- or fibroids of the uterus - could, in some cases, be problematic, not only for the effects that are found at the level of the organism, but also for the identification of symptoms. In most cases, uterine myomas are in fact asymptomatic, for which the woman does not notice the presence of these benign neoplasia: statistics reveal that 50% of uterine myomas do not involve symptoms, so the detection of the tumor is the consequence of a fortuitous event. The finding of many fibroids is, in fact, accidental, and the ascertainment can be confirmed by an ultrasound or by a simple gynecological inspection.
In any case, the volume, morphology and location of the uterine myoma represent factors that heavily affect the symptoms.Metrorrhagia: unexpected bleeding in the intermenstrual period (common condition in submucosal and intramural uterine myomas); Polymenorrhea: bleeding at irregular and frequent intervals before 24 days (a condition that could be confused with an anticipation of the menstrual cycle); Menorrhagia: abnormal menstrual bleeding, longer and more abundant; Anemia: effect of excessive bleeding, consequently it is often associated with metrorrhagia and menorrhagia; Abdominal swelling Perception of heaviness in the lower part of the abdomen: typical sensation caused by large caliber myomas, mainly located near the bladder; Sacral and lumbar pains: typical symptom of highly developed and voluminous myomas; Difficulty urinating and necessity to urinate often: myomas attached to the bladder tend to compress it, stimulating it; Constipation: caused by myomas near the rectum; Pain in general And discomfort during intercourse, usually generated by pedunculated fibroids.
registers a rapid evolution and an excessive increase in volume, to the point of obstructing the fallopian tubes. Furthermore, the implantation of the egg could be hindered if the myoma expands to the point of occupying the entire organ.
In some cases, uterine fibroids in pregnant women can increase in size or hinder delivery due to changes in uterine contractions.
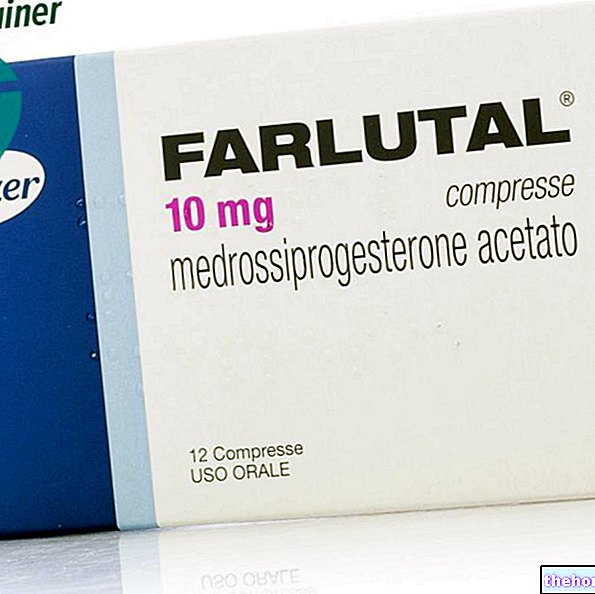
The drugs that can be administered for the resolution not only of the symptoms, but also of the myoma itself, are, in general, progestogens: the hormonal treatment, however, could cause serious undesirable effects, the symptoms of which can be very similar to those of menopause: among these, mood modulations and hot flashes stand out.
Surgery is another option for the resolution of fibroids, a treatment reserved only for women who have severe symptoms (eg the fibroid covers the entire uterus or the neoplasm is very painful). Surgical excision is not recommended in pregnant women with myoma, as the operation could generate complications and bleeding.
Tags:
recipes nutrition-and-health doping
In any case, the volume, morphology and location of the uterine myoma represent factors that heavily affect the symptoms.
: abdominal menstrual pain. Typical symptom of submucosal fibroids, consequence of the continuous contractions of the uterus as an act of defense of the organ, in an attempt to “eliminate” the fibroids;
In some cases, uterine fibroids in pregnant women can increase in size or hinder delivery due to changes in uterine contractions.
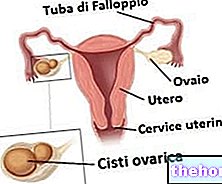
, ascites and ovarian neoplasms in benign form).
recommends only periodic visits, usually once or twice a year; for large fibroids, which cause a problematic symptom picture or, in any case, if the patient complains of "annoying" symptoms, the doctor could recommend a drug treatment or surgical excision.The drugs that can be administered for the resolution not only of the symptoms, but also of the myoma itself, are, in general, progestogens: the hormonal treatment, however, could cause serious undesirable effects, the symptoms of which can be very similar to those of menopause: among these, mood modulations and hot flashes stand out.
Surgery is another option for the resolution of fibroids, a treatment reserved only for women who have severe symptoms (eg the fibroid covers the entire uterus or the neoplasm is very painful). Surgical excision is not recommended in pregnant women with myoma, as the operation could generate complications and bleeding.
To conclude, the symptoms caused by myomas should not be underestimated, although in most cases, they remain benign. We have seen how many uterine fibroids do not involve some symptoms, therefore, a periodic gynecological check-up is also essential to ascertain the possible presence of uterine myomas.

.jpg)