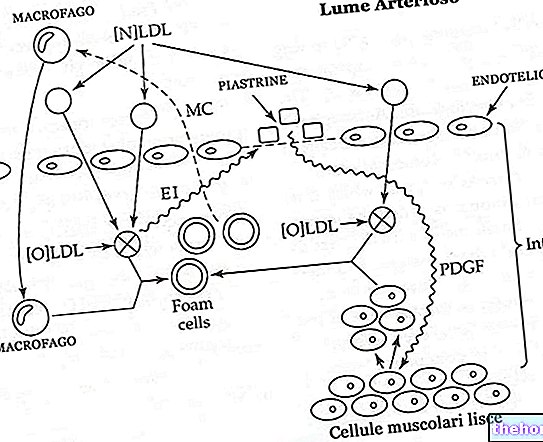
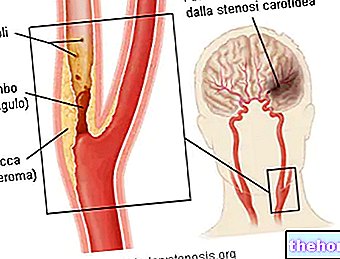
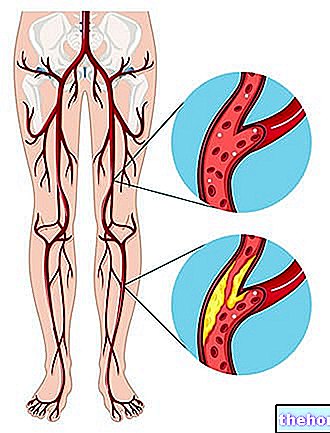
Among the leading causes of death in the world, myocardial infarction is, in most cases, related to thrombo-embolic phenomena and atherosclerosis; however, it may also be due to the phenomenon of coronary spasm induced by the use of drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines.
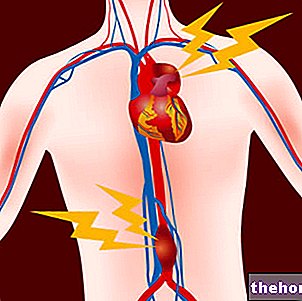
Myocardial infarction presents with various symptoms: chest pain (angina pectoris), dyspnoea (shortness of breath), fatigue and a sense of anxiety are the typical manifestations, but it should not be forgotten that an individual suffering from a heart attack could also experience dizziness, cold sweat, nausea, vomiting and / or pain in one or both upper limbs (especially shoulders and arms), jaw, back and / or neck.
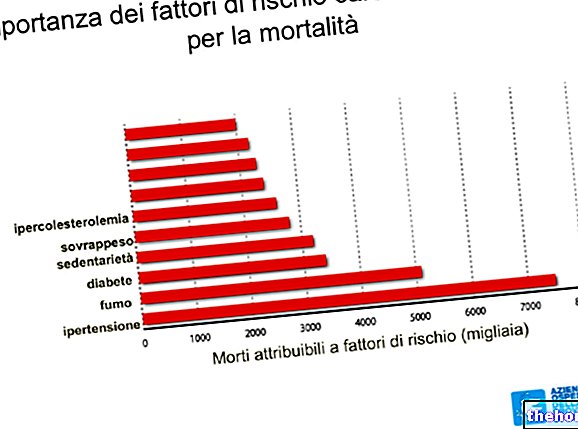
Confirming its correlation with thrombo-embolic phenomena and atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction most frequently affects smokers, overweight or obese people, diabetics, excessively sedentary individuals and those suffering from hypertension, hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia.
"Myocardial infarction represents a" medical emergency; this means that those affected need immediate treatment, otherwise the consequences could be fatal.
in women they are a much debated and discussed topic, especially in recent decades, in which there has been an increase in the incidence of heart attack in the female population.
In particular, what is interesting is the fact that, in women than in men, some manifestations that have always been considered typical of myocardial infarction are less frequent, while others considered more unusual are observed more often.
For example, a classic symptom of heart attack, which is less common in women than in men, is posterior chest pain; while a more unusual symptom, which women experience more often than men, is back pain.
Despite the various studies, the reason for the aforementioned differences is still not clear; however, for a woman, knowing that they exist can help in the early diagnosis of a myocardial infarction: being aware that a heart attack can occur without necessarily causing intense and almost unambiguous chest pain can be life-saving. .