Generality
The deaf-mute individual (therefore, affected by deaf-mutism) is a person who suffers from both deafness and mutism.

However, from a scientific point of view, the term "deaf-mute" is preferred to use the expression "prelinguistic deaf" (that is, an individual who became deaf before the "acquisition of language".
Causes
As mentioned, the deaf-mute is an individual who was born deaf, or who developed deafness within the first two years of life, and who - as a result of this disorder - developed mutism despite perfectly functioning speech organs.
Silence occurs because the learning of language depends on the child's listening to the words and their repetition. It is clear, therefore, that in an individual who is deaf from birth this form of learning cannot be put into practice.
The deafness responsible for deaf-mutism manifests itself in the child from birth, or shortly after, depending on the cause that triggered it.
In this regard, we can divide the causes that lead to the onset of deaf-mutism into three large groups.
Pre-natal causes
Pre-natal causes cause the newborn to be deaf even before birth and, therefore, to be born already without hearing (congenital deafness).
Fall within this group:
- The hereditary causes. That is, parents can pass on genetic mutations to their child that cause deafness to develop.
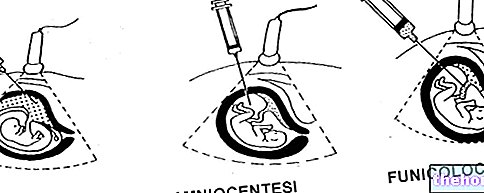
- Contraction of particular infections or diseases by the mother during pregnancy, which can damage the hearing of the unborn child (an example is constituted by the contraction of rubella by the pregnant woman).
- Intoxication of the mother with substances such as drugs, alcohol, tobacco and / or medications.
Perinatal causes
Perinatal causes (also called neonatal causes) cause the baby to become deaf at the time of birth.
In most cases, they depend on trauma suffered by the newborn during birth, including anoxia (which can arise in the case of difficult and complicated births) and mechanical traumas that the child may experience during the birth. childbirth.
Postnatal causes
Finally, postnatal causes can cause deafness in the child during his first years of life, before he can acquire the use of speech.
Among the main causes of postnatal deafness, we remember:
- Pathologies such as encephalitis and meningitis;
- Viral infections such as mumps or measles
- Drug poisoning such as gentamicin or streptomycin.
Cures and Remedies
Unfortunately, there is no real cure for deaf-mutism, but it is necessary to tackle the problem with a multidisciplinary approach.
First of all, as soon as you realize the child's hearing problem, it is essential to understand the degree of deafness that afflicts him, through the execution of special audiometric tests.
The doctor, thanks to these tests, will determine if the deafness is complete, or if the child is able to perceive some sounds. In the latter case, the doctor will have to identify the frequency of sounds that the child is able to perceive and will have to intervene by prescribing the use of adequate hearing aids to the patient.
These prostheses generally have a high amplifying power and allow the child to hear sounds that otherwise he would not be able to perceive. In other cases, however, prostheses can be used that are able to modify the frequencies of sounds in the frequencies that the child is able to perceive, so as to allow him to perceive as many sounds as possible.
Of course, promptness in "identifying the problem and" adopting the aforementioned solutions is essential to ensure that the child can begin to learn language in a short time, possibly with the help of speech therapy.
At best, in cases where the deafness is not excessively severe and is readily identified and treated, children can even get to receive a very normal education on a par with their peers.
In the most serious cases, in which the prosthesis cannot be used or is in any case not effective, there is no way to counteract deafness. lip reading and sign language. This type of techniques is generally taught in special schools for the deaf and dumb also present in Italy.
Finally, for a deaf-mute child, psychological support and educational-social support are of fundamental importance, since the condition of not being able to communicate with peers or with their families - or in any case to communicate in a different way from the people around them - it could cause problems and damage to him even on a psychological level.