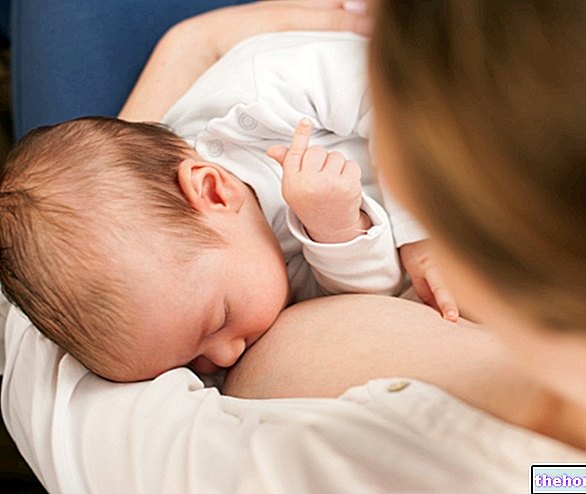
When it comes to breastfeeding, there are no fixed rules; distribution, frequency and duration of the same, in fact, vary from one child to another. In such a context, it is possible to draw up at most some general indications, to ensure that the child takes adequate quantities of milk and prevent unpleasant problems both to the mother and to the baby. On the other hand, exact and pre-printed information cannot be divulged at all, precisely because the duration and characteristics of each feeding are the result of the "magical" experimentation between mother and child.
Characteristics of feedings
- The duration of a feed depends on many factors. Since most of the milk is sucked in the first 5-10 minutes, many babies spontaneously finish it