Usually asymptomatic, the anteverted uterus does not represent a serious condition and, from a medical-clinical point of view, is certainly less relevant than the retroverted uterus.
In most cases, the antiverse uterus is a congenital feature, just as blue eyes and blond hair can be; more rarely, it is a consequence of circumstances such as: pregnancy, childbirth, caesarean section, endometriosis and surgery involving the pelvic organs.
Diagnosis of the anteverted uterus is easy and is based on pelvic examination and / or pelvic ultrasound.
The antiverse uterus does not require any treatment, because it has no repercussions on female fertility or on the "course of a" possible pregnancy.
Brief reminder of the uterus
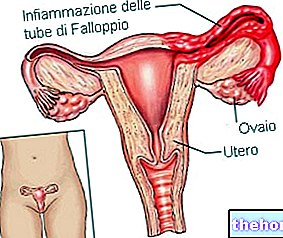
Learn and hollow, the uterus is the female genital organ, which serves to accommodate the fertilized egg cell (ie the future fetus) and to ensure its correct development, during the 9 months of pregnancy.
It resides in the small pelvis, precisely between the bladder (anteriorly), the rectum (posteriorly), the intestinal loops (above) and the vagina (below).
In the "span of life, the uterus changes its shape; if up to pre-pubertal age it has an elongated appearance similar to a glove finger, in adulthood it looks a lot like an inverted (or inverted) pear, while in the post-menopausal phase it gradually reduces its volume and becomes crushed.
From a macroscopic point of view, doctors divide the uterus into two distinct main regions: a more enlarged and voluminous portion, called the body of the uterus (or uterine body), and a smaller portion, called the neck of the uterus (or cervix).

The "antiverse uterus is a very common condition; many women, however, are unaware that they are carriers, since, as mentioned above," on the contrary, it tends not to have any significant clinical significance.
What would be the normal position of the uterus?
The anatomical normality of the female human body would like the uterus to have only a slight inclination forward, towards the abdomen.
In other words, a uterus is in a normal position when it is bent forward, but not too far (because otherwise we should speak of an antiverse uterus).
In light of this, the antiverse uterus can be interpreted as an "accentuation of the normal position of the uterus" or as a "natural" variant of the normal position of the uterus.
Uterus Antiverse and Uterus Antiflex: the differences
The condition of an antiverse uterus should not be confused with the condition of an anti-inflected uterus, in which there is always an inclination towards the uterus, however this inclination affects only the body of the uterus.
, which makes it an unsuspected condition.In those rare circumstances in which the antiverse uterus is symptomatic (ie responsible for symptoms), it causes a sense of pressure or real pain in the anterior pelvis (pelvic pain).
When is the Antiverse Uterus symptomatic?
The antiverse uterus is a symptomatic condition, when the inclination of the uterus is very accentuated and determines a strong compression at the level of the inner wall of the lower abdomen.
When the forward inclination of the uterus is very accentuated, we speak of a severe antiverse uterus.
Uterus Antiverse and Fertility
At one time, based on old knowledge, doctors believed that the anteverted uterus impaired female fertility, in other words, they believed that a uterus tilted excessively forward reduced a woman's ability to conceive.
Today, however, thanks also to the data that has emerged from new research, they know for sure that the beliefs of the past were wrong and that the antiverse uterus represents only in rare cases and only when it is associated with important medical conditions an obstacle to a woman's fertility.
Did you know that ...
In a country like the United States, the main causes of female infertility are ovulation problems, abnormalities of the uterine cervix and fallopian tubes and the presence of so-called uterine polyps.
Uterus Antiverse and Pregnancy
When the doctors discovered that the "anteverted uterus does not normally affect the fertility of the woman, they also ascertained that the excessive forward inclination in the uterus does not interfere with the course of a" possible pregnancy. In other words, the presence of an antiverse uterus is not a source of danger during pregnancy, neither for the mother nor for the fetus.
Uterus Antiverse and Sexual Life
Generally, the antiverse uterus does not cause dyspareunia, which is pain during sexual activity.
In the event that it is, however, it is good for the woman concerned to contact her doctor and rely on his advice / indications.
When to see a doctor?
The "antiverse uterus is a condition to be brought to the attention of the attending physician, when it causes a sense of pressure or pain in the pelvic area or when, as stated above", on the contrary, it is responsible for dyspareunia (very rare).
pelvic.
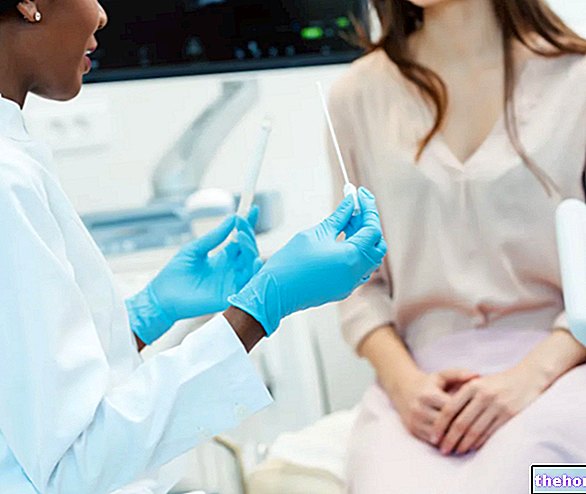
Pelvic exam
The pelvic exam is an objective examination, during which the doctor (usually a gynecologist) examines manually, first from the outside and then also from the inside (thanks to a speculum), the vagina, the uterus (in particular, the cervix), the rectum, the ovaries and the pelvis. In other words, it is an analysis of the major pelvic organs.
Lasting a few minutes, the pelvic exam allows a general assessment of a woman's gynecological health.
In the presence of a condition such as the anteverted uterus, the pelvic examination is usually highly significant; only in rare circumstances, in fact, is it insufficient for definitive diagnosis.

Pelvic ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound is a simple external ultrasound of the lower abdominal area.
Completely painless and without any repercussions on the health of patients (NB: it uses ultrasound and not ionizing radiation), pelvic ultrasound allows a sufficiently detailed study of all pelvic organs, that is: bladder, terminal part of the intestine ( rectum and sigmoid), the prostate-vas deferens-seminal vesicles complex in men, and the uterus-vagina-fallopian tubes-cervix-ovaries complex in women.
In the context of an anteverted uterus, pelvic ultrasound represents the diagnostic confirmation examination, which ascertains and enriches the data that emerged during the pelvic examination.