The main causes of vertebral fracture are: car accidents, accidental falls from above, physical collisions that characterize contact sports, acts of violence and all those diseases that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis.
Depending on the dynamics of the injury, the vertebral fracture may have different connotations and may or may not be associated with the injury of the spinal cord and / or neighboring spinal nerves.
Vertebral fractures produce back pain and, combined with a spinal cord injury, are also responsible for neurological disorders.
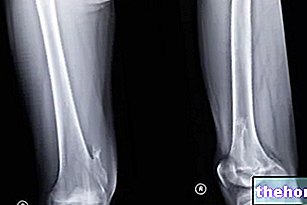
For an exhaustive diagnosis of vertebral fracture, the following are essential: physical examination, medical history, imaging and sometimes neurological evaluation.
Treatment of a vertebral fracture varies according to the type of fracture.
Vertebral fracture is an extremely variable condition in terms of severity; depending on the cause, in fact, the vertebrae can fracture more or less severely and can undermine the integrity of the spinal cord.
Vertebrae: a brief review

To fully understand the information contained in this article on vertebral fracture, it is essential to know, at least in broad terms, the anatomy of the vertebrae.
- The vertebrae are the irregularly shaped bones that make up the vertebral column, ie the supporting axis of the human body as well as the structure responsible for hosting and protecting the spinal cord;
- The vertebrae are 33-34 in all. Starting from the top, the first 7 form the cervical tract of the vertebral column (cervical vertebrae); the subsequent 12 form the thoracic tract (thoracic vertebrae); the next 5 form the lumbar tract (lumbar vertebrae); the subsequent 5 form the sacral tract (sacral vertebrae or sacrum); finally, the last 4/5 form the coccygeal tract (coccygeal or coccyx vertebrae).
- Although their specific anatomy varies in relation to the spinal tract considered, all vertebrae have:
- A cuboid-shaped element in a ventral position, called the vertebral body;
- An arched formation in the dorsal position, called the vertebral arch;
- A hole between the arch and the body, whose name is vertebral hole;
- A prominence in the center of the outer edge of the arch, called the spinous process;
- A prominence on each external side of the vertebral arch, called the transverse process.
Synonyms
Vertebral fracture is also known as a spinal fracture.
, the vertebrae fracture when a very severe trauma exerts more pressure on them than they are able to bear.Episodes of vertebral fracture, therefore, arise from a very intense traumatic phenomenon affecting the vertebrae or vertebrae involved in the injury.
What are the Causes of Spinal Fracture?

The main causes of vertebral fracture are:
- Car accidents, in 45% of cases;
- Involuntary falls from a height, in 20% of cases.
- Physical clashes during the practice of certain sports (eg rugby, American football and soccer), in 15% of cases.
- Acts of violence, in another 15% of cases.
- Diseases such as, for example, osteoporosis or vertebral tumors, in the remaining 5% of cases.
Did you know that ...
Diseases such as osteoporosis or vertebral tumors are associated with vertebral fracture, as they favor the weakening of the vertebrae.
Who is Most at Risk of Spinal Fracture?
Statistics in the hand, they are more at risk of vertebral fracture:
- People between the ages of 18 and 25. According to some estimates, 80% of people with a vertebral fracture fall into this age group;
- The men. As for vertebral fractures, the frequency ratio between men and women is 4 to 1;
- Individuals with osteopenia or osteoporosis;
- Those who practice sports in which physical contact is required;
- Those who practice jobs where there is a significant risk of falling.
Types of Vertebral Fracture
Doctors distinguish vertebral fractures on the basis of injury dynamics and any involvement of the spinal cord. From this it follows that there are at least 5 types of vertebral fracture:
- The compression fracture;
- The burst fracture;
- The flexion / distraction fracture (or Chance fracture);
- The fracture with dislocation;
- The fracture of the transverse process.
Other types of vertebral fractures, which this article will not describe but will only mention because they are still important, are: the fracture of the first cervical vertebra (or Jefferson's fracture), the fracture of the second cervical vertebra (or Hangman's fracture) and Clay's fracture. -Shoveler.
Vertebral Compression Fracture

Vertebral compression fractures are characterized by an injury limited to the anterior part of the body of the affected vertebrae or vertebrae. This means that, in vertebral compression fractures, the back of the affected vertebrae (s) is intact.
Episodes of vertebral compression fracture below are typical of those suffering from osteoporosis or other diseases that weaken the bones.
Clinically, the vertebral compression fracture is not particularly severe.
BURST VERTEBRAL FRACTURE
Unlike vertebral compression fractures, vertebral burst fractures are characterized by an extensive injury to several points of the body of the vertebrae or vertebrae involved; this particularity gives rise to numerous bone fragments.
Typically, episodes of spinal burst fractures are the result of a hard landing on the feet after a fall from a high height.
In fact, on the occasion of a burst vertebral fracture, we witness the crushing of the affected vertebrae or vertebrae.
Vertebral burst fractures are very dangerous: the numerous bone fragments they give rise to can damage the spinal cord.
VERTEBRAL FRACTURE FROM FLEXION / DISTRACTION
Vertebral flexion / distraction fractures are characterized by an extensive injury, most often, to the anterior, central and posterior compartment of a vertebra; in fact, therefore, in vertebral flexion / distraction fractures c "is a total involvement of the vertebra.

