If the associated symptoms last less than three weeks, acute laryngitis is common; if, on the other hand, they continue beyond, and if the larynx is anatomically altered, we speak of chronic laryngitis.
The causes of laryngitis are numerous: the acute form is generally due to viral infections or excessive use of the voice; the chronic form, on the other hand, is usually caused by: cigarette smoking, alcohol abuse, gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic sinusitis and / or inhalation of irritants.
The main symptoms are hoarseness and sore throat.
Diagnosis and therapy depend on the type and the triggering causes. A classic acute virus-related laryngitis resolves spontaneously within a week; a chronic laryngitis instead deserves more attention.
Seat of the vocal cords, the larynx performs three fundamental functions:
- It channels the air towards the trachea, then towards the lungs.
- It allows phonation, through the vibration of the vocal cords.
- Thanks to a cartilage valve called the epiglottis, it prevents food, which is about to be swallowed, from entering the trachea and obstructing the airways.

Figure: the larynx and the main cartilage structures that make it up are highlighted in red. As can be seen, the larynx is located at the beginning of the trachea, borders the pharynx above and is in front of the esophagus, which is the first tract of the digestive canal. From the site: ponsuke2.s98.xrea.com

Figure: the larynx and vocal cords. From the site: ponsuke2.s98.xrea.com
Externally, the larynx can be placed in correspondence with the so-called Adam's apple (anterior protrusion of the neck more evident in men than in women).
or fungal, or from excessive use of the vocal cords. The chronic form, on the other hand, is generally due to the inhalation of irritants, cigarette smoke, gastroesophageal reflux disease or chronic sinusitis.In the next two sub-chapters an accurate description of all the possible causes that can trigger a "laryngeal inflammation is reported.
ACUTE LARYNGITIS
Acute laryngitis can arise as a result of:
- Viral infections. Viral origin is the most common form of laryngitis. The main viruses capable of inflaming the larynx and / or vocal cords are: i Rhinovirus (ie the viruses responsible for most colds), human influenza viruses, human parainfluenza viruses, chickenpox virus, mumps virus, coronaviruses and adenoviruses.
- Bacterial infections. Acute laryngitis of bacterial origin is much less common than the viral form. The main bacteria potentially capable of causing acute laryngeal inflammation are: Corynebacterium diphtheriae (the pathogen of diphtheria) e Bordetella pertussis.
- Fungal-type infections. The fungal infections most frequently associated with acute laryngitis are candidiasis and aspergillosis. The first is caused by a fungus of the genus Candida; the second is induced by such a mold Aspergillus.
The people most at risk of fungal laryngitis are immunosuppressed individuals, AIDS patients and those undergoing chemotherapy or prolonged corticosteroid treatment. - A vocal effort caused by "shouting a lot or" using the voice a lot. When you scream for a long time, the vocal cords vibrate faster and for an inordinate amount of time, so they become inflamed, resulting in laryngitis.
Laryngitis arising from vocal strain is also called "mechanical laryngitis".
Other causes of "mechanical laryngitis":
- Direct trauma to the larynx, for example a blow to the throat during an accident or sports injury.
- Prolonged cough
- Frequent clearing of the throat
CHRONIC LARYNGITIS
Usually, chronic laryngitis is due to the perpetuation of certain circumstances or to the onset of particular morbid states. In detail, it can be triggered by:
- Chronic inhalation (for example for work purposes) of irritants, such as chemical fumes, toxic substances, allergens, secondhand smoke or dusts.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is the ascent, in the esophagus and sometimes up to the throat, of the acid content present inside the stomach.
- Chronic sinusitis. It is an inflammatory state that affects the sinuses and paranasal sinuses, characterized by sore throat, headaches, nasal obstruction and nasal discharge.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Cigarette smoke. Heavy smokers often suffer from chronic laryngitis.
- Profession of singer. Those who sing by profession may be subject, after years of activity, to a "permanent alteration of the larynx and vocal cords.
- Cancer of the larynx.
- Paralysis of the vocal cords. It can be the result of a nerve injury, a neoplasm of the lungs, very strong trauma, surgery (thyroidectomy or spinal surgery) etc.
In addition, although more rarely than in the acute form, chronic laryngitis can be caused by some pathogenic microorganisms, such as:
- The bacteria Streptococcus group A beta hemolytic, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (the "bacterial agent of tuberculosis), Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, Mycobacterium leprae (the leprosy bacterium), Actinomyces And Treponema pallidum (the syphilis bacterium).
