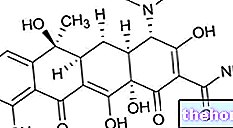
Definition
Epididymitis is the title of the chapter concerning scrotal disorders: it is an "inflammation of the epididymis" (thin, long and twisted duct that connects each testicle to its vas deferens).
Causes
In most of the diagnosed cases, epididymitis is caused by bacterial / fungal / viral infections (in particular, E. Coli, gonorrhea, chlamydia and more rarely candidiasis and tuberculosis), bacterial prostatitis, urethritis. However, the element the causal most implicated in epididymitis is by far the reflux of urine inside the epididymis (→ extreme physical effort, weight lifting).
Symptoms
Epididymitis is characterized by testicular swelling and pain (not surprisingly, the testicle can easily become inflamed in case of epididymitis, causing orchitis) often associated with: difficulty urinating, dyspareunia, abdominal pain, pain when urinating, painful ejaculation and / o bloody, fever, urethral discharge after squeezing the glans.
Tuberculosis epididymitis: more complex symptoms, characterized by swollen nodules, at the level of the lower area of the testicle
The information on Epididymitis - Epididymitis Treatment Drugs is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Epididymitis - Epididymitis Treatment Drugs.
Medicines
In case of nonspecific epididymitis, the patient is usually treated with broad spectrum antibiotic drugs, such as third generation cephalosporins and quinolones. For epididymitis associated with sexually transmitted diseases, a more targeted pharmacological treatment is indicated. To alleviate the painful symptoms, it is possible to take anti-inflammatory and painkilling drugs, to be associated with antipyretics if epididymitis is also accompanied by alteration in body temperature. The elevation of the epididymis, absolute rest and, possibly, the application of ice at the scrotal level are recommended.
The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against epididymitis, and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the active ingredient and the dosage most suitable for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment:
Quinolones:
- Ofloxacin: in case of non-specific epididymitis, it is recommended to take a dose of 200-400 mg every 12 hours, for 10 days. When it comes to epididymitis from sexually transmitted diseases, the recommended dose is 300 mg every 12 hours, for a period of 10 days: in the latter case, the sexual partner must also undergo antibiotic treatment, to avoid the spread of the disease. infection. In particular, this drug is particularly indicated for non-gonococcal epididymitis in subjects over the age of 35 and for patients sensitive to Ceftriaxone or Doxycycline.
- Levofloxacin (eg. Levofloxacin, Tavanic, Aranda, Fovex): administer 500 mg of the drug orally once a day for 10 days. Recommended for venereal disease epididymitis: in this regard, the partner must also be treated with antibiotics.
- Norfloxacin (eg Norflox, Flossac, Sebercim): for nonspecific epididymitis, it is recommended to administer the drug at a dosage of 400 mg twice a day (every 12 hours) for two weeks.
- Enoxacin (eg. Bactidan, Enoxen): indicated for non-specific epididymitis. Administer 200 mg of the drug orally every 12 hours for 14 days.
Cephalosporins:
- Ceftriaxone (eg. Ceftriaxone, Pantoxon, Ragex, Deixim): indicated for the treatment of epididymitis associated with sexually transmitted diseases. The dosage is: 250 mg of drug to be taken intramuscularly (single dose) for gonococcal infections (gonorrhea If epididymitis is caused by chlamydial infections, it is preferable to administer doxycycline, at a dosage of 100 mg twice a day, for 10 days.
Tetracyclines:
- Doxycycline (eg. Doxycicl, Periostat, Miraclin, Bassado): it is recommended to administer 100 mg of the drug twice a day for 10 days, to be taken, possibly, together with Ceftriaxone, as indicated by the doctor.
The combination doxycycline + third generation cephalosporin is recommended in case of first treatment from epididymitis from sexually transmitted diseases
- Tetracycline (eg. Tetrac C, Pensulvit, Ambramycin): it is recommended to take 500 mg of the drug orally every 6 hours, for 10 days. Tetracycline is useful as an alternative to doxycycline.
Anti-inflammatories / painkillers: therapeutic aids to alleviate the painful epididymitis-dependent symptoms are useful for relieving inflammation and for alleviating the pain deriving from inflammation
- Ibuprofen (eg. Brufen, Kendo, Moment): take orally from 200 to 400 mg of active ingredient (tablets, effervescent sachets) every 4-6 hours, as needed. In some cases, the analgesic can be given intravenously (400 to 800 mg every 6 hours, as needed)
- Naproxen (eg. Aleve, Naprorex): it is recommended to take one capsule of 550 mg twice a day (every 12 hours, unless otherwise instructed by the doctor), as needed
- Acetaminophen (or Paracetamol: eg. Acetamol, Buscopan compositum, Tachipirina) for acute epididymitis pain associated with altered body temperature. Taken orally in the form of tablets, syrup, effervescent sachets, or suppositories, the drug is generally administered at a dosage of 325 - 650 mg every 4-6 hours for 6-8 consecutive days, to lower the fever.
Opioids: if the pain deriving from epididymitis is unbearable, opioids are recommended (only for acute and excruciating pain)
- Hydrocodone (eg Vicodin, not sold in Italy) the dosage must be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the patient's response. Generally, one tablet is prescribed every 4-6 hours: never exceed 5 tablets per day. It is also possible to associate antipyretic drugs, in case of fever associated with testicular pain and inflammation.
In case of scrotal abscess or repeated epididymitis events despite pharmacological interventions, it is recommended to subject the patient to a "partial or total" surgical excision of the epididymis.
Total abstention from sexual intercourse is essential until complete recovery from epididymitis.
Other articles on "Epididymitis - Drugs for the Treatment of" Epididymitis "
- Epididymitis in Brief: Summary on Epididymitis
- Epididymitis
- Epididymitis: Symptoms and Classification
- Epididymitis: diagnosis and therapies