Premise
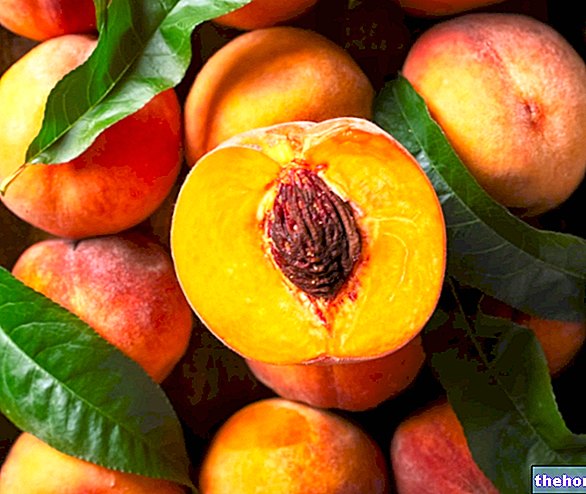
From time immemorial the fig tree has been appreciated for its (false) homonymous fruits, very sweet, fleshy and exquisite, which also attract the curiosity of insects and birds. The fig is a xerophilous plant, therefore adapted in arid environments with a hot and dry climate, and is therefore typical of subtropical and temperate areas.

Generality
The fig plant is an arboreal species belonging to the family of Moraceae: such Ficus, there is both the species F. sativa charge, that F. carica caprificus, respectively domestic fig (real fig or female plant) and wild fig (caprific or, simply, male plant).
After a brief analysis of the general characteristics of the fig tree, we will analyze in more detail the peculiarities of the female plant and its male variant.
The fig looks like a rather mighty tree, with heights generally varying from 6 to 10 meters; the bark that covers the tortuous trunk is rough and gray, and the branches end with pointed buds, covered with greenish scales. The branches are masked by large green leaves, oblong, rough, with oval outlines: again, the leaves have 3 lobes (three-lobed) or 5 (five-lobed), each of which is outlined by a rather irregular and toothed outline.
What most people call fruit is actually a false fruit: the fig, in fact, is a syconium, a fleshy and very sweet infructescence, covered with a delicate skin varying in color from red to green, and from bluish to gray. . Inside the fig, there are very small flowers, consisting of an opening (hostile), which acts as an entrance for the hymenoptera. The real fruits are instead numerous small achenes, positioned in the cavity of the inflorescence: each achene (the so-called sow) is set in the very sweet and delicious pulp. [taken from it.wikipedia.org/]
- House fig (female plant)
The female fig tree stands out for its massive and powerful stem, wrapped in a smooth gray bark; the root system is rather expanded, albeit superficial. The female fig tree can reach considerable heights, sometimes exceeding 8-10 meters in height. The female fig is also distinguished and above all by three factors:
- Presence of purely female flowers
- Production of early figs (or fioroni) and real figs. Early trees begin to form in autumn and are characterized by sterile female flowers, while real figs, born in spring and ripened in summer, bear female flowers that can be both fertile and sterile, depending on the species considered.
- It has the function of producing the seeds contained in the fruit
[taken from http://www.agraria.org/]
- Caprifico (male plant)
If in the female plant of the fig tree only the female ones are born, in the male the flowers are also masculine, as well as being feminine. The fruits produced are not edible; the male fig has the function of producing pollen.
Fertilization occurs by a specific insect.
Soil and climate
As we have seen, the fig is a typically xerophytic plant; therefore, when the temperature drops below 10 ° C below zero, the plant most likely dies. Although the fig adapts very easily to the soils and areas in which it is planted, it loves clayey and sandy soils, vice versa the fig suffers soils with a high degree of humidity.
Dried fig
The drying of figs is an excellent "food preservation" technique: this custom is mostly widespread in southern Italy, where the warm climate favors homogeneous drying. The fig must be harvested when fully ripe and then dried in the sun with the aid of physical or chemical treatments.

