and weakness).
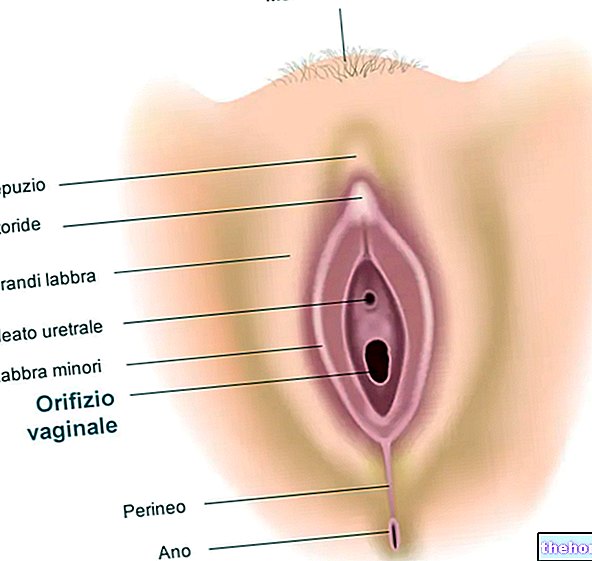
In women, intimate burning can be divided into:
- Internal intimate burning: it is felt in the internal female genitalia (cervix and vagina) or in the urinary tract;
- External intimate burning: occurs in the vulva and labia majora.