- The mushrooms Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum And Sporothrix schenckii.
- The protozoa of the genus Leishmania.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The precise incidence of laryngitis (both acute and chronic) is unknown; this is because the number of diagnosed cases is undoubtedly lower than the number of real cases; moreover, the acute form (usually self-limiting) is more frequent than the chronic one.
As regards the age of greatest onset and the most affected sex, the only reliable data concerns chronic laryngitis: according to some estimates, the latter would be more common among middle-aged and male people (NB: recently yes a decrease in the difference between men and women is observed, easily explained by the increased number of smokers).
Usually, the symptoms and signs typical of acute laryngitis appear suddenly and tend to worsen in a short time, within two to three days at the most.
The manifestations of chronic laryngitis, on the other hand, have a gradual onset and slowly worsen over several weeks or months.
MOST COMMON EXPRESSIONS OF LARYNGITIS
The most common symptoms of laryngitis are:
- Hoarseness
- Loss of voice or difficulty speaking
- Sore throat
- Dry throat
- Dry and irritating cough
- I constantly need to clear my throat
- Sensation of itchy throat
- Slight alteration in body temperature
- Respiratory difficulties. They are uncommon in adults and frequent in children, who have a narrower trachea.
WHEN LARIGITE IS ASSOCIATED WITH OTHER HEALTH DISORDERS
Since laryngitis is often caused by viruses that can also cause colds, flu, tonsillitis or pharyngitis, it is very likely to be accompanied by other ailments, such as headache, runny nose, tiredness, generalized joint pain and lymph nodes. swollen neck.
DURATION OF SYMPTOMS
Acute laryngitis typically lasts a week, although in some cases it can persist for a few more days. Chronic laryngitis, on the other hand, can last for a long time, even for several weeks or months.
WHEN TO CONTACT THE DOCTOR?
Most laryngitis heals spontaneously, without the need for special medical treatments or consultations.
If, however, the symptoms last for some time (weeks or months) and are of significant intensity, it is good to contact your doctor and request an appointment.
Attention: children with laryngitis who manifest respiratory problems represent a very delicate and potentially very dangerous situation. Therefore, it is advisable to consult your doctor immediately, describing in detail all the symptoms of the suffering child.
The symptoms that, in a child, must arouse the attention of the parents and the doctor are:
- Loud breathing
- Respiratory difficulties
- Excessive drool production
- Difficult swallowing
- High fever, even at 39 ° C
OBJECTIVE EXAMINATION
During the physical examination, the doctor analyzes the entire symptom picture and clarifies the patient's personal medical history (ascertaining the health conditions at the time of diagnosis, the illnesses suffered in the past, any allergies, etc.).
Furthermore, it is essential for the doctor to determine if he is dealing with a smoker, an alcohol abuse person, a chronic sinus sufferer, a professional singer or a worker in some industrial plant (the aforementioned circumstances being all potentially decisive in a background of laryngitis).
BLOOD TESTS AND PHARYNXIC SWAB
The doctor uses blood tests and analysis of a throat swab to determine whether or not the patient is suffering from some infectious disease.
In both cases, these are quick, economical and potentially capable of providing various information useful for diagnostic purposes.
LARYNGOSCOPY
Laryngoscopy is the diagnostic test that allows you to assess the health of the larynx and vocal cords. There are two types of laryngoscopy: indirect and direct.

- Indirect laryngoscopy. Carried out in the doctor's office, it is a very simple procedure, which requires the use of two objects: a mirror, to be inserted into the patient's throat, and a light source, with which to illuminate the mirror and see the larynx in reflection. Usually, it does not involve any anesthesia; however, if the patient under examination is bothered by the presence of the mirror, it may be useful to practice a "local anesthesia".
- Direct laryngoscopy. This procedure involves the insertion, in the throat (near the larynx), of an optical fiber instrument equipped with a camera and light source. This instrument, called a laryngoscope, can be flexible or rigid: if it is flexible, it is inserted through the nose and requires local anesthesia; if it is stiff, it is inserted through the mouth and requires general anesthesia.
Compared to indirect laryngoscopy, direct laryngoscopy is much more precise and, when performed with the rigid laryngoscope, also allows the collection of a sample of laryngeal tissue for a possible biopsy examination.
