The most common sites of cartilage lesions are the joints - which present the so-called articular cartilage - the respiratory organs of the throat and thorax (larynx and trachea), and external anatomical structures, such as the nose or the auricle.
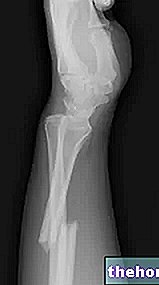
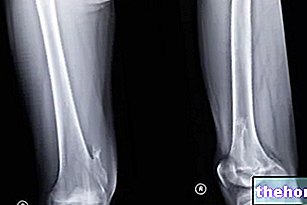
Symptoms of injury to a cartilage vary in relation to the site of the injury. For example, injury to a joint cartilage produces pain in the affected joint, associated with stiffness, swelling, motor difficulties, etc .; the lesion of the laryngeal or tracheal cartilage, on the other hand, is responsible for pain in the throat or chest and breathing problems.
Cartilage is a tissue that almost never heals spontaneously; this implies that, in the presence of lesions to a cartilage, the treatment is mostly surgical.
Review of what Cartilage is
Also known as cartilage tissue, cartilage is a connective tissue with a support function and extremely flexible and resistant.
Made up of particular cells called chondrocytes and devoid of blood vessels, the cartilage of the human body is not all exactly the same, but has different characteristics, depending on the anatomical site and the specific tasks to which it is responsible. Hence, as a consequence of the aforementioned characteristics, the anatomists have decided to distinguish the cartilage tissue into 3 major types:
- Hyaline cartilage. Smooth, flexible and bluish-white in color, it is the most common type of cartilage in the human body. Examples of locations where it can be found are: ribs, nose, trachea, bronchi, larynx and joint surfaces;
- The elastic cartilage. Opaque yellow in color, it is a type of cartilage that stands out above all for its elasticity. Examples of locations where it can be found are: auricles, Eustachian tubes and epiglottis;
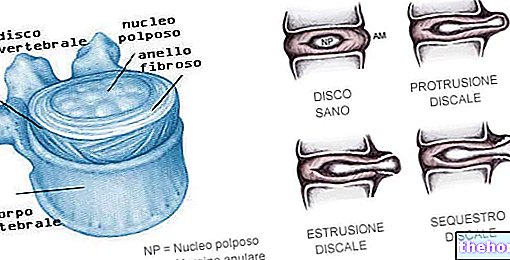
- Fibrous cartilage.Whitish in color, it is the most common type of cartilage in the joint, as it is very resistant to mechanical stress. Examples of sites where it can be found are: intervertebral discs, knee menisci and pubic symphysis.
Is it serious?
As a rule, cartilage has no blood vessels, so no blood circulates there; this means that, if damaged, it is unlikely to heal spontaneously, as would happen in the case of injured skin or fractured bones.
A cartilage injury is all the more serious, the more extensive the damage is.
Most Common Locations of Cartilage Injury

The cartilage most subject to injury is, without a doubt, the cartilage present in the joints, ie the so-called articular cartilage; to follow, there are lesions of the cartilage belonging to the respiratory organs of the throat and thorax - in other words, larynx and trachea - and the lesions of the cartilage of the nose and ears (auricle).
, hip and shoulder.In most cases, traumatic injuries to the articular cartilages are the result of sports injuries (the sports most at risk are football, rugby, American football and basketball) or injuries suffered during strenuous work, which undermine the integrity of the joints;

- The lesion of the cartilage constituting the respiratory organs of the throat and chest. The cartilages of organs such as the larynx or trachea can be damaged as a result of violent blows to the throat or chest.
In the majority of cases, traumatic lesions of the cartilage of the larynx and trachea are the result of car accidents or, once again, of sports injuries; - The lesion of the cartilage that forms the nose or auricle. The cartilages of the nose and auricles can be damaged by repeated cuts, rubbing and burns.
Degenerative Diseases of Cartilage
Premise: a disease is degenerative when it gradually and irremediably alters first the anatomy and then the function of an organ or tissue.
There are various degenerative diseases capable of producing cartilage lesions; as a rule, these degenerative diseases are joint diseases, so the lesions in question concern the cartilage of the joints.
Arthrosis is one of the best known and most widespread degenerative diseases that cause damage to the cartilage.
Also known as osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis is the inflammation of one or more joints, resulting from the progressive degeneration of the articular cartilage (articular cartilage is the cartilage that covers the surface of the bones involved in a "joint).
;
SURGICAL TREATMENT

Surgery for joint cartilage injuries includes various treatment options, including:
- The so-called joint cleaning. It is indicated when the injured cartilage has sharp edges, which could damage adjacent joint structures.
Briefly, it can consist of smoothing or removing the imperfections developed by the articular cartilage following the injury; - Stimulation of the bone marrow. It consists in drilling the bony surface on which the damaged articular cartilage rests, up to the internal blood vessels; this work of drilling, in fact, leads to the formation of blood clots inside the damaged cartilage, followed by the generation of new cartilage.
Unfortunately, the new cartilage obtained with this surgical technique has different characteristics from the original articular cartilage; specifically, it is less elastic; - Joint mosaicplasty. It is in fact an autologous cartilage transplant; in fact, it involves the removal of a piece of healthy cartilage from another area of the patient's body and the application of this piece in place of the damaged cartilage.
Joint mosaicplasty is a good solution only when the cartilage lesions are small (eg: in the presence of arthrosis it is completely unsuitable); - The implantation of autologous chondrocytes. It consists in taking some chondrocytes from the damaged cartilage, cultivating them in the laboratory for 1-3 months in order to produce others and, finally, implanting the result of the cultivation where there is the cartilage lesion.
Treatment of a Laryngeal or Tracheal Cartilage Injury
In lesions to the cartilage of the larynx or trachea, the therapy is only surgical and consists of an intervention aimed at restoring the normal anatomy of the injured organ.
Treatment of a Cartilage Injury of the Nose or Ears
In the event of injury to the cartilage of the nose or ears (auricle), there is the possibility of surgical intervention to restore the appearance of the affected area.
Did you know that ...
The operations to remedy the cartilage lesions of the nose or auricle are maxillofacial surgery.