What is pus?
Pus is a more or less thick, yellowish or greenish, creamy fluid that forms at the site of an infection.
The pus consists of:
- a variable amount of serum or plasma;
- degenerating white blood cells;
- live and dead bacteria;
- fragments of necrotic tissue and other residues of the defense process.

Figure: A Pustule, a small collection of pus in the skin
The main decaying white blood cells found in pus are neutrophils, phagocytic cells capable of engulfing and digesting the bacteria with which they come into contact; considerable amounts of lymphocytes are also found in chronic inflammatory processes.
Contrary to what one might think due to its disgusting appearance, the presence of pus indicates a good response of leukocytes to inflammation and to the chemotactic factors that are released in response to it.
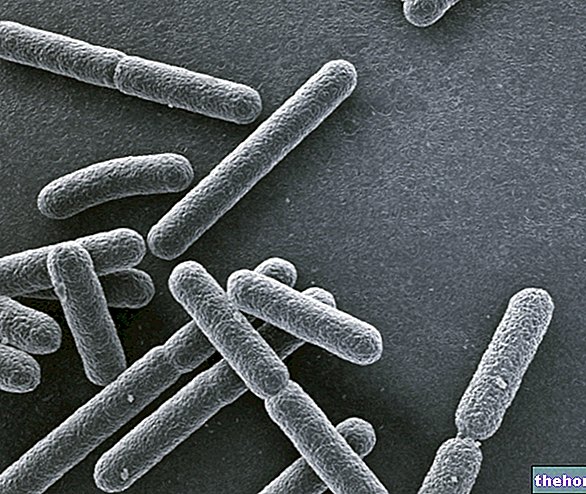
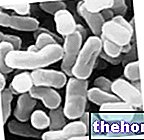
Pyogenic bacteria
Pus is a pathological material, so the presence of bacteria both in the microscopic examination and in the culture one, usually has a high diagnostic importance.
Pyogenic is defined as that which determines the production of pus; examples of pyogenic bacteria or germs are Staphylococcus aureus, lo Staphylococcus haemolyticus, the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the Nesseiria Gonorrhoeae (causative agent of blenorrhagia, a sexually transmitted disease that occurs with purulent secretions from the penis or vagina).
A large number of bacterial species can be classified as pyogenic. The most common include:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Escherichia coli
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Salmonella typhi
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Actinomyces
- Burkholderia mallei
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The Staphylococcus aureus it is the most common cause of boils.
Source: wikipedia.org
The adjective purulent refers to anything that contains, consists of, or produces pus (eg. Purulent inflammation); if associated with mucus, the adjective "mucopurulent" is used.
Empyemas, Abscesses and Pustules
Collections of pus are called
- empyemas if they are found in pre-formed cavities
- abscesses if they are present in newly formed cavities
- phlegmons if they have a tendency to spread.
Pustules are small raised, pus-filled lesions that form in the epidermis; they are a typical sign of acne and pustular psoriasis.
Treatment
In the presence of small pus-filled pimples, it is sufficient to apply a warm-moist compress to promote drainage, followed by local disinfection.
Before and after the operation it is important to wash your hands thoroughly (the pus can in fact contain live bacteria that can infect other areas of the skin or infect other people).
In general, however, it is a good rule to avoid tormenting these small collections of pus too much, which tend to disappear spontaneously within a few days.