The tendency to freckles is inherited from the parents. These pigmented spots usually appear from a young age and are common in people with fair skin and blond or red hair (phototype 1 and 2). Ephelides appear mainly in areas exposed to light (face, upper parts of the chest and upper limbs and décolleté).
Compared to freckles, freckles have a lighter color and a seasonal variation, that is, they typically accentuate in summer, with exposure to the sun, and tend to diminish during the winter season (they are not, therefore, permanent). of the freckles can improve with the application of lightening creams and light peelings.
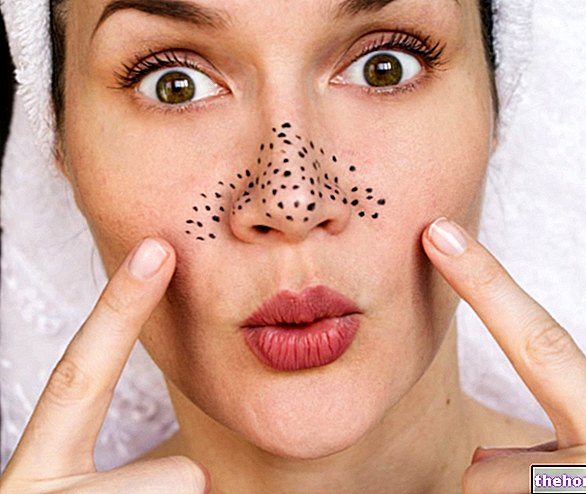
Freckles
Freckles are hyperchromic skin discolorations, due to an increase in the number of melanocytes in the basal layers of the epidermis; the melanin produced in a higher quantity, therefore, is concentrated in some cells. The freckles appear as flat or slightly raised spots, of a color that varies from light to dark brown and irregular shape.
Freckles can occur in different parts of the body, regardless of the exposure of the skin to sunlight: generally, they are evident on the face, shoulders, upper limbs and back of the hands, but they can also appear in areas hidden from light and at the level of the mucous membranes.
Being hyperpigmentation due to an accumulation of melanin, intense and prolonged exposure to the sun can accentuate and make these spots more numerous. Unlike the ephelids, they do not disappear in the winter period (they are permanent); in the case of freckles, then, the color change from summer to winter occurs, but in a less intense way. Freckles can be removed by the dermatologist with a laser or diathermocoagulation.
worsens with exposure to sunlight and intense artificial lighting. This annoying sensation, in particular, can be found in cases of uveitis, corneal abrasions, conjunctivitis, keratitis and acute glaucoma.
Furthermore, solar ophthalmodynia can depend on meningitis, headache and various feverish states. In other cases, it is a consequence of irritation secondary to the incorrect use of contact lenses.
To prevent solar ophthalmodynia and promote ocular well-being, it is possible to use shielding lenses, according to law, which filter most of the ultraviolet rays.
(Seasonal affective disorder) or seasonal mood disorders. Women suffer from it more and, not surprisingly, SAD is also more common among people who live far from the equator, where there is less light in winter. And it is precisely the scarcity of light that is called into question as a trigger for certain biological adjustments, which according to scholars would explain the reduction in mood in the winter months.
In this regard, it has been seen how in winter the levels of SERT, the transport protein of serotonin, increase. SERT binds to serotonin in the synapse, returning it to the presynaptic neuron and preventing it from interacting with its own receptors. Since serotonin is also known as a good mood hormone, the higher the SERT levels, the greater the tendency to depression; not surprisingly, several antidepressant drugs act on the SERT protein to increase serotonin levels and with them a good mood.
Another biochemical explanation of SAD concerns the increased secretion of melatonin in response to low light; this phenomenon could explain the increased sleepiness and less activity that many people complain about in the winter months.
or cell membranes.
The symptoms are the same as for sunburn: redness, itching, swelling and burning, up to real burns with the appearance of blisters. They can occur in areas where the topical medicine has been applied or, if the drug is taken orally or parenterally, they can affect all areas exposed to the sun. The dose of the drug and the frequency of treatment also make a difference. The reactions are more pronounced if the sun exposure has been intense or prolonged: they generally last a few days and can leave brown spots. The danger is greater if the exposure coincides with the peak concentration of the active ingredient in the blood. Among the most common drugs that can interact with the sun are: antibiotics (tetracyclines, quinolones and sulfonamides), oral contraceptives (pill), anti-inflammatories (especially those to be applied to the skin, such as ketoprofen-based gels / patches) and antihistamines (promethazine).
A separate discussion deserve the so-called photoallergic reactions that occur only in predisposed individuals the symptoms do not appear immediately, but once sensitized they are also triggered by small doses of the drug.
