Introduction on contraception
In the vast sexual panorama, contraceptive methods are the subject of great interest, especially among young and very young people who are still sexually inexperienced.

In the current reality, the "age of the much sought-after" first time "tends to be more and more precocious. From what has been said, it is well understood how information on the different contraceptive methods is essential to not only reduce the risk of unwanted pregnancies but also limit the transmission of venereal diseases (STDs).
Let's start by specifying that no contraceptive method - other than abstinence - offers TOTAL protection from unwanted pregnancynor from sexually transmitted diseases. Despite what has been said, it is however necessary to reiterate that the improvement of some contraceptive methods is such as to minimize the risk of failure.
Some examples...
Among the barrier contraceptive methods, the condom (used correctly) offers protection from unwanted pregnancies and venereal diseases ranging from 85 to 99.8%. from unwanted pregnancies which is close to 100% (while offering no protection from venereal diseases).
But let's go step by step. What is a "barrier" method of contraception? And what is meant by "hormonal birth control"? Are there other alternative methods of contraception?
We therefore try to clarify the many contraceptive methods currently available, in order to inform all those who want to live a serene sex life protected from unwelcome surprises.
"Perfect" contraceptive
Everyone is free to live their sexuality as they see fit. Of course, using appropriate contraceptive methods - when an unexpected pregnancy would be a problem - is synonymous with intelligence and maturity.
The choice of a contraceptive practice rather than another is clearly subjective, and depends on its effectiveness, practicality and perception of the risk that the couple associates with the occurrence of an unexpected pregnancy. In addition to the "risk" of pregnancy, one must keep considering the real possibility of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, a probable occurrence in case of unprotected intercourse with multiple and occasional partners.
To cope with the problems described above, some requirements have been identified that a "perfect" contraceptive method should possess:
- Maximum protection from unwanted pregnancy
- Maximum protection from sexually transmitted diseases, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, condyloma acuminata, candidiasis, AIDS, syphilis, genital herpes etc.
- Ease of use
- Little / no side effects
- Low cost
- Easy availability
- Restoration of the total capacity of conception in case of abandonment of the contraceptive method
- Little or no perception of the method during intercourse
- Harmless to a possible unborn child in case of failure of the contraceptive method
Choice of method
The choice of a contraceptive method rather than another is influenced by several elements:
- Percentage of contraceptive failure
- Risk of sexually transmitted diseases
- Regular / occasional partner
- Perception of the "severity" of a "possible unexpected pregnancy
- State of general health
- Possible contraindications of the chosen method of contraception
- Advantages / disadvantages of the contraceptive method
- Practicality of use
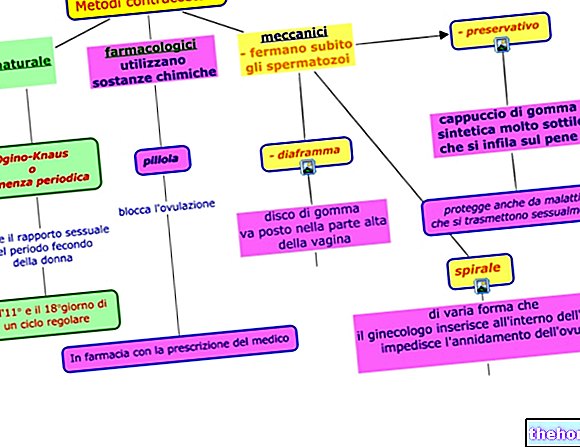
Types of contraceptives
Having said this, we illustrate in the table all the different types of contraceptive methods, which we will describe in detail in the next articles.
- Condom
- Cervical cap (little used)
- Diaphragm: possibly to be combined with spermicides
- Female condom
- Occlusive pessary (ancient contraceptive practice, currently not used)
- Cervical sponges (contraceptive method not used in Italy)
- Estrogen-progestin pill
- Minipill (composed exclusively of progestins)
- Contraceptive patch
- Vaginal ring
- Injectable contraceptives
- Spiral Hormonal IUD
- Implantable hormone sticks
- Morning after pill
- Copper IUD spiral
- Yuzpe Method (No longer used due to the conspicuous side effects)
- Spiral copper IUD (implantable in the uterus)
- Spiral Hormonal IUD (implantable in the uterus)
- Hormone sticks (implantable under the skin, on the inside of the arm)
- Spermicides (available in the form of vaginal pessaries, sprays, or gels)
- "Ogino-Knaus" method
- Billings method
- Basal temperature method
- Coitus interrupted
The only contraceptive method capable of ensuring total coverage from sexually transmitted diseases and canceling the risk of unwanted pregnancies is complete abstention from sexual intercourse (abstinence).
Other articles on "Contraceptives - Types of Contraceptives"
- Mechanical Contraceptives - Barrier Methods
- Hormonal contraceptives
- Contraceptives D "Urgency - Morning After Pill and Spiral
- Implantable contraceptives: IUD coil and sticks
- Chemical Contraceptives or Spermicides
- Natural Contraception


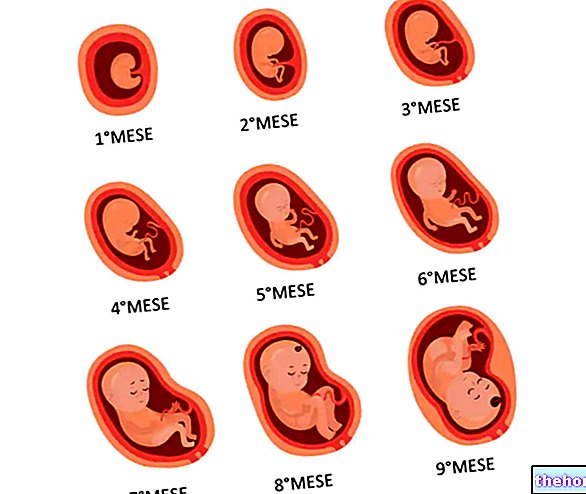

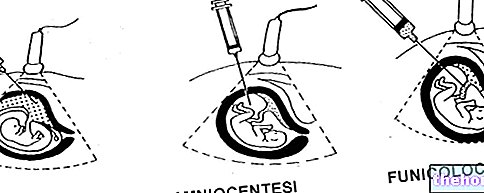


.jpg)


















