it is limited to 5-10 adults and generally does not exceed 30-40 units.
Scabies: Who is Most at Risk?
Scabies is pandemic, being spread all over the world, and periodically, it can give rise to small epidemic outbreaks.
The disease can affect anyone, in any age group, without distinction of sex or ethnicity, regardless of social level or hygiene. However, travel to endemic areas, conditions of promiscuity and poor sanitation are factors of More often young adults (who are transmitted by sexual contact with the mite) or elderly bedridden by disease are affected. Immunosuppression also aggravates its course.
Why are children particularly susceptible to scabies?
Children are particularly susceptible to scabies due to the sharing of spaces or objects in kindergartens and schools: the use of shared towels, the exchange of clothes or hats, sleeping in the same cot during rest in kindergartens and close contact with siblings and playmates can contribute to the infection.In childhood, moreover, the horny layer of the skin is thinner, therefore the defenses against parasitosis are reduced.
In the event of a case of scabies, the ASL and the school follow scrupulous procedures to prevent the spread of the infection. For the first 24 hours from the beginning of the specific treatment, it is necessary that the infected child does not go to school. For classmates, on the other hand, health surveillance must be adopted to check whether symptoms appear within 6-8 weeks.
, is favored by crowding and poor hygienic conditions; however - not necessarily linked to these factors - it can affect people of all social classes, regardless of personal hygiene and without distinction of age or sex. This observation is confirmed by the recent increase in episodes of scabies in the most industrialized countries; all this can be explained on the basis of immigration waves from developing countries, promiscuity, frequent international travel and long stay in crowded places (even if of excellent hygiene).and the symptoms of scabies appear about a month after infection, the time necessary for the development of dermal sensitization.
The incubation period of scabies is about three weeks; in case of reinfestation the symptoms can appear more quickly, on average within 1-4 days, since the individual is already sensitized.
Scabies: How Is It Recognized?

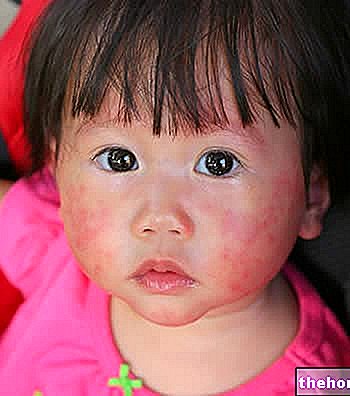
Scabies causes a "skin rash, consisting of erythematous papules, on a large part of the body, associated with widespread and persistent itching. The discomfort typically worsens at night and is essentially related to a" hypersensitivity to the protein products of the mite. Sarcoptes scabiei (and also contained in the parasite's feces). We remember, in fact, that this parasite is able to nest under the skin and lay its eggs in small tunnels that it specifically digs into the thickness of the epidermis.
Other characteristic signs of the disease are skin burrows, which appear as linear or wavy traces, thin and slightly scaly, from a few mm to 1-1.5 cm long. In some cases, the symptoms of scabies can be atypical.
mediated by the release of epidermal cytokines; this explains the subsequent appearance of intense itching and the typical erythematous-papular rash.
Skin lesions
- Burrows of scabies
They represent the most characteristic lesion of the infection; these consist of fine, greyish streaks, a few millimeters long (at most, they reach 1.5 cm) and with a kind of vesicle with serous contents at the extremity.
The elective sites for scabby tunnels or burrows are the hands (interdigital spaces, lateral surfaces of the fingers), the flexor surface of the wrist, the anterior pillars of the armpits, the mammary areola, the umbilical region, the buttocks, the genital organs and the palm-plantar region.
However, they are not always visible, as scratching can create lesions that mask or destroy the burrows. Through scratching and / or the immune reaction, the burrows can then evolve into papules, nodules, ulcers and crusts, in the presence of an underlying redness (rash).
- Nodules of scabies
They are small reddish, noticeably itchy spots, which have a typical localization in the armpits and in the genital area. In children, they can appear on the palms or soles of the feet.
- Other nonspecific lesions
These are secondary lesions to "scratching" and others that resemble those of "eczema and" urticaria. In crusted scabies, the most severe form of the disease, scaly rashes, scabs, alopecia, and nail involvement also occur.

Possible Complications of Scabies
The irresistible urge to scratch is often associated with scratching lesions, which can become complicated following bacterial superinfections, leaving room for boils, folliculitis and impetigo.
In some cases, the symptoms of scabies can extend to the entire body surface, apparently due to an "exaggerated allergic reaction.
Scabies: Location of Lesions
The cutaneous signs of scabies occur more frequently between the fingers and toes, on the wrists and elbows, in the armpits, at the waist, on the external genitals or on the lower areas of the buttocks; these are areas where the skin, thinner and more delicate, favors the penetration of the parasite.
Infection does not typically occur in the skin of the face or scalp, except in infants and immunosuppressed people.
In children, the rash can also affect the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, the face and the scalp; in adult women, the localization of the mammary areoles is typical, while in men the skin of the penis is often affected.
Deepening: Scabies SymptomsScabies in Children
In children, the disease can mimic dermatitis; in many cases it is associated with the appearance of blisters and pustules on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
What is Norwegian Scabies?
