Causes of Broca's aphasia include: stroke (main cause), brain trauma, dementia (eg Alzheimer's disease), brain tumors and encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
In those affected, Broca's aphasia is responsible for: agrammatism, grammatical deficit, production of non-fluent and stunted speech, difficulty in formulating complete sentences, articulating sounds or words and repeating what others have said, problems with writing and speech. reading, and, finally, a sense of frustration related to the inability to express oneself. Despite all these consequences, however, Broca's aphasia does not affect the patient's intelligence.
To make the diagnosis of Broca's aphasia, the following are essential: a doctor-patient interview, anamnesis, physical examination and a radiological examination, such as CT or nuclear magnetic resonance, of the brain.
Broca's aphasia is a treatable condition with more or less satisfactory results, through therapies that vary from patient to patient, depending on the triggering cause.
Review of the medical meaning of the term "Aphasia"
In medicine, the term "aphasia" indicates the loss of the ability to compose and / or understand spoken and / or written language, due to the lesion of one of those areas of the brain responsible for processing the aforementioned ability.
having a key role in the ability of the human being to be able to compose both spoken language and written language.
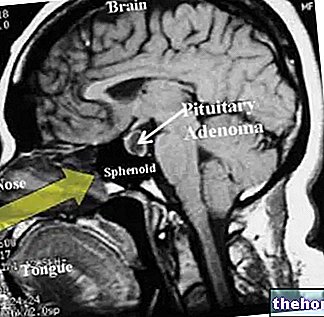
Broca's area is located on the lateral surface of the frontal lobe (outermost surface of the aforementioned lobe), to be precise on the so-called inferior frontal gyrus.
Active in only one of the two cerebral hemispheres (the left, in most people), the Broca area constitutes, together with the Wernicke area present on the temporal lobe, the nervous complex whose good health is essential to keep intact the ability of the human being to compose and understand spoken language and written language.
Causes of Broca's Aphasia
The main causes of Broca's aphasia are stroke episodes located in the Broca area or in its immediate vicinity.
After the stroke, the other possible causes of Broca's aphasia of note are:
- Trauma to the brain that undermines the integrity of Broca's area;

- Brain tumors that appear at or in the immediate vicinity of Broca's area;
- Encephalitis, ie inflammation of the brain;
- Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, such as frontotemporal dementia.
HOW THE ICTUS DAMAGES THE PITCHER AREA AND GENERATES APHASIA
To understand…
In medicine, the word "stroke" means the "interruption of the blood supply to a" brain area, followed by the necrosis of the latter "due to lack of oxygen.
A stroke in the area of Broca involves the lesion of the latter (triggering Broca's aphasia), because it deprives it of the oxygenated blood necessary for its correct functioning and survival. After all, every tissue in the human body, when it no longer receives the right supply of oxygenated blood, at first it malfunctions and subsequently (especially if the lack of blood supply is profound) it undergoes necrosis (ie it dies).
Did you know that ...
Statistics show that 12% of post-stroke aphasia cases are Broca's aphasia.
Risk factors
Risk factors for Broca's aphasia include:
- The factors that predispose to stroke, ie mainly: cigarette smoking, hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, overweight, unbalanced diet, hypercholesterolemia and high triglycerides;
- The practice of sports in which it is quite common to be the victim of head trauma (eg rugby, American football, etc.);
- Aging, as it is associated with a higher likelihood of developing dementia;
- The use of means of displacement related to the risk of head trauma (eg: motorcycle, scooter, etc.).
It is important to specify that, if the brain damage affects other functional areas in addition to Broca's area, the aforementioned symptom picture is enriched by further disorders. For example, if the brain injury also includes Wernicke's area, the patient will manifest also difficulties in understanding spoken and written language, in following directions, etc.
Did you know that ...
The lesion of Wernicke's area (temporal lobe) is responsible for a form of fluent aphasia, known as receptive aphasia or Wernicke's aphasia, in which the patient presents productive speech but has great difficulty in understanding spoken language and language written.
Does Broca's Aphasia affect intelligence?
By itself, Broca's aphasia does not affect the patient's intelligence. The Broca area, in fact, is not related to intellectual abilities, but only controls the ability of the human being to speak and write.
of the word.

The speech therapy treatment for the circumstance in question consists of a series of exercises - such as the repetition of phrases or words - aimed at restoring a certain ability to speak. Initially, the practice of such exercises takes several hours a day, so it requires considerable application and patience on the part of the patient.
The recovery of language skills varies from patient to patient, depending on how severe the lesion in Broca's area is: a mildly severe lesion can be recovered with good results; conversely, a very deep lesion leaves very little room for improvement.
Did you know that ...
To patients with Broca's aphasia, speech therapists teach simple ways to communicate, such as very short sentences, but with a clear meaning, or draw something explanatory, in the presence of a request that is particularly difficult to express in words.
Broca's aphasia due to brain trauma: recovery
Recovery from Broca's aphasia due to head trauma is often spontaneous, ie it does not require specific therapy.
In essence, therefore, when Broca's aphasia results from a brain trauma, the patient improves the ability to speak without the intervention of specific medical figures, but only having the patience to wait for the natural resolution of the triggering cause. Obviously, there are specific medical treatments for victims of brain trauma, but these are valid in any situation, regardless of whether the affected brain area is Broca's area.
How to help an individual with Broca's aphasia
To be of support to an individual with Broca's aphasia, in his recovery path (thus avoiding making him feel a burden and without marginalizing him from the social context), it is very important:
- Remember that Broca's aphasia does not affect the intelligence of patients, who, therefore, are people capable of understanding exactly what they meant before losing the use of the word;
- Treat the patient as a normal person, including him in conversations (even if he says nothing or is limited to a few words), asking him questions, involving him in daily activities, etc. This type of attitude is based on what was stated in the previous point: Broca's aphasia does not alter the intellectual abilities;
- Interview with the patient with simple sentences and questions, so that the answers are not too demanding and difficult.
Involving an individual with Broca's aphasia in a complex discussion worsens his mood, as all his difficulties in expression emerge (and he is fully aware of it).
How long can recovery take?
Recovery from Broca's aphasia can last for days, weeks or even years; it all depends on the severity of the lesion affecting Broca's area and on factors, such as age, general health, attention reserved care, support from family members, etc.