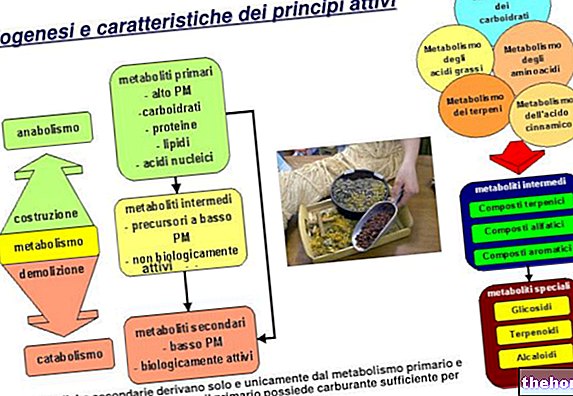
Gentian, a perennial herbaceous plant (Genzianaceae family) of which rhizome and root are used, has both herbal and liqueur use. Gentian root is a drug with eupeptic, febrifugal properties and, associated with cinchona, is also antimalarial.
After harvest, if the drug is to have a herbal projection, it is immediately treated with technical factors, which block or enormously delay the hydrolysis and oxidation processes; if, on the other hand, it must have a liqueur profile, it is left to ferment in particular structures, where the enzymes and degradation processes begin to work; this activity leads to an improvement in the quality of use of that drug. Therefore, the liqueur properties of the Gentian are improved by letting those elements work that in many cases are a source of negativity, because they can determine, but not in this case, a qualitative decline. .
The technical factors must take into account all these aspects, it is therefore necessary to understand what are the elements that alter the morphological aspects and not of a drug. To prevent the oxidation-reduction or hydrolysis reactions from taking hold, and all the metabolic phenomena in general:
it is necessary to allow less time to pass from collection to technical intervention.
The processing places must be close to the collection points, precisely to minimize the time factor.
Often, however, the plant or part of the plant collected must undergo transport; for this reason, suitable mechanical means will be used for stacking and transporting the source.
The means of transport must respect the same standards of hygiene that were observed at the time of collection; they cannot, for example, transport plants or drugs on containers that have transported animals. Therefore, it is necessary to respect those cleaning criteria that will guarantee, in the subsequent phases, to work a vegetable source that has kept its qualities intact, thanks to a correct sequence of operations that from the harvest lead it to the technical processing laboratories.
All these steps must relate to operational criteria that take into account hygiene and cleanliness, and that focus mainly on the part of the plant that will become an integral drug, ascertaining the absence of other organic material (parts of the plant that are not drugs or other plants, insects, animals) and inorganic (soil, metals, glass).
The technical interventions that are applied to limit the degradation phenomena of future drugs are different. As regards the phenomena of hydrolysis, the source is deprived of water, this is because the hydrolytic reactions are characterized by the presence of enzymes that act in the presence of water and if this is removed these reactions cannot take place. of water is the first to be carried out, and it is also what is carried out on the vast majority of plant sources; this is because the hydrolysis phenomena are the first that occur after harvesting and are also those that alter in a more drastic and irreversible way the quality of the natural source that the drug is giving.
To remove the water and decide the strategies to be used, I have to take into account the source and the type of part used: seeds (a little water), fruits (a lot of water) or roots (fleshy or not). It will therefore be necessary to adopt different methods of removal. , by type and drasticity.
More articles on "Strategies to limit post-harvest degradation of a drug"
- Post - drug harvest degradation
- Pharmacognosy
- Drying, drying on racks