Norwegian (or crusted) scabies is a particular clinical form of parasitosis, so called because it was described in 1848 in Norway. It manifests itself with scaly-crusted lesions, especially in the palms and soles, on the back of the hands and on the knees. Unlike the classic clinical form, itching is moderate or absent, so the diagnosis is delayed and thus increases the risk of infecting other people. Norwegian scabies is extremely contagious and mainly affects immunosuppressed subjects as a result of diseases (e.g. neoplasms, AIDS and neuropathies) or treatments (e.g. transplants or therapy with corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs). The host's decreased immune defenses favor the massive proliferation of mites Sarcoptes scabiei on the skin and make Norwegian scabies very difficult to cure.
; the dye penetrated into the tunnel by capillarity is not removed by cleaning, making its path clearly evident. At this point, it is possible to remove the scabious tunnel with a cutting edge or insert a very thin needle to pick up the mite. , crotamiton or permethrin. Galenic preparations prepared by the pharmacist on the advice of the dermatologist are often used.
It is very important to apply these products all over the body, from the neck down, after a hot and prolonged bath followed by a "vigorous friction of the skin (scrub), especially in the areas where there are cunicular lesions; this care is intended to expose the mites and the eggs contained in the burrows to the active principle. After 8-12 hours from the application, the antiscab products must be removed with water.
Oral antihistamines and emollients for topical use help to relieve itching, which often, supported by irritative phenomena (even the psychic component should not be underestimated), persists for several days; antibiotics can be used in cases of bacterial superinfections.
Monitoring and prophylactic treatment should be extended to all cohabitants and subjects in close contact with the scabby, such as sexual partners and cohabitants; to stem the spread of the infestation, the patient must abstain from work in public establishments, from boarding schools or other communities until the disinfestation work is completed.
For further information: Scabies - Drugs for the treatment of ScabiesIsolation of the patient with Scabies
Scabies is a disease subject to mandatory notification by the doctor who diagnoses it.
The Public Hygiene Service that receives this report undertakes to carry out an "epidemiological investigation to trace the alleged methods of contagion and extend the investigations also to the people with whom the patient has had close contact.
The patient with scabies must be treated with appropriate therapy and isolated for at least 24 hours from the start of treatment. Isolation requires the patient to remain separated from all other people, with the exception of those who care for him
Disinfection of environments and clothing
To eradicate scabies, the disinfestation of domestic environments and personal effects plays a fundamental role; it is therefore necessary to carefully sanitize clothing in contact with the skin, linen and bed linen (pillowcases and sheets) by boiling or washing in hot water (at least 60 ° C, better 90 ° C) and soap. Brushes and combs must also be treated at high temperatures.
Anything that cannot be washed at high temperatures should be exposed to the air for at least 2 or 3 days. The mite, in fact, does not survive far away from human skin.
Alternatively, the effects can be stored in sealed plastic bags and left inside for a week or so and then exposed to the air.
Sofas and cushions can be steam-washed at a high temperature and then wrapped in waterproof bags for a few days. Alternatively, they can be closed in a waterproof plastic bag in which a pyrethrum-based insecticide spray is sprayed and which is left closed for at least 24 hours and then the effects are exposed to the air.
Whoever lends himself to the disinfection or assistance of scabies patients must be equipped with suitable protective clothing (in particular gloves and disposable gowns).
Why can the itch remain after the scabicide therapy?
At the end of the treatment with the scabicide drug, the skin irritation may persist for some time, with the difference that the itching no longer occurs at night (as is typical during the infestation).
The scabicide kills the mite, but the body residues of the parasite remain in the skin and continue to create an allergic stimulus, which subsides spontaneously after about two weeks. Once the scabies has been treated, to relieve itching it can still be It is useful to resort to the intensive use of emollients, the application of topical corticosteroids or the intake of antihistamines by mouth.
Sometimes persistent itching results from treatment failure. This may be due to incorrect treatment, reinfestation (or relapse) or resistance to therapy. It is therefore necessary to perform another course of treatment or change product.
What to do in case of Scabies? Practical directions
- Avoid body contacts as much as possible until recovery: scabies is a contagious disease and the person who has contracted the parasitosis must remain in isolation for a few days to avoid transmitting the mite. Sarcoptes scabiei to others.
- Take a daily shower or bath before applying the scabicide topical medicine recommended by your doctor; it is recommended to rub the entire skin intensely to eliminate superficial scales.
- The nails should be cut short as they are an important source of dissemination of the mite with scratching.
- The antiscab treatment must also be carried out at the same time by people in close contact with the patient.
- Underwear, mattress covers, sheets and pillowcases must be changed (avoid shaking them so as not to spread the mites) and washed at 60 ° C every day, at least until the end of the treatment.
- All garments worn should be washed at 60 ° C or dry-washed; garments that are not machine washable should be placed in waterproof plastic bags and hermetically sealed for 2 weeks, then exposed to the air; alternatively, they can be placed for 24 hours at a temperature below 10 ° C (in the refrigerator or outside during the winter).
- To disinfect the house (sofas, upholstered armchairs, mattresses and floors) it is advisable to use instruments with a high temperature steam jet.
- After eliminating the scabies, the itching may persist due to the hypersensitivity developed; in this case, it is advisable to use cortisone and antihistamines.