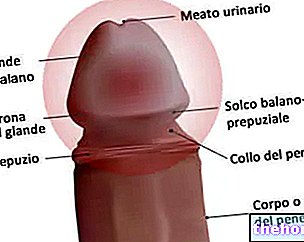
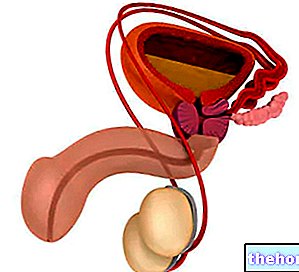
The term infertility is an adjective used to define poor efficacy in conception. This problem can affect only one of the two partners or both.

We talk about infertility when the couple is unable to conceive within 12 months with regular intercourse and without the use of contraceptives. Some authors postpone the limit up to 24 months.
Infertility is not always justifiable. Sometimes there are interfering factors that hinder conception but, in most cases, the couple and doctors are unable to justify this difficulty (it could be multifactorial).
The material published is intended to allow quick access to advice, suggestions and general remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of infertility; these indications must in no way replace the opinion of the treating physician or other healthcare specialists in the field who are treating the patient.
What to do
- Before considering the presence of any pathologies it is necessary to make sure that:
- Sexual intercourse is regular: to tell the truth, this criterion is strictly subjective. Not all couples have the same rhythms; however, these can change considerably even during the history of the couple itself. There is no limit to be respected but generally one is led to believe that an acceptable frequency falls within a weekly period of time (at least once a week).
- Contraceptives are not used: of any kind they may be. This clarification is necessary as for both the woman and the man, there is the possibility of using contraceptives (more or less safe) without the partner noticing it. Before starting the attempts at conception it is always better to establish a dialogue to understand if it is a unanimous choice.
Taking the basic assumptions for granted, in order to increase the chances of conception it is necessary:
- Having intercourse during the period of ovulation: this lasts about 24 hours and is not always easily recognizable. The most recommended systems are:
- Ovulation calendar: in a regular cycle of 28 days, the moment of ovulation coincides with the 14th day. This parameter changes according to the average duration of the cycle.
- Measurement of the basal temperature: during the ovulation of the woman the temperature is 0.2-0.5 ° C higher than the norm.
- Cervical mucus analysis: the presence of a “transparent jelly” in the cervix (which can be scrutinized from the vagina) indicates the moment of ovulation.
- Fertility test: it consists in wetting a special strip with urine that reacts to the specific hormonal concentration indicating or not the ovulation activity.
- Other less simple systems to perform are:
- Saliva examination: in the fertile period, observing the salvo under a microscope can show the presence of a fern-shaped pattern (similar to crystals) caused by the presence of specific hormones.
- Verification of the position of the cervix: during the fertile period this rises, widens and takes on a softer consistency.
- Some obvious but inaccurate signs are also: increased sexual desire and increased breast tension.
- Also have intercourse two or three days before and two or three days after the day of ovulation.
- Keep sperm quality high: This can be achieved by ejaculating about once a day:
- Abstaining for several days in an attempt to "accumulate" as much as possible is not a correct choice as it favors the stagnation of seminal fluid.
- It is also inadvisable to ejaculate shortly before sexual intercourse aimed at conception, as the newly synthesized sperm may contain many incomplete spermatozoa.
- Choose the sexual relationship management system best suited to the couple's trend:
- Having sex on all fertile days: it is suitable for easily adaptable couples. It is probably the most effective method. It requires being able to detect with certainty the moment of optimal fertility.
- Having sex every week: it works especially for very "regular" couples who struggle (for various reasons) to change their habits. In this way you are guaranteed to get at least one day of the fertile period right. NB: By ejaculating only once a week, the quality of the sperm is not optimal.
- Continuing to have intercourse for the pleasure of it: many couples "break down" in an attempt to conceive as soon as possible. It mainly affects men; sometimes women who do not reach orgasm easily are also victims of it, as increasing the frequency usually reduces the duration of the intercourse. It occurs when the pace becomes so high that it causes boredom and almost aversion. Let's not forget that the chances of getting pregnant are about 20% every month and often the search lasts over six months (sometimes a year and cases that exceed two years are not very rare).
- Lower the level of stress to a minimum: this applies to the couple in general but it is a useful precaution especially for women. It is no coincidence that many conception takes place during holidays and rest. After all, stress compromises the hormonal axis that is directly involved in female fertility.
- After the act, it may be helpful for the woman to remain in a reclined and declined position (with a thickness under the hip).
- Feed properly: Reproduction is a very laborious and expensive process. The human organism does not effectively support the processes of fertilization and pregnancy in a state of malnutrition. It must not lack any nutrients and are particularly important: certain vitamins, fatty acids and essential amino acids.
- Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI or BMI) Normal: this applies mainly to females, but males are not totally immune:
- The body of an underweight woman (BMI amenorrhea. A female without a menstrual cycle can normally be fertile but the chances are much lower.
- The same is true of obesity. This condition is related to type 2 diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary (a disease capable of reducing fertility). These are not conditions that reduce fertility in a short time but it is advisable to intervene for preventive purposes to prevent the polycystic ovary from appearing.
