in the urine (bacteriuria) is a condition that is a probable sign of ongoing urinary infections.
Bacteriuria can be associated with the typical symptoms of cystitis (urgent need to urinate, fever, pain in the lower abdomen, etc.) or be asymptomatic, that is, not related to any type of malaise.
For this reason, a urine culture is prescribed, a particular urine test to check for the presence of bacterial strains responsible for the infection.
The microscopic observation of the bacteria in the urine sediment can offer indications on the identity of the pathogens in question. Their exact identification is obtained, however, by inseminating the infected urine on special culture media (urine culture).
Tags:
Cosmetic Surgery Power supply fitness-tutorial
Bacteriuria can be associated with the typical symptoms of cystitis (urgent need to urinate, fever, pain in the lower abdomen, etc.) or be asymptomatic, that is, not related to any type of malaise.
For this reason, a urine culture is prescribed, a particular urine test to check for the presence of bacterial strains responsible for the infection.

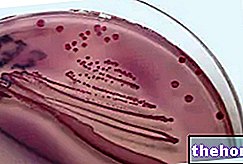
The bacterium most frequently identified in the urine is the "Escherichia coli.
or from the anal area, in men from the prostate (in the presence of concomitant prostatitis). or by urine culture, if there is an infection of the urinary tract (urethra, urinary bladder, renal pelvis or kidney) or of the genital tract.The microscopic observation of the bacteria in the urine sediment can offer indications on the identity of the pathogens in question. Their exact identification is obtained, however, by inseminating the infected urine on special culture media (urine culture).
Important for prognostic and therapeutic purposes is the determination of the bacterial load, which is obtained by counting, that is, determining the number of germs present in a given volume of urine.