Generality
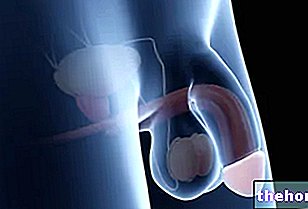
The pubic symphysis is the cartilaginous joint that connects the right pubic body with the left pubic body. The pubis, also known as the pubic bone, is the lower and anterior region of the iliac bone.
The pubic symphysis resides in front of and slightly above the urinary bladder and has two very different cartilage components: on the two so-called articular surfaces, there is a lining of hyaline cartilage; between one joint surface and the other, there is a disc of fibrocartilage.
The pubic symphysis also includes a series of ligaments that give it stability.
The function of the pubic symphysis is to help the other sections of the hipbone and the sacrum support the weight of the human upper body.
Among the pathologies of the pubic symphysis, the most important is, most likely, the diastasis of the pubic symphysis.