- Practicing physical activity: an active lifestyle has been shown to prevent infertility but the mechanism is not clear. It probably depends on the fact that sportspeople generally follow a healthier lifestyle. Sporting activity certainly facilitates blood circulation and tissue oxygenation.
- If possible, try to conceive at an appropriate age: old age progressively decreases the possibility of conception and increases that of complications.
- Preventing and treating sexually transmitted diseases: applies to men and women. Both can be damaged (even permanently) due to genital infections.
In the event that all this is not enough to guarantee fertility (after a year or two from the beginning of the attempts), it becomes necessary:
- For her, carry out a gynecological check-up with the aim of finding:
- Ovarian limiting factors: they compromise ovulation. They are due to hormonal alterations: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), anovulation, ovarian failure, premature menopause.
- Uterine factors: more involved in infertility rather than sterility. They involve anatomical alterations of the uterus, such as congenital or acquired malformations, also responsible for repeated miscarriages.
- Tubal factors: anomalies that hinder the egg-spermatozoon meeting. They are: absence, impermeability or obstruction, salpingitis.
- Cervical factors: anatomical or functional alterations that interfere with the flow of spermatozoa. They are waterproofing and previous surgery.
- For him, carry out a check by the andrologist with the aim of finding:
- Genetic factors: directly or indirectly associated with sperm abnormalities: cystic fibrosis, Klinefelter's syndrome, etc.
- Anatomical factors: implies obstructions of the sperm passage ducts and varices. They can be congenital or acquired.
- Environmental factors: smoking, alcohol, drugs, etc.
- Other: such as mumps (mumps) viral disease, hormonal dysfunctions etc.
NB: The most used analysis is the spermiogram, which evaluates: sperm volume, sperm count, sperm concentration, total motility, progressive motility, vitality, morphology, sperm pH, leukocytes, MAR test.
- Couple infertility:
- Combinations of several factors.
- Immunological and / or genetic factors: when both subjects are perfectly healthy, infertility may be due to immunological incompatibility (antibodies on the surface of spermatozoa and female cervical mucus) or genetic.
If the cause of infertility is reversible:
- Take advantage of medical treatments that can solve your specific problem.
What NOT to do
- Indulge in sexual intercourse sporadically or in any case in an insufficient manner.
- Use contraceptives.
- Try to conceive especially in the period away from ovulation.
- Attempt to conceive only on the day in which ovulation hypothetically occurs.
- To rely too much on ovulation calculation systems.
- Ejaculate infrequently (for example, only once a week).
- Ejaculate just before attempting to conceive.
- Losing interest in sexual activity and practicing forced conception.
- To exceed the limit of tolerance and to stop the attempts for the excessive effort.
- Keep your general stress level high.
- Having nutritional deficiencies: generalized or specific.
- Being or becoming underweight.
- Being or becoming overweight.
- Being sedentary and leading an irregular lifestyle.
- Excess with physical activity: for women this affects the balance of body mass and hormonal balance.
- For men, some speculate that prolonged cycling (competitive levels) can compromise prostate health; it is a "hypothesis not yet scientifically proven.
- Smoking: nicotine and other substances contained in tobacco and paper compromise the health of spermatozoa; in particular, they damage DNA and reduce mobility.
- Abuse of alcohol: the correlation to infertility is less clear than smoking. However, considering that it is a harmful habit (in any case to be terminated during pregnancy), it is advisable to stop before conception. Ethyl alcohol is a toxic molecule for all tissues and gonads are no exception.
- Attempting conception in old age.
- Contracting or not adequately treating STDs (especially bacterial).
- After a year or two from the beginning of the attempts, in compliance with what is suggested in the previous chapter, DO NOT contact your doctor for a diagnostic procedure (for him and for her) in search of pathologies or limiting factors.
- With the awareness of being infertile due to pathologies or reversible limiting factors, DO NOT take advantage of specific medical treatments.
What to eat
- In case of obesity, it is advisable to reduce the weight. To lose weight it is sufficient to reduce the caloric intake by about 30%, leaving the (balanced) distribution unchanged; we recommend a percentage of fat of 25% and the choice of foods that do not stimulate the insulin surge.
- In case of underweight, it is advisable to increase the total mass of the organism. This mainly concerns women. To gain mass it is sufficient to increase the caloric intake by about 10%, leaving unchanged the (balanced) distribution; a fat percentage of 30% of total calories is recommended.
- Foods rich in omega 3: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic (DHA) and alpha linolenic acid (ALA). In addition to exerting an anti-inflammatory role, they appear to be directly related to a good composition of the sperm and the health of the ovum. The first two are biologically very active and are found mainly in: sardine, mackerel, bonito, sardinella, herring, alletterato, ventresca di tuna, garfish, seaweed, krill etc. The third is less active but constitutes a precursor of EPA; it is mainly contained in the fat fraction of certain foods of vegetable origin or in the oils of: soy, linseed, kiwi seeds, grapes etc.
- Foods rich in antioxidants: by effectively fighting the oxidative stress of the whole organism, it is also possible to improve the composition of the sperm and the health of the egg.
