Generality
Rast Test - acronym for RadioAllergoSorbent test - is the name of a "second level allergological diagnostic investigation. This test" is based on the assumption that a person allergic to a certain substance has specific antibodies against that allergen in the blood. Therefore, through the

As anticipated, the Rast Test is a second level exam; as such it is carried out only in cases where:
- The results of the skin allergy tests (prick test) do not reflect the clinical history (possible false negative in the presence of suggestive allergic symptoms);
- Presence of skin alterations, such as skin dermographism or extensive dermatitis, which contraindicate the execution of the prick test;
- Taking antihistamine and cortisone drugs that would make the prick test result unreliable.
In fact, the rast test has a much higher cost than the prick test and allows you to test only a limited number of allergens.
The advantage of the rast test is that it can be performed regardless of any concomitant treatments based on corticosteroids or antihistamines, and skin conditions or medical problems that contraindicate the execution of skin tests.
The Rast test is contraindicated in case of:
- Negativity to skin tests
- Total IgE less than 20 ng / l
- Diseases not related to IgE
What's this
The RAST test is a laboratory test that measures the level of specific IgE (immunoglobulins) produced towards a particular substance (allergen) in the venous blood.
- On a practical level, the blood taken is put in contact with an allergen; if the sample contains specific IgE towards this substance, a bond is established. At a later stage, the blood is brought into contact with radioactively labeled anti-IgE antibodies: the greater the radioactivity that is detected, the greater the quantity of specific IgE present in the blood.
The RAST test allows to confirm, in association with skin tests, the diagnosis of the suspected allergy in the patient.
Because it is measured
The RAST test (or specific IgE dosage) is a blood test useful to highlight if a person suffers from an allergy and to determine which specific substance is susceptible to (eg pollen, mites, pet derivatives, mold, latex , food allergens, etc.).
This analysis is indicated by the doctor in the presence of symptoms that lead to think of an allergic manifestation, such as:
- Rhinitis: nasal congestion and irritation of the respiratory tract, with sneezing (in rapid succession) and a runny nose (rhinorrhea);
- Asthma: wheezing, chest tightness, wheezing (whistling sound when exhaling) and dry cough;
- Conjunctivitis: light discomfort, tearing, redness, itching, swelling and irritation of the eyes;
- Gastro-intestinal disorders: itchy or itchy palate or throat, difficulty swallowing, abdominal pain, muscle spasms, vomiting and diarrhea;
- Sleep disturbances, general malaise and weakness;
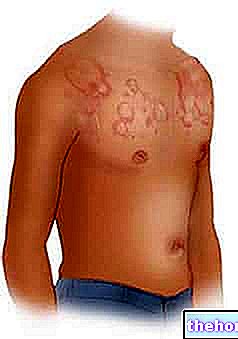
- Hives, atopic dermatitis and eczema with redness and itching.
The RAST test is used to confirm the result of the Prick test (skin allergy test), especially in doubtful cases. The analysis also provides an indication of the patient's degree of sensitivity to exposure to the allergen.
Normal values
Compared to other immunoglobulin classes, normal IgE values show wide fluctuations in relation to different ages.
Normal IgE values (kU / L):
- Infants: 0.5 - 2 kU / L
- 1 month to 1 year: <20 kU / L
- From 1 to 5 years: <70 kU / L
- From 5 to 10 years: <100 kU / L
- From 10 to 12 years: <200 kU / L
- From 12 to 19 years: <150 kU / L
- From 19 years onwards: <200 kU / L
High specific allergen IgE
The finding of an increase in specific allergen IgE on the RAST Test confirms the presence of an "allergy disease".
Low specific allergen IgE
Low levels of specific allergen IgE are not usually associated with medical problems and / or pathological consequences.
How it is measured
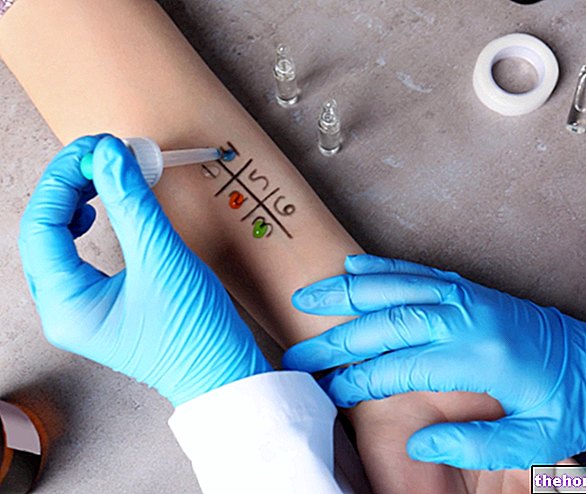
- A small blood sample is drawn through a syringe fitted with a fine needle.
- The sample is typically carried out from a vein in the forearm, as in any other blood test. The site where the puncture will be performed is previously disinfected. Sometimes, to make the sample vein more evident, a tourniquet is applied upstream .
- After collection, the rast test allows an in vitro etiological diagnosis through the use of specific equipment on the sample taken.
Preparation
For the execution of the RAST Test it is not necessary any specific preparation, nor fasting.
Even drugs, except for antihistamines and cortisone (used to neutralize the symptoms of allergy), do not affect the result, although it is advisable that the doctor is always aware of which drugs the patient is taking.
Interpretation of Results
Generally speaking, if the research value of a certain allergen remains normal, it means that you are not allergic to that substance.
If the result of the RAST TEST is, on the other hand, higher than the normal one, you can be sure that you are allergic to that substance. Furthermore, the higher the value, the greater the extent of the disorders associated with the allergy.
You can also identify multiple substances to which you are allergic at the same time.
0,1 - 0,35
Very low
2
0,35 - 0,7
Low
3
0,7 - 3,5
Moderate
4
3,5 - 17,5
High
5
17,5 - 50,00
Very high
6
50 - 100
Very high
7
>100
Extremely High / Abnormal







.jpg)


















