Information on Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Food supplement based on Melatonin
FORMAT
Pack of 60 tablets
COMPOSITION: Stabilizer: microcrystalline cellulose; Anti-caking agent: magnesium stearate and silicon dioxide; Melatonin.
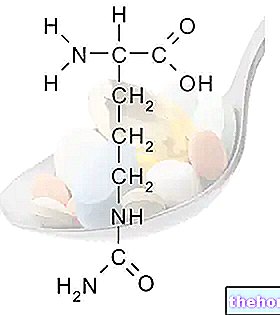
PER CAPSULE: Melatonin 5 mg
Product features Melatonin 500 - Eurosup

The epiphysis plays a role of mediator between the external environment and the endocrine activity, regulating its activity according to the photoperiod. The presence of photoceptors, in fact, seems to modulate the production of melatonin considerably, inhibiting it in the presence of light and promoting it in absence of light stimuli. All this translates into a rhythmic production of melatonin, which is maximized during the night and then significantly reduced during the day. It is therefore possible to consider this substance as the "biological clock of the human organism, because by activating different types of receptors, disseminated in the brain (especially hypothalamic), can act as a sedative and hypnotic inducing sleep. The production of melatonin is maximum during the first 7 years of life, and then gradually decreases (in reality the levels of synthesis remain constant, while the blood volume increases), and becomes minimal in the elderly, where the reduced innervation on the one hand and the epiphysial calcification on the other, seriously compromise the endocrine functionality of this gland. Fortunately, oral integration of melatonin has been shown to temporarily reduce the endogenous secretion of this hormone, delaying the exhaustion and aging of the pineal gland and preserving its functionality.
Although there are many studies in the literature, it is still not possible to trace a complete profile of all the potential functions of this molecule; therefore we will describe the main biological aspects in which it is involved:
- Sleep / wake rhythm: by interacting with receptors disseminated at the hypothalamic level, melatonin can exert a hypnotic and sedative effect;
- Biological protection: exercised not only on the pineal gland, but generalized to the whole organism (given the protective action described against nucleic acids subjected to chemical stress);
- Antioxidant processes: melatonin is directly involved in the oxygen and nitrogen free radical detoxification system, contributing - together with its metabolites - to the total antioxidant capacity;
- Immune system: it is able to enhance the body's immune defenses, antagonizing the immuno-depressive effects induced by acute stress and improving both the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the differentiation and activation of the lymphocyte cellular component;
- Metabolic pathways: recent evidence is showing an important role for melatonin, and its MT1 receptor, in glucose metabolism. In fact, receptor activation seems to improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type II diabetes and associated diseases such as obesity.
Melatonin in sports practice
Although it is difficult to justify and describe the advantages deriving from the intake of melatonin in sports, the scientific literature provides some interesting points of reflection on possible applications of this supplement:
- Improvement of hormonal function: The biological clock role of melatonin could be particularly important for improving hormone secretion in individuals subjected to intense training. Although the literature is not very rich in such studies, there is some scientific evidence that correlates the increase in nocturnal secretion of GH to the administration of melatonin.
- Protective action: the antioxidant action of melatonin could be important in counteracting the oxidative damage induced by intense physical exercise.
- Metabolic action: despite the lack of scientific evidence on humans, in animal studies melatonin induced a reduction in lactate synthesis, probably associated with the metabolic effect on glucose tolerance previously described.
- Thermoregulatory action: some evidence suggests that the drop in body temperature, recorded following the intake of melatonin, can be beneficial for athletes subjected to training and performance at high temperatures.
Rationale - Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Although the ideas for its application in sports are interesting, it must be remembered that the main therapeutic indication of melatonin is related to the treatment of various sleep disorders; however, there are studies that certify its efficacy in neurodegenerative and endocrine diseases. and metabolic. In sports, however, there is no improvement in melatonin-dependent performance or body composition, although there is evidence relating to its hormone-regulatory and antioxidant usefulness.
Method of use recommended by the company - Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Swallow one serving (1 tablet) preferably in the evening, one "hour before bedtime.
Method of use in sports Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
In most studies, dosages ranging from 300 mcg up to 5/6 mg are administered. In sports, the suggested dosage is that of 3 milligrams, although there are studies to support the efficacy of only 0.5 mg. In any case, melatonin should be taken at least one "hour before bedtime, in order to be available during the sleep phase. falling asleep. The nocturnal intake is also important to reproduce the cycardian nature of its synthesis, avoiding a hormonal deregulation that could even be counterproductive.
Synergy - Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Several studies seem to agree on the greater effectiveness of the synergy when taken together with zinc. A generalized improvement is in fact obtained both on the strengthening of the immune defenses, and on the antioxidant effect and on the metabolic aspect, improving the sensitivity to insulin.
Some studies show that in case of prolonged intake of zinc and melatonin, supplementation with magnesiomagnesium is also necessary.
The validity of the simultaneous administration of melatonin and vitamin B6 is still under observation, even if the first works show an improvement in the endogenous synthesis of this hormone, with an enhancement of the biological effects related above all to the modulation of the immune and hormonal activity.
