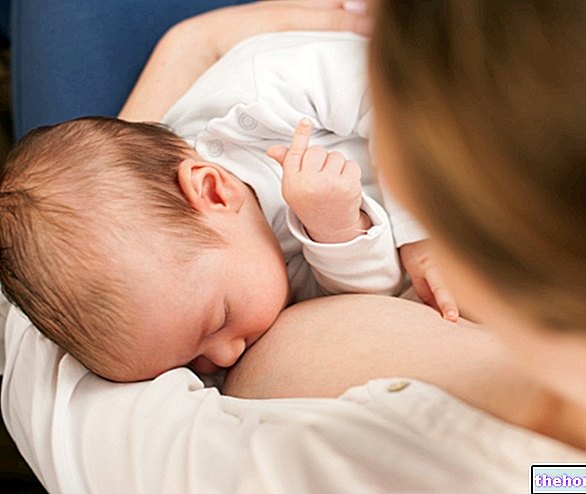
A characteristic sign of pregnancy is the increase in sensitivity and in the size of the breasts. This change underlines how the maternal organism is preparing to provide the right nourishment to the unborn child.
Increasing the production of breast milk seems an important goal for many new mothers, given the widespread and often unjustified fear that the milk produced is not enough to cover the nutritional needs of the baby.
How milk production takes place

An aspect closely linked to the increase in milk synthesis concerns the diet of the nurse. First of all, it does not matter if in this period the diet will be a little more abundant than usual, indeed, better, because calories are provided which are useful for the production of milk.
Negative factors on milk production
The milk produced by the mother can sometimes be insufficient due to the presence of one or more factors, such as:
- STRESS STRESS due to childbirth or pregnancy; this element greatly affects the production of breast milk;
- REDUCED JET OF MILK. To remedy this inconvenience it is enough for the mother to take water and constantly breastfeed the newborn.
- HORMONAL CAUSES RELATED TO THE THYROID. Dysfunctions affecting the thyroid gland can appear in the period immediately following childbirth or during pregnancy, with a negative effect on milk production;
- DEHYDRATION. Poor fluid intake decreases the mother's milk production. Conversely, drinking enough, even during the night, supports milk production. Many mothers feel the urge to drink a lot at the time of breastfeeding. They can do this very well but this will not always make them produce more milk, in fact, it is important to remember that sometimes drinking too much can reduce the production of breast milk.
- ACCIDENTAL INTAKE OF ANTI-GALACTOGUE SUBSTANCES. Some substances that hinder milk production can be found in some foods or medications (see below). These anti-galactogogues counteract the production of breast milk.
- INSUFFICIENT CALORIES. It is advisable for the mother to consume 350 to 700 calories more daily to cover the energy needs necessary for the production of milk;
- LACK OF SLEEP. Rest hours also affect milk production. The nurse would need 8 to 10 hours of sleep a night; this provides substantial aid to milk production.
The mother can therefore maximize milk production simply by avoiding the factors just outlined. In addition to circumventing these obstacles, the mother can take certain foods and / or herbs that have a so-called galactagogue effect. However, please note that the intake of certain herbs or plant products during pregnancy and / or breastfeeding is generally not recommended. Therefore, if you intend to take them, it is good to always seek the advice of the doctor. It is forbidden to do one's own thing.
As anticipated, the suckling of the newborn is the most important stimulus to the production of breast milk. Therefore, excessive administration of other foods (for example supplementation with infant formula) and various feeding disorders, such as insufficient number, inadequate time, hasty, uncomfortable or stressful environment, and premature detachment of the baby can negatively affect this. small from the breast.
Foods that affect milk production
To cope with low milk supply, many mothers use a completely natural remedy. This strategy consists in taking some galactogogue foods and herbs during the entire breastfeeding period.
Foods capable of stimulating milk production are also referred to as galactagogues (or galactophores). In fact, there are substances - which can be synthetic or natural - whose function is to stimulate, therefore increase, the production of breast milk.