In any case, it is advisable to always check what is reported in the package leaflet of the medicine for compatibility with sun exposure and always use an adequate sun protection by choosing from the best sun creams on the market. If it is not possible to suspend or postpone treatment, avoid the sun both while taking the drug and for the next two weeks.
healthy, lasting and uniform is obtained gradually, after about 7-10 days of exposure to the sun.
Once a beautiful complexion is obtained, it can be intensified with creams, oils and balms formulated with substances capable of promoting the production of melanin (the pigment responsible for tanning).
Tanning intensifiers usually contain tyrosine, which makes the melanin produced by the skin more available and optimizes the stimulation of the sun's rays.
The ingredients often include substances capable of helping melanin in photoprotection, such as beta-carotene.
Tanning intensifiers generally do not contain sunscreens, so it is important to continue to protect yourself with a photoprotector and not to expose yourself too much to the sun, especially avoiding the hottest hours of the day.
it has the function of alleviating the effects resulting from sun exposure and improving the condition of the skin.The tanning and the production of melanin are, in effect, a defense of the organism to a stressful situation. In fact, in the first instance, solar radiation causes an inflammatory response in the skin, which manifests itself with redness, dehydration, burning sensation, erythema and other more or less annoying symptoms.
Therefore, it is necessary to provide the skin with nutrients (such as argan and shea), antioxidants (vitamins), anti-reddening and soothing substances (aloe, allantoin, calendula and panthenol).
The constant application of milk, creams and butters after sun exposure also preserves the compactness of the superficial skin layer and restores the hydrolipidic film, counteracting dehydration and peeling.
Aftersun should always be used, from the first days of exposure, applying it generously and all over the body.
formulated with nourishing and emollient substances to prevent the skin from flaking, wash after wash. At the end, then, it is useful to abound with a soothing and moisturizing after-sun, to apply and massage until completely absorbed.
Once a week, it may be helpful to use a gentle scrub. In fact, exfoliation removes the opacity given by dead cells on the skin surface and restores uniformity and brightness to tanned skin.
or zinc oxide, which make them very similar to a protective sunscreen. Unfortunately, anti-UV clothes can lose their characteristics after repeated washing or if they are too adherent (so the fibers stretch on the skin).How to choose the protection factor
The level of sun protection for fabrics is indicated on the labels with the initials UPF (ultraviolet protection factor). Maximum protection is guaranteed by garments with UPF 50+.
In addition to the protective factor, the garments conforming to the UNI standards also bear the symbol of a yellow sun on the label and the reference to the number of the EN 13758-2 standard.
Where can they be found
UV protection clothing can mainly be found in sportswear stores. Usually, they are synthetic (natural fibers offer less protection) and are recognizable by the texture of the fabric, generally denser than normal, and by dark or bright colors (they absorb the sun's rays better than white).
they need protection. In fact, exposure to ultraviolet rays can favor the progressive opacification of the lens, a structure that filters and projects light onto the retina. Furthermore, solar radiation is involved in the "induction or progression of photokeratitis, retinopathies and macular degeneration linked to" age.
To protect your eyesight, therefore, it is important to wear a pair of glasses with extremely high quality dark lenses, equipped with an ultraviolet filter in accordance with the law, able to block solar radiation as much as possible.
For sunglasses, there are 4 degrees of anti-UV protection; Level 4 is recommended in situations where there is strong exposure to the sun and glare (beach, high altitudes or ski slopes).
In any case, it is advisable to check that the CE mark, the certification of the quality and safety indices and the category to which it belongs are always indicated on the packaging; the most suitable are the lenses of category CE 3 or 4.
; in addition, it is important to get a tan step by step.On the skin exposed to UV rays, a series of symptoms typical of an allergic reaction occur: itching, burning, wheals and irritation. In rare cases, when very large skin areas are involved, headaches, dyspnoea, dizziness, nausea, weakness, syncope and other systemic manifestations can also occur.
The etiology is unclear, but probably the triggering factor (ultraviolet light) activates endogenous skin elements that act as photoallergens, which lead to mast cell degranulation, as occurs in other types of urticaria. Solar urticaria can be classified based on the components of the UV spectrum (UVA, UVB, and visible light) that determine it.
Symptoms of solar urticaria usually last from a few minutes to a few hours. However, it can become chronic and worsen or worsen over the years.
The treatment of solar urticaria is complex and may include the administration of antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and desensitization therapy (phototherapy).







.jpg)


















