Typically, it is an acute condition, which is temporary in duration and sudden onset.
The main cause of nervous breakdown is stress that can result from difficult situations, such as intimate relationship problems, health problems, financial problems, work problems, etc.
The most common symptoms of a nervous breakdown are: anxiety, worry, depressive disorders, low interest in the pleasures of life, and emotional frailty.
The main treatment reserved for those suffering from nervous breakdowns is psychotherapy.
The use of drugs depends, in part, on the symptoms and, in part, on any conditions associated with neurasthenia.

STUDIES ON THE BRAIN
Several researchers have studied the brains of people with nervous breakdowns to understand what happens to them or if something happens to them.
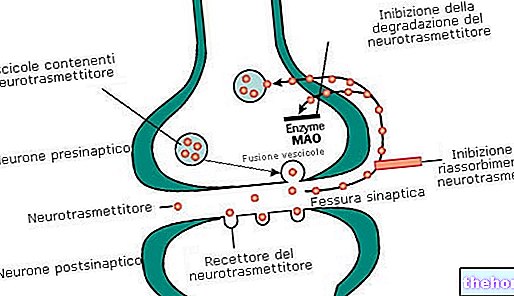
Curiously, some of the studies carried out reported that, within the brains of some patients, there was an imbalance of neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that allow cells in the nervous system, so-called neurons, to communicate with each other.
The finding of a neurotransmitter imbalance in only some patients is not sufficient to give a biological explanation to the nervous breakdown. Therefore, further scientific studies and more in-depth investigations are needed.
SIMILARITY WITH THE PANIC ATTACK
Nervous breakdown resembles a panic attack in several ways, including stress as a causative agent.
Other elements in common between nervous breakdown and panic attack are: the sudden onset and temporary nature of symptomatic manifestations.
Please note: a panic attack is an episode of discomfort, anxiety or fear, which arises suddenly and is temporary.
The characteristic symptoms of nervous exhaustion are sensations, which can affect the quality of life of patients more or less markedly.
Specifically, following a nervous breakdown, an individual can develop:
- Sense of anxiety, worry or fear of something indecipherable.
- Typical disorders of depression (depressive disorders) and a negative mental attitude towards life and the events that characterize it (recurrent pessimism, distrust, etc.).
- Sense of little interest in what they usually like.
- Sense of loss outside of one's home. This results in the tendency to remain confined to the house and to avoid contact with the outside world.
- Emotional fragility. This leads to a certain ease of crying and sadness.
- Passivity in the face of events and a sense of lack of mastery of one's life.
- Strong insecurity.
- Physical frailty and ease of fatigue, even after minimal effort.
- Trouble sleeping at night.
- Confusion of thought.
- Disinterest in their own personal care.
In very rare cases, nervous breakdowns can also be responsible for: mood swings, hallucinations, paranoia and flashback (i.e. sudden memories of past events).

CONSEQUENCES OF ANXIETY
The sense of anxiety has various consequences: it determines, for example, an increase in blood pressure, dizziness, dizziness, tremors, feeling of sickness or pain in the stomach, etc.
CONSEQUENCE OF DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS
The consequences of depressive disorders that can result from a nervous breakdown usually consist of: weight gain or loss, social isolation, lack of interest in family relationships, disinterest in working life and suicidal thoughts.
CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH "NERVOUS BREAKDOWN
In some situations, the nervous breakdown is dependent on the presence of real mental illnesses, which it would be good to identify and treat in a specific way.
Mental illnesses associated with nervous breakdown include:
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Acute Stress Disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Acute depression. It is important to emphasize that there is a certain difference between suffering from depression and manifesting the typical disorders of depression. The first situation is much more serious and more difficult to treat than the second.
- Borderline Personality Disorder
Note: laboratory tests are used to exclude that the symptoms are due to some biological problem.
IMPORTANCE OF PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION
First of all, the psychological evaluation allows us to establish whether the symptoms that the patient complains of are really attributable to a nervous breakdown.
After that, it allows to outline the characteristics of neurasthenia, to trace its causes and to identify any associated mental illnesses.
Understanding the characteristics, causes, and any disorders associated with a nervous breakdown in detail is important for therapy planning.
, psychodynamic psychotherapy and expressive therapy.
Alongside psychotherapy, pharmacological treatment also plays a not insignificant role.
The choice of the most suitable drugs depends on the characteristics of the nervous breakdown:
- A nervous breakdown involving anxiety or worry may require the use of anxiolytics.
- A nervous breakdown that causes depressive disorders or is associated with acute depression prompts the therapist to prescribe antidepressants.
- A nervous breakdown associated with schizophrenia may require the administration of antipsychotics.
- A nervous breakdown associated with bipolar disorder may motivate the prescription of mood stabilizers.
ALTERNATIVE REMEDIES
Thanks to their anti-stress effect, they can promote relaxation and help prevent future nervous breakdowns, not strictly medical remedies such as yoga, aromatherapy, progressive muscle relaxation and hypnosis.
AN IMPORTANT ADVICE
Experts strongly advise against trying to overcome a nervous breakdown without any outside help. In fact, the support of a therapist skilled in the matter is, many times, fundamental.
Also, according to experts, it is very important for a person suffering from a nervous breakdown to talk to family and friends.