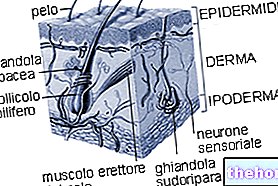
A "healthy, intense and lasting tan requires punctual attention since the spring months.
To learn more: Best Sun Creams 2021: the 5 Most Effective and Safe , eyes and hair. Usually, phototype I (complexion, very light colored eyes and hair and poor ability to tan) is the most susceptible to sunburn. This does not mean that people with dark complexions or who belong to different skin types are less sensitive to UV rays and do not need to protect themselves adequately by preparing their skin for the sun before getting a tan. It should be remembered, in fact, that a possible skin reaction to sunlight is also influenced by the amount of UV rays absorbed.
In this regard, another important element to consider for a "healthy tan is the time of day in which you are exposed: between 10 and 16, the sun is more dangerous, especially where there are light-reflecting surfaces, such as snow, water and sand.
Not all parts of the body are equally sensitive: the eyelids, nose and lips are more susceptible to sunburn than the arms and legs.
Furthermore, the elderly and children under three years of age should be considered particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays (attention: within the first six months of life, they should not necessarily be exposed to direct sunlight, since the defense systems skin are still imperfect).
Exposing oneself gradually and with due precautions is equivalent to preventing this series of inconveniences and enjoying the benefits that the sun undoubtedly possesses. The synergistic action of external photoprotection (sun protection products) and internal (supplements, diet) is therefore , essential to make the sun an ally of our well-being and prevent exposure from causing health problems.
For further information: Sun Cream for Babies: the Best for the skin of Babies and Toddlers , as it intervenes in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism. Produced in the skin by the action of ultraviolet rays (UV) starting from 7-dehydrocholesterol, cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) is, in fact, an indispensable element for the development and strengthening of the skeleton.
Without forgetting that vitamin D has beneficial effects on the immune system.
Exposure to sunlight stimulates the release of brain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which regulate sleep rhythms and promote good mood.
Sunlight has a positive effect on the body also by relieving rheumatic pains and by stimulating the release of brain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which act as natural "antidepressants", promoting good mood and regulating sleep rhythms.
In addition to giving the skin a warmer shade, the sun stimulates the production of some antioxidant and protective substances at the skin level with a certain filtering activity against the same UV radiation. In addition, moderate exposure works by improving some dermatological diseases, such as acne, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis.
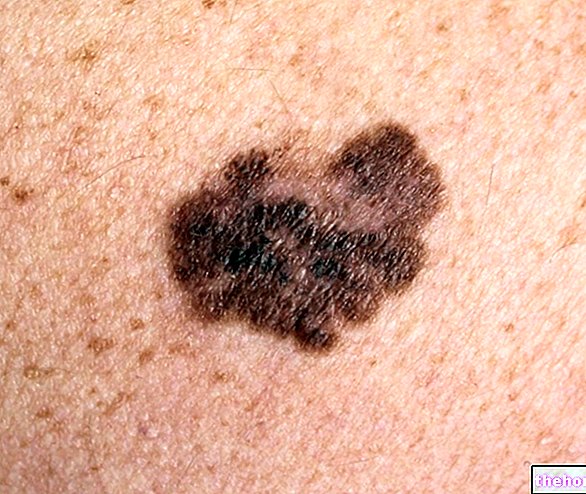
There is, however, the downside, namely the damage that can result from "excessive sun exposure. Not adequately protecting the skin, in fact, means incurring a series of photobiological reactions responsible for acute harmful effects (erythema, burns and reactions photosensitivity) and chronic (increased risk of developing skin cancers). Ultraviolet rays also have the ability to generate free radicals, responsible for oxidative stress that promotes premature aging of the skin.
What is valid for the skin is also valid for other parts of the body, such as hair. In fact, even in this case, it is advisable to use specific sunscreen for the hair.
in combination with a diet rich in fruit and vegetables and moisturizing and revitalizing cosmetics.
Before delving into the useful tricks to prepare for a "perfect and healthy tan, it is worth remembering a few simple rules:
- UV protection. Redness and burns are prevented by using sunscreen products suitable for your skin type. The shielding capacity of these cosmetics is indicated by a number preceded by an abbreviation (SFP), considering that a very high sun protection factor is equal to 50+. To make the application more pleasant, sunscreens can be chosen according to personal preferences (there are textures in cream, fluid, gel, milk and stick). In any case, these products must be applied evenly, in correct doses, before of exposure, without forgetting to renew the application several times a day, especially after sweating or after getting wet or dry.
- Do not rush. Another recommendation for tanning without damage is to sunbathe in small doses, gradually accustoming the skin to sun exposure. Intense and occasional sunbathing can be particularly dangerous, especially in subjects with fair skin (phototype I and II) , with many moles and predisposed to developing sun burns.
- Allow the skin to recover. If, despite these precautions, the skin is hot and red in the evening, you can use a soothing and repairing cream or a nourishing and refreshing after-sun milk. The ingredients to look for in the formula are plant extracts, such as those of aloe, green tea, mallow and chamomile, which have a calming and softening effect.


Australian Gold SPF 30 sunscreen offers good protection and the satisfaction of seeing our complexion change quickly thanks to the "instant bronzer" function. The product is a spray, which further facilitates its use and avoids the annoying greasy effect typical of many creams. Australian Gold is free of mineral oils, paraffin and alcohol. It is also perfect for going to the beach because it is water resistant. offers an ideal protection against UV rays.This sunscreen has many positive reviews, because it is considered effective and pleasant by users.
, it is possible to prepare the skin by taking specific food supplements for tanning. Their function is to counteract the oxidative damage induced by the sun (responsible for photoaging) and stimulate the synthesis of melanin, in order to obtain a beautiful golden and uniform complexion. This is possible thanks to the mix of substances useful for improving photoprotection and counteracting the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays, such as carotenoids (including beta-carotene, astaxanthin, lycopene and lutein), vitamins (A, C and E), antioxidants and trace elements. (such as zinc, selenium, copper and magnesium).
The supplements must be taken as part of a healthy diet and must always be used in synergy with traditional sun creams.