- Vitamins: the antioxidant vitamins are carotenoids (provitamin A), vitamin C and vitamin E. Carotenoids are contained in vegetables and red or orange fruits (apricots, peppers, melons, peaches, carrots, squash, tomatoes, etc.); they are also present in crustaceans and milk. Vitamin C is typical of sour fruit and some vegetables (lemons, oranges, mandarins, grapefruits, kiwis, peppers, parsley, chicory, lettuce, tomatoes, cabbage, etc.). Vitamin E can be found in the lipid portion of many seeds and related oils (wheat germ, corn germ, sesame, kiwi, grape seeds, etc.).
- Vitamin C and vitamin E seem to have a positive effect (independent of the antioxidant capacity) on the composition of the sperm and on the health (therefore also on the receptivity) of the egg.
- Saline: the antioxidant minerals are zinc and selenium. The first is mainly contained in: liver, meat, milk and derivatives, some bivalve molluscs (especially oysters). The second is mainly contained in: meat, fish products, egg yolk, milk and derivatives, enriched foods (potatoes, etc.).
- Polyphenols: they are divided into simple phenols, flavonoids, tannins. They are very rich: vegetables (onion, garlic, citrus fruits, cherries, etc.), fruit and relative seeds (pomegranate, grapes, berries, etc.), wine, oil seeds, coffee, tea, cocoa, legumes and whole grains, etc.
- Foods rich in vitamin D: plays a decisive role in the synthesis of steroid hormones and products of the gonads (male and female). They are rich in it: egg yolk, fishery products, cod liver, etc.
What NOT to Eat
- Bad fats: they are contained in margarines and hydrogenated oils. These are used as ingredients in: fast food (french fries, hamburgers, etc.), salty snacks (pop corn, potato chips, nachos, etc.), sweet snacks (chocolates, bars, snacks, etc.) and packaged baked goods (focaccia, croutons, croissants, etc.).
- Foods that promote obesity: it is advisable to eliminate all junk foods and drinks, in particular fast food, sweet or savory snacks and sweet and alcoholic drinks. It is also necessary to reduce the frequency of consumption and the portions of: pasta, bread , pizza, potatoes, derivatives, fatty cheeses, fatty meats and fish, cured meats, sausages, sweets, etc.
Natural Cures and Remedies
- Supplements: all food supplements that contain the molecules mentioned in the "What to eat" paragraph are useful:
- Omega 3.
- Antioxidants (vitamin, saline, polyphenolic).
- It is advisable to emphasize above all the intake of vitamin E and vitamin C.
- Vitamin D.
- A beneficial role has also been hypothesized for magnesium and carnitine, but the scientific evidence is wavering.
- Herbalist:
- Peruvian Maca: it is a root similar to Ginseng. It can be eaten or used in purified extract. It appears to increase sperm production and sperm mobility.
- Ayurvedic Medicine:
- Mucuna pruriens: is a legume. Its seeds are said to have several therapeutic characteristics; among these, also an increase in fertility.
Pharmacological treatment
Grouping all drugs into one paragraph is very complicated, as the causes of infertility are numerous and require different treatments. Below we will report only the most used ones:
- Drugs for ovarian and testicular stimulation: these are hormones or derivatives to be taken orally or intramuscularly (GONAL-F based on follicle stimulating hormone, GONASI and Pregnyl based on chorionic gonadotropin, LUVERIS based on luteinizing hormone, MENOGON a base of Menotropin etc.). The efficacy varies according to the cause of infertility. In women they can have significant side effects such as multiple pregnancies and gastrointestinal disorders.
Prevention
- For the woman, carry out a periodic gynecological check-up.
- Check the rhythm of the menstrual cycle in the female.
- Avoid sexually transmitted diseases.
- Avoid underweight and female amenorrhea.
- Avoid obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary in women.
- Eat in an adequate and balanced way.
- If present, treat varicocele or testicular cancer in humans.
- Do not delay attempts at conception until old age (over 35 years).
- Do not drink, do not smoke and do not take drugs.
- Reduce or avoid stress.
- Some suggest avoiding the cell phone in the trouser pocket; radiation can impair fertility.
Medical Treatments
For infertility or sterility caused by anatomical factors, it is possible to perform:
- Surgery:
- In men the following are frequent: removal of varicose veins in the testicles (varicocele).
- In women: removal of uterine polyps, submucosal fibroids, adhesions to the uterine cavity, ovarian cysts, endometritis, etc.
- Assisted reproduction. The best known and used techniques are:
- Artificial insemination: it consists in depositing the male semen inside the woman's uterus with the use of a cannula inside the cervical orifice.
- In vitro fertilization: it is based on the collection of an oocyte via the vagina and subsequent fertilization in the laboratory with a sperm isolated from the sperm.
- Intratubal gamete transfer: consists of the laparoscopic removal of the oocytes, the selection of mature ones and the transfer to a cannula containing the male's seminal fluid. The whole is then placed inside a tuba to release its contents.
- Intracytoplasmic spermatozoa: similar to in vitro fertilization but in this case the sperm is injected directly into the egg.