Generality
Barbiturates are a class of drugs capable of depressing the central nervous system. They possess anxiolytic, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, sedative and anesthetic properties.

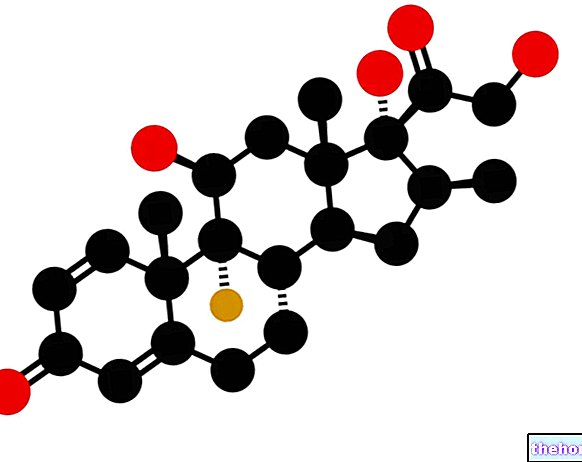
General structure of barbiturates
Furthermore, barbiturates have analgesic properties and were once used in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for the treatment of headaches and tension headaches.
These drugs derive from barbituric acid and - from a chemical point of view - are diacylureas.
Generally, the effects of barbiturates are dose-dependent, i.e. they depend on the amount of drug administered.
Depending on the type, dose and route of administration chosen, barbiturates may have hypnotic sedative, anticonvulsant or anesthetic activity.
However, today barbiturates are considered obsolete drugs and are no longer used - except in specific cases - due to their narrow therapeutic index and their toxicity. Their use has been replaced by the use of safer drugs, such as - for example - benzodiazepines.