Definition
Acromegaly is a rare, chronic and disabling syndrome characterized by an excessive production of growth hormone (also known as GH, from the English "Growth Hormone") and which affects adult patients. In fact, this disease is often diagnosed among 20 to 50 years of age, therefore after the stage of puberty.
Causes
As mentioned, acromegaly is caused by an excessive production of growth hormone. This excessive production is often caused by the presence of a particular type of benign tumor that affects the pituitary, ie the gland responsible for the production of GH itself. More specifically, the tumor we are talking about is the GH-secreting pituitary adenoma.
However, the presence of a pituitary tumor is not the only factor that can lead to the development of acromegaly. In fact, even the use of growth hormone-based pharmacological treatments to increase muscle mass can favor the onset of this syndrome.
Symptoms
In patients suffering from acromegaly there is an excessive volumetric increase in the bones and soft tissues which leads to alterations of the hands, feet, supraorbital arches, mandible and maxilla (mandibular and maxillary prognathism).
These characteristic symptoms, however, evolve rather slowly, so much so that acromegaly is often noticeable only when it is at an already advanced stage.
Furthermore, visceromegaly, headache (due to the presence of pituitary tumor), increased appetite, joint and muscle pain, joint swelling or stiffness, glycosuria, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, hyperhidrosis, hirsutism, hyperprolactinaemia, may also occur in patients with acromegaly. hypertension, galactorrhea, amenorrhea or changes in the menstrual cycle, erectile dysfunction, prognathism, hoarseness, dental malocclusion, etc.
The information on Acromegaly - Acromegaly Treatment Drugs is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Acromegaly - Acromegaly Treatment Drugs.
Medicines
Treatment of acromegaly aims to decrease growth hormone production and reduce any pituitary tumor mass. For this, specific drugs are usually prescribed such as somatostatin analogues, bromocriptine and growth hormone receptor antagonists.
Surgery can be used to remove the tumor mass. In the event that this is not possible, or in the event that the surgery has not led to the desired results, the doctor may decide to intervene by subjecting the patient to radiotherapy. . However, the latter approach is considered a second choice treatment.

The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against acromegaly and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment.
Somatostatin analogs
Somatostatin analogues are drugs of synthetic origin whose chemical structure resembles that of somatostatin (an endogenous hormone that inhibits the release of growth hormone).These active ingredients have specific therapeutic indications for the treatment of acromegaly.
- Octreotide (Sandostatin ®): octreotide is available in pharmaceutical formulations suitable for intravenous or subcutaneous administration. The intravenous administration of the drug can only be performed by specialized personnel, while the subcutaneous injection can also be practiced by the patients themselves. , but only after having received adequate training from the doctor or nurse.
The exact amount of octreotide to be used for the treatment of acromegaly must be determined by the physician.
- Lanreotide (Ipstyl ®): This active ingredient is available as a prolonged-release suspension for injection which must be administered intramuscularly. Again, the dose of lanreotide to be used must be determined by the physician on an individual basis for each patient.
Bromocriptine
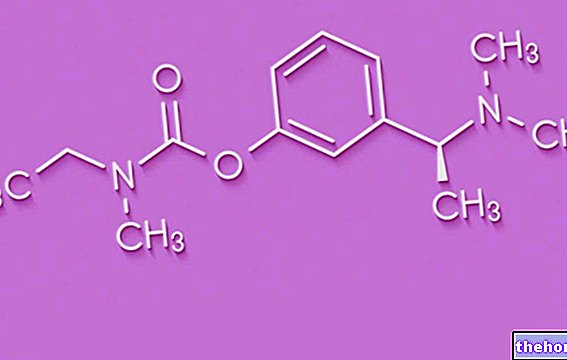
Bromocriptine (Bromocriptina Dorom ®) is a semi-synthetic dopaminergic receptor agonist derived from the natural ergotamine alkaloid.
It is a drug that can be used to treat different types of disorders and diseases, including acromegaly.
Bromocriptine is available in pharmaceutical formulations suitable for oral administration. The starting dose of bromocriptine that is usually used is 2.5 mg per day. Thereafter, the doctor will gradually increase the amount of the drug until the ideal maintenance dosage is reached for each patient. However, generally, the maintenance dose ranges from 10 to 20 mg of bromocriptine per day.
Growth hormone receptor antagonists
Growth hormone receptor antagonists are usually given to patients who do not respond to other treatment strategies undertaken against acromegaly. These drugs - as antagonists of the GH receptor - prevent the latter from carrying out its excessive activity which is at the basis of the development of acromegaly, thus allowing an improvement in the quality of life of patients suffering from this syndrome.
- Pegvisomant (Somavert ®): the starting dose of pegvisomant usually administered is 80 mg, to be administered subcutaneously under the direct supervision of the physician. Thereafter, the dose can be reduced to 10 mg of the active ingredient per day, always administered by subcutaneous injection.