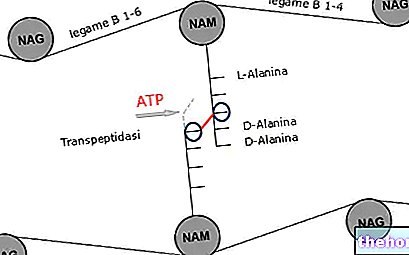
caused by a mycobacterium, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (or Koch's bacillus).
Tags:
genetic-diseases sexually transmitted diseases sports-supplements
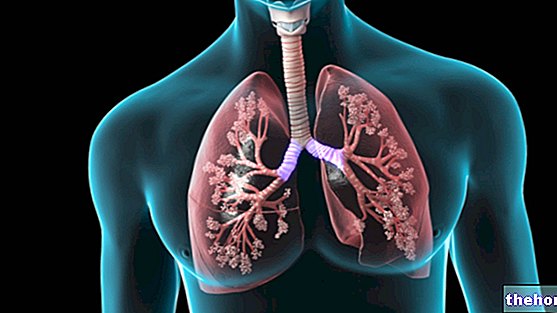
In most cases, tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs, progressively destroying the alveoli, that is the small "sacs" located at the end of the bronchioles, in which the exchanges between oxygen and carbon dioxide take place. However, other organ parts of the body may be involved, such as bones, larynx, intestines, urinary tract, glands, and lymph nodes.
Tuberculosis is a potentially serious disease and, if not treated properly, can lead to death.



.jpg)