BIOPSY OF THE LARYNX: WHAT IS IT AND WHEN IS IT USED?
The biopsy of the larynx consists of the collection, and subsequent microscopic analysis, of a sample of laryngeal tissue. It is usually done when doctors suspect (or want to make sure it's not ongoing) that there is a malignant tumor of the larynx.
The collection procedure is performed by direct laryngoscopy with a rigid laryngoscope.
Other useful tests in case of suspected laryngeal malignancy:
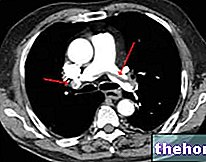
- CT scan (or computerized axial tomography): it is a very precise diagnostic imaging test, which however exposes the patient to a minimal amount of ionizing radiation.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (MRI): This is a reliable diagnostic imaging test that is completely harmless to the patient.
ALLERGIC TESTS
If there is a suspicion that laryngitis is caused by an allergy to certain volatile substances (dust, chemical fumes, etc.) or to certain foods, the doctor will certainly prescribe allergy tests.
WHICH SPECIALIST IS BEST TO CONTACT?
Often, when a general practitioner finds chronic and / or severe laryngitis, the patient advises to consult an otolaryngologist, that is, a doctor who specializes in treating diseases of the ear, nose and mouth.
Most laryngitis heals within 7 days and without resorting to special treatment. Nevertheless, for an even faster and more effective resolution of the ailments, doctors recommend putting into practice certain remedies and / or countermeasures (such as drinking plenty of water, avoiding talking too much, etc.).
If laryngitis is chronic, the situation is more complex and delicate: to heal, in fact, the doctor must plan a specific therapy, based on the triggering causes.
REMEDIES TO ACCELERATE HEALING
To speed up healing and relieve symptoms caused by laryngitis, it is very useful:

- Avoid talking too much and too loudly. Shouting or talking a lot inflames the vocal cords; therefore, if the latter are already inflamed, it is not advisable to urge them further.
- Get plenty of fluids, especially water, to avoid becoming dehydrated. Alcoholic beverages and coffee should be avoided until the symptoms have completely resolved.
- Wash with mouthwash or water and salt solutions. Although these substances do not reach the larynx directly, they are still very effective in keeping the throat moist and reducing its inflammatory state.
- Take anti-inflammatory and pain relieving medications, such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen or aspirin. Such medicines are appropriate when the patient complains of a nagging pain in the throat, headache, fever, etc. (hence the symptoms of a "flu or a severe cold).
Attention: Individuals under the age of 16 should not be given aspirin, as it could cause the so-called Reye's syndrome. - Make hot-humid or menthol-based inhalations to clear the airways and lungs of mucus. Always with the same aims, doctors also recommend hot showers and the use of a portable air humidifier in the rooms where you spend most of your time.
- Do not smoke (if you are a smoker), avoid breathing passive smoke and do not frequent dusty and dry environments.
MAIN TREATMENTS FOR CHRONIC LARYNGITIS
If the "origin of chronic laryngitis c" is:
- A "bacterial infection requires antibiotic therapy.
- Excessive alcohol consumption or cigarette smoking, it is good to stop drinking (or at least drastically moderate alcohol intake) and smoking, respectively.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease, take the most appropriate medicines for this type of disorder (antacid drugs); these preparations consist of substances which decrease the acidity of gastric secretions.
- An "allergy, it is necessary to avoid coming into contact with responsible substances (the so-called allergens) and to obtain antihistamine drugs for emergency cases (for example, when you inadvertently ingest a food to which you are allergic or when inhaling a dust towards which one is intolerant).
- A professional use of the voice, it is advisable to regularly learn and practice some targeted vocal exercises, which allow to safeguard the vocal cords and the larynx in general.
- A cancer of the larynx, the malignant tumor must be removed and / or treated with laser, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
WHEN TO USE CORTICOSTEROIDS?
Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, which, when used in excessive doses and for long periods of time, can cause serious side effects.
Main side effects of corticosteroids:
- Osteoporosis
- Glaucoma
- Hypertension
- Overweight and obesity
- Gastric ulcers
In case of laryngitis, their intake is considered by the attending physician only if the symptoms are very intense and the situation is rather critical.
It is strongly not recommended to take them without a prescription.