Key points
Tetraplegia is a severe movement disorder characterized by the progressive or immediate loss of sensation and mobility of the limbs (both lower and upper). The inability to move or coordinate the limbs can be total or partial based on the severity of the trauma suffered.
Causes
Tetraplegia is the result of injury to the spinal cord at the level of the cervical spine. Among the predisposing factors for quadriplegia are: car accidents, violent falls, sports injuries, accidents at work and violent crimes.

Symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of quadriplegia depend on the cervical point where the trauma occurred and the severity of the nerve injury. In general, the clinical picture of tetraplegia is characterized by: involuntary contraction of voluntary muscles, difficulty or inability to coordinate movement, respiratory deficits, numbness of the limbs, urinary and fecal incontinence, paralysis of the limbs.
Diagnosis
In the case of paralysis of the limbs, the diagnostic assessment is important to trace the triggering cause. The most used investigative tests are: CT, MRI, radiographs, myelography and transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Therapy
There is no complete cure for quadriplegia. Currently, the administration of NSAIDs, muscle relaxants and corticosteroids can partially relieve pain and relieve symptoms. When necessary, the patient undergoes specific surgical treatments.
Definition of quadriplegia
Among movement disorders, quadriplegia plays an important role. Due to a severe cervical spinal cord injury, quadriplegia causes loss of sensation and muscle strength in the limbs (upper and lower). Severe trauma to the first and second cervical vertebrae leads instead to the death of the subject.
A little anatomy to understand ...
The cervical spine is composed of 7 vertebrae identified with the letter C, and progressively numbered from C1 to C7. The upper cervical spine is made up of the atlas (C1) and axis (C2) vertebrae, while the lower portion is composed of the remaining 5 vertebrae (C3-C7).
Trauma of the spinal cord enclosed in the C1 and C2 vertebrae leads to the death of the victim. Injuries in the lower cervical spine are instead responsible for paralysis in the arms and legs (tetraplegia).
Tetraplagia is therefore a highly disabling disease. Scientists are mobilizing to seek effective therapy or treatment in repairing spinal cord injuries; tant "is that the research aimed at this purpose is active all over the world. To date, therapies are available corrective, able to correct - even without totally restoring - minor spinal injuries, guaranteeing tetraplegic patients a fairly satisfactory quality of life.
Causes
Tetraplegia is the immediate expression of a direct or indirect trauma to the spinal cord contained in the C3-C7 cervical vertebrae. paraplegia.
The risk factors for quadriplegia are:
- Car accidents → most spinal cord injuries are caused by traffic accidents with high-speed motor vehicles
- Violent falls
- Sports injuries (including football, horse riding, hockey, and shallow water diving)
- Injuries from extreme sports (e.g. motor skydiving, skydiving, jet skis)
- Accidents at work
- Gunshot and stab wounds (violent crimes)
In all the situations listed above, the spinal cord can undergo direct laceration (caused by that precise trauma) or indirect (due to bone splinters, bruises or glass / metal fragments which, due to the accident, damage the marrow) .
In some cases, an already weakened spine is more prone to trauma. For example, patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis or spinal stenosis are particularly exposed to the risk of quadriplegia, even following minor traumatic events.
Quadriplegia can affect anyone. Despite what has been stated, individuals between the ages of 15 and 35 represent the most affected category of all. The death rate from quadriplegia tends to be higher in children with spinal injuries.
Trauma to the cervical spinal cord → interruption of the nerve impulse necessary for voluntary movement → paralysis of the limbs (quadriplegia)
Tetraplegia from brain injury
Brain injury quadriplegia deserves further study. Unlike the traumatic variant, tetraplegia from brain injury (both during childhood and in adulthood) is due to extensive damage to the brain, precisely in the areas of the brain responsible for voluntary control and mobility.
Patients with this form of tetraplegia are completely non-self-sufficient and permanently need assistance to fulfill every need.
Symptoms
The symptoms of quadriplegia depend on the cervical point where the trauma occurred and, clearly, on the extent of the injury.
It should be emphasized that spinal cord injuries can be partial (incomplete quadriplegia) or total (complete quadriplegia). In the first case, the traumatic injury allows the victim to maintain a certain sensitivity and partly control the movement governed by nerve impulses generated below the neurological level of the lesion. The complete quadriplegia instead determines the total immobility (joint paralysis) of the subject.
In general, the clinical picture of "classical" quadriplegia is characterized by:
- Uncontrolled contraction of voluntary muscles
- Difficulty / inability to control voluntary movements
- Breathing difficulty, caused by paralysis of the respiratory muscles
- Pain (when felt)
- Numbness and progressive / immediate weakening of the limbs
- Loss / reduction of sensation in the limbs
- Loss of ability to control the anal and bladder sphincters: constipation / incontinence / bladder spasms
- PLEASE NOTE: The severity of the symptoms depends on the location and intensity of the trauma suffered
In particular, the symptoms of quadriplegia differ according to the location of the trauma. The table summarizes the symptoms resulting from a generic injury to the spinal cord (cervical area), differentiated according to the vertebrae involved in the trauma.
Cervical vertebra
hit
Symptoms caused by trauma
C1-C2
Severe trauma results in the person's death
C3
Loss of diaphragm functionality
C4
Loss of biceps and shoulder function
C5
Inability to move or move biceps, shoulders, wrists and hands
C6
Limited wrist movement control + complete loss of hand movement
C7
Limited control of the ability to move the upper limbs is allowed but movement of the hands and fingers is denied
Patients who have sustained a severe traumatic injury above the C7 vertebra are unable to manage normal daily activities.
In addition to the symptoms described above, it is not uncommon to also find further prodromes, such as: alteration of heart rate, sweating, increase in body temperature and pressure changes.
Diagnosis
A spinal cord injury is a "full-fledged clinical emergency." The medical team proceeds with a thorough physical examination associated with neurological tests.
The diagnosis of tetraplegia mainly makes use of:
- Imaging tests (CT, MRI, x-rays)
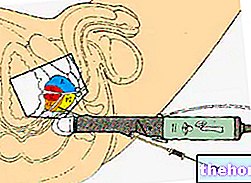
- Myelography: is a radiological test of the spinal cord and meningeal membranes, consisting in the injection of a contrast medium to identify any pathological affections affecting the marrow
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation: non-invasive diagnostic technique that allows you to assess the health of the neuronal circuits within the Central Nervous System (CNS)
The results of these tests allow to identify the exact location of the trauma and the severity of the quadriplegia.
Therapy
To date, there is still no completely resolving cure for quadriplegia. However, scholars are mobilizing towards innovative therapies based on CNS regeneration systems with the help of stem cells. Only by restoring the structural and functional integrity of the injured marrow could the patient regain complete control of sensitivity and joint movements.
However, patients with quadriplegia can be treated following different strategies. We remind you that in addition to the violence of the injury, the time elapsed between the moment of the trauma and the start of therapy is essential to determine the patient's prognosis.
Treatment options currently available for traumatic cervical spine injuries are:
- Administering corticosteroids to reduce swelling, as edema could damage the spinal cord and cause quadriplegia
- Administration of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants to relieve pain
- Botox injections, indicated to reduce muscle spasticity
- Surgery, aimed at removing fluids, tissues or bone fragments that are pressing on the spinal cord
- Spinal traction (when possible): allows and facilitates the movement of the spine
- Physical, occupational and rehabilitation therapy: useful for coping with the disability caused by quadriplegia