Nutritional properties
As we all know, figs are highly energetic fruits: in fact, they provide 47 Kcal per 100 grams of product. Water constitutes 82% by weight. The fig has a high carbohydrate content (11%), about 2% fiber, 1% protein and very little fat (0.2%). Figs are a concentrate of mineral salts, especially potassium, magnesium and iron, but also antioxidant vitamins play an important role.
Video Recipes - Homemade fig jam
Fig Jam - Pectin Free Jam
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to the Video Recipes Section
- Watch the video on youtube
For fig lovers, we also recommend following our other fig-based video recipes, such as the Butter-free Tart with Figs, Gratinated Figs with Ice Cream and Figs stuffed with Ricotta
Therapeutic properties
The fig is not only an exquisite and succulent fruit: its use is also exploited in the phytotherapeutic field for its multiple therapeutic virtues.
In recent years, the nutritional value of figs has been enhanced by the research of the chemicals contained in them:
- Emollient and expectorant properties of fig fruits;
- Remineralizing properties;
- Properties bechiche (relieves persistent cough) and emmenagogues (leaves and fruits);
- Laxative properties (fibers): unlike Indian figs (astringent properties), rich in tannins;
- Disinfectant / anti-inflammatory virtues of the mouth and oral cavity in general (latex decoction); [adapted from Reasoned dictionary of herbal medicine and phytotherapy, by A. Bruni and M. Nicoletti]
- Keratolytic properties of latex: the application of latex directly in the insect bite reduces pain in situ;
- Caustic properties: the latex gushing from the cuts is rich in proteases and amylases: in this regard, it is a good natural remedy to eliminate warts. In any case, the latex of the fig tree must be used with caution, in order to avoid suffering heavy skin irritation;
- Anti-inflammatory, digestive, emmenagogues attributed mostly to the leaves containing coumarins, furocoumarins (can create photosensitization episodes), bergapten and psoralen. In some sensitive subjects, the simple contact with the leaves can generate phenomena of skin irritability, emphasized by exposure to the sun. It is therefore recommended to promptly rinse with fresh water after contact with fig leaves, in addition to immediate removal. from solar sources for a few hours;
- Curdling properties: in the past, the latex of the fig was used to curdle milk;
- Potential Tanning Properties: The widespread custom of applying fig latex to the skin to facilitate "tanning" needs to be re-evaluated. It has been observed that the application of fig latex on the skin before sun exposure is dangerous for the skin, as well as irritating: in fact, this practice must be discredited because it is responsible for burns and sometimes serious skin lesions;
- Gastric anitisecretive properties (macerate of fig buds).
Fig in short, a summary of the properties of the fig "
Other Foods - Fruits Apricots Sour cherries Cashews Pineapple Watermelon Orange Avocado Banana Persimmon Persimmons Apple Chestnuts Cedar Cherries Coconut Watermelon Dates Feijoa Fig of India Figs Strawberries Berries Passion fruit (Maracujà, Granadilla) Jujube Kiwi Raspberries Coconut milk Lemons Almond milk Mango Apples Quinces Pomegranate Melon Blackberries Mustard Medlar Olives Taggiasca Olives Fermented Papaya Pears Peaches Plantains (Cooking Bananas) Pomelo Grapefruit Pink Grapefruit Plums, prunes Fruit juices and fruit juices Grape juice Plums Grapes Sultanas and Raisins OTHER ITEMS FRUIT Categories Food Alcoholics Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and derivatives Legumes Oils and fats Fish and fishery products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Second courses Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice cream and sorbets Syrups, liqueurs and grappas Prepare Basic tions ---- In the kitchen with leftovers Carnival recipes Christmas recipes Light diet recipes Women's, mom's and dad's day recipes Functional recipes International recipes Easter recipes Gluten-free recipes Diabetic recipes Holiday recipes Valentine's Day recipes Vegetarians Protein recipes Regional recipes Vegan recipes