Typically, vertebral flexion / distraction fractures occur in frontal car crashes, in which the person involved wore an abdominal seat belt. This circumstance in fact causes an anomalous sliding forward in the upper part of the body, while the pelvis remains stationary on the car seat, as it is blocked by the abdominal seat belt.
The vertebral flexion distraction fracture is unlikely to involve parts of the spine other than the thoracic or lumbar spine.
Did you know that ...
Spinal flexion / distraction fractures are often associated with abdominal injuries.
VERTEBRAL FRACTURE WITH LUXATION
Vertebral fractures with dislocation are characterized by the injury of one vertebra and part of the ligaments that connect it to neighboring vertebrae.
Usually, vertebral fractures with dislocation involve the entire structure of the vertebrae or vertebrae involved.
Spinal fracture with dislocation is an unstable, often severely debilitating fracture that is accompanied, in many cases, by injury to the spinal cord and / or adjacent spinal nerves.
VERTEBRAL FRACTURE OF THE TRANSVERSE PROCESS
Vertebral fractures of the transverse process are marked by the injury of one or more of the transverse processes present in a vertebra.
The vertebral fracture of the transverse process is a stable fracture, therefore not particularly serious.
Typically, spinal fracture episodes of the transverse process are the result of abnormal rotation or lateral bending of the spine.
in the back.Sometimes moderate, sometimes intense (depending on the extent of the fracture), this pain has the particularity of worsening with movement.
If the vertebral fracture is accompanied by an injury to the spinal cord and / or spinal nerves, the symptom picture will be enriched by neurological disorders, such as:
- Loss of control of the anal and / or bladder sphincter
- Sense of numbness along the limbs;
- Tingling along the limbs;
- Sense of long art muscle weakness.
It should also be noted that, in the event of vertebral fractures near the head, the energy of the injurious trauma could spread to the brain and cause loss of consciousness.
Most Common Locations of Vertebral Fracture
Any vertebrae in the spine can suffer a fracture.
However, most episodes of vertebral fracture involve the vertebrae of the thoracic spine or lumbar spine.
If conditions require it, the doctor may also add a neurological examination to the aforementioned investigations.
It should be noted that, when the vertebral fracture is the result of trauma that could have damaged the spinal cord, the doctor has the duty to establish the patient's vital parameters before any other assessment relating to the extent of the injury; carried out in an emergency regime, this approach protects the patient from any maneuvers that could worsen the situation.
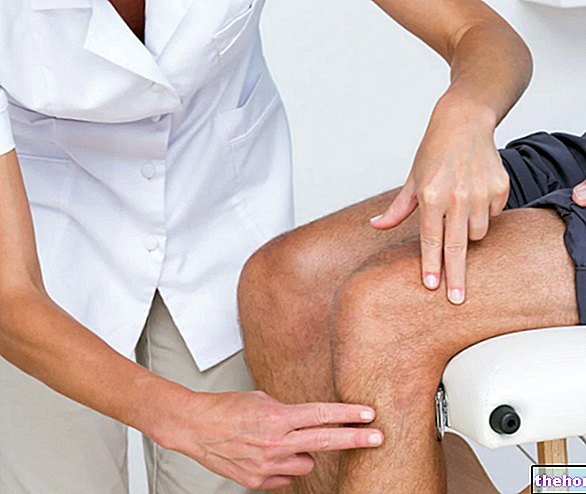
Physical examination
In a patient with a suspected vertebral fracture, the physical examination consists of a careful inspection of the painful area, combined with an examination of the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and limbs.
Physical examination is unlikely to establish the type of vertebral fracture present.
Anamnesis
The anamnesis consists in the collection, through specific questions, of all those data of medical interest useful for identifying the triggering cause and the predisposing factors for a certain condition.
In the case of vertebral fractures following serious trauma to the spinal column, the anamnesis is difficult to execute, as the patient is not in a position to respond. In such situations, important help could come from those who witnessed the accident.
On the other hand, when the vertebral fracture is the result of non-weakening of the bones, the evaluation of the clinical history is a fundamental step in the diagnostic process.
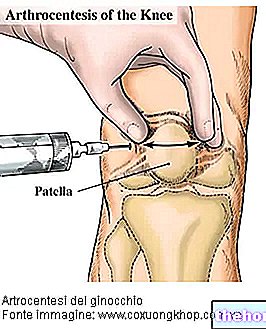
Test of Imaging

The tests of imaging they are used to confirm the presence of a vertebral fracture and to establish its extent and its possible consequences for the spinal cord.
Among the tests of imaging useful for the diagnosis of vertebral fracture, include X-rays, CT and nuclear magnetic resonance, obviously all referring to the spine.
Neurological examination
The neurological examination allows the doctor to determine whether the vertebral fracture has somehow involved the spinal cord or the neighboring spinal nerves.
prior to the injury.The duration of physiotherapy varies according to the type of vertebral fracture.
Complications of the Treatment
Treatment of vertebral fractures forces the patient to bed rest; the resulting immobility is a dangerous factor favoring the phenomenon of venous thrombosis along the limbs, especially the lower ones.
Furthermore, in addition to this dangerous complication, the possible complications that can arise from the recourse to surgery and that characterize this therapeutic option, regardless of the sector of application (these complications consist of infections, haemorrhages, etc.) should be noted.



-cause-e-rimedi.jpg)