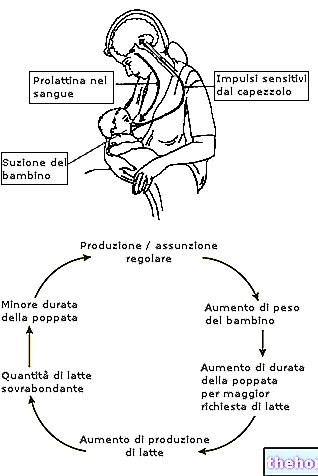
In the human organism, the most powerful galactogogue action is carried out by prolactin and oxytocin. The first hormone is able to stimulate the glandular component of the breast to produce milk, while the second "squeezes" the alveoli by channeling the milk into the milk ducts and favoring its escape through the nipple.
Some foods that appear to increase milk production are:
- ASPARAGUS
- APRICOTS
- WATERCRESS
- PARSLEY
- OATMEAL
- PECAN WALNUT
- GREEK HAY (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
- BORAGE (Borago officinalis)
- GREEN BEANS
- DANDELION
- BEETS
- SWEET POTATO
- FENNEL
- VERBENA
- HOPS (Humulus lupulus)
- CARROTS
- PEAS
- DARK BEER (with or without alcohol)
These foods can be eaten by the mother every day without problems, with the exception of beer, which is allowed only once a day, in moderation (it is prohibited, like all other alcoholic beverages, during pregnancy).
Sage, cabbage and peppermint, instead of exhibiting a "galactogogic activity, perform the reverse action", thus hindering the production of breast milk. In addition to natural products, attention must also be paid to various drugs, such as antihistamines, diuretics, hormonal contraceptives (estrogenic or estrogenic) and all those medicines that contain ephedrine and derivatives (prohibited during pregnancy).
Like all medical herbs, various supplements and medicines require a doctor's approval prior to use.
During breastfeeding, mothers who usually consume a lot of coffee or caffeinated drinks (such as Coca-Cola) must limit the consumption of these drinks. Caffeine, in fact, reduces the production of breast milk and induces excessive nerve stimulation of the newborn. It should be clear that the consumption of a cup of coffee or a drink containing caffeine does not cause any problems for the mother or the baby, while in the case of excessive consumption the infant could suffer from the large amount of caffeine taken with the milk by the nurse.
Useful tips
- To increase breast milk production, it is important that sucking occurs immediately after delivery, and continues with a certain frequency (the "WHO recommends 8 to 12 feedings per day). Equally important is that the breast does not get too full of milk. , because this induces the production of a factor (Prolactin Inibiting Factor) that opposes milk production. It is therefore important that the mother empties her breast with a certain constancy, in order to support - and if possible increase - the production of milk, while preventing breast engorgement.
To deepen the topic see: number and characteristics of feedings. - Drink a lot while breastfeeding and follow a correct and healthy diet;
- Take galactogogic substances in order to increase milk production, but only after obtaining the authorization from the doctor;
- Avoid substances that can interact with milk production;
- Make sure that the mother is calm, relaxed and reassured about the suitability of the milk produced;
- The mother should get enough rest, in order to regain strength and stimulate milk production;
- The newborn should spend a lot of time with the mother to strengthen physical contact between the two.
- During the 24-hour period, the newborn should suck the mother's breast at least 8 times. The night feedings are very useful, because in this phase the infant is more likely to suck large quantities of milk; moreover, they prevent the breast from engorging annoyingly.
- To increase milk production while avoiding nipple trauma, the position of the baby during the feeding is very important (see in-depth analysis);
- As you wait for her to start or resume making her own, explain to the mother how to use other types of milk to replace her own.
- Always keep an eye on the weight, urine and faeces of the unborn child. Reduced urine output, infrequently issued hard and dry stools, insufficient weight growth and failure to regain weight at birth within 15 days of life are the most important signs that the baby is not getting enough milk.
- The motivation of the mother is also important to increase milk production, and she must "be free from the influence of negative psychological factors (refusal of the baby, worry, stress, negative attitude towards breastfeeding, etc.). moral support plays a vital role.