Side Effects Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
Although recent studies have confirmed the high tolerability and safety of the active ingredient, there are cases in the literature in which, even at a dose of 3 mg / day, nausea, irritability, nightmares and vascular alterations have been observed.
Furthermore, by acting as a mild hypnotic and sedative, melatonin may interfere with the ability to concentrate. By enhancing the immune response, the substance could also worsen the conditions of patients with allergic or autoimmune diseases.
Precautions for use Melatonin 500 - Eurosup
The product is contraindicated in cases of renal or hepatic pathology, cardiovascular disease and / or hypertension, allergies and autoimmune diseases, during pregnancy, during lactation, under the age of 12 and in adolescents not yet trained.
In case of prolonged use (over 6/8 weeks) the doctor's opinion is necessary.
This article, elaborated on the critical rereading of scientific articles, university texts and common practice, is for information purposes only and therefore has no medical prescription value. It is therefore always required to consult your doctor, nutritionist or pharmacist before undertaking the use of any supplement.. Learn more about the critical analysis of Melatonin 500 - Eurosup.
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2002 Jun; 23: 213-7.
The effect of pyridoxine administration on melatonin secretion in normal men.Luboshitzky R, Ophir U, Nave R, Epstein R, Shen-Orr Z, Herer P.
Georgian Med News. 2007 Dec;: 35-8.
rsling M, Wheeling M, Williams A. The effect of melatonin administration on pituitary hormone secretion in man. Clin Endocrinol. 1999; 51: 637-42. doi: 10.1046 / j.1365-2265.1999
Melatonin supplementation to rats subjected to acute swimming exercise: Its effect on plasma lactate levels and relation with zinc.
Kaya O, Gokdemir K, Kilic M, Baltaci AK.
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006 Feb-Apr; 27 (1-2): 263-6.
Effects of a single dose of N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine (Melatonin) and resistance exercise on the growth hormone / IGF-1 axis in young males and females.
Nassar E, Mulligan C, Taylor L, Kerksick C, Galbreath M, Greenwood M, Kreider R, Willoughby DS.
Effects of melatonin supplementation on exercise-induced changes in conduction velocity distributions.
Ayaz M, Okudan N.
Improvement of the conductive capacities of the nerve fibrea.
Melatonin: aeromedical, toxicopharmacological, and analytical aspects.
Sanders DC, Chaturvedi AK, Hordinsky JR.
J Anal Toxicol. 1999 May-Jun; 23: 159-67. Review.
BMJ. 2006 Feb 18; 332: 385-93. Epub 2006 Feb 10.
Buscemi N, Vandermeer B, Hooton N, Pandya R, Tjosvold L, Hartling L, Vohra S, Klassen TP, Baker G.
Safe in the short term
Pharmacokinetics of orally administered melatonin in critically ill patients.
Mistraletti G, Sabbatini G, Taverna M, Figini MA, Umbrello M, Magni P, Ruscica M, Dozio E, Esposti R, DeMartini G, Fraschini F, Rezzani R, Reiter RJ, Iapichino G.
J Pineal Res. 2010 Mar; 48: 142-7. Epub 2010 Jan 8.
Significance and application of melatonin in the regulation of brown adipose tissue metabolism: relation to human obesity.
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Fuentes-Broto L, Paredes SD, Reiter RJ.
Obes Rev. 2010 Jun 16. [Epub ahead of print]
Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 Feb 18. [Epub ahead of print]
Contreras-Alcantara S, Baba K, Tosini G.
Endocrinology. 2009 Dec; 150: 5311-7. Epub 2009 Oct 9.
Sartori C, Dessen P, Mathieu C, Monney A, Bloch J, Nicod P, Scherrer U, Duplain H.
Int J Exp Pathol. 2007 Feb; 88: 19-29.
Hussein MR, Ahmed OG, Hassan AF, Ahmed MA.
Endocrinology. 2003 Dec; 144: 5347-52. Epub 2003 Sep 11.
Prunet-Marcassus B, Desbazeille M, Bros A, Louche K, Delagrange P, Renard P, Casteilla L, Pénicaud L.
Saudi Med J. 2006 Oct; 27: 1483-8.
Hussain SA, Khadim HM, Khalaf BH, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Sahib AS.
Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006 Apr; 96: 729-39. Epub 2006 Feb 28.
Effects of resistance exercise session after oral ingestion of melatonin on physiological and performance responses of adult men.Mero AA, Vähälummukka M, Hulmi JJ, Kallio P, von Wright A.
J Pineal Res. 2005 Nov; 39: 353-9.
Atkinson G, Holder A, Robertson C, Gant N, Drust B, Reilly T, Waterhouse J.
Ergonomics. 2005 Sep 15-Nov 15; 48 (11-14): 1512-22.
Atkinson G, Jones H, Edwards BJ, Waterhouse JM.
J Pineal Res. 2007 Jan; 42: 28-42.
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Terron MP, Flores LJ, Reiter RJ.
J Pineal Res. 2009 Sep; 47: 184-91. Epub 2009 Jul 13.
Veneroso C, Tuñón MJ, González-Gallego J, Collado PS.
Saudi Med J. 2006 Oct; 27: 1483-8.
Hussain SA, Khadim HM, Khalaf BH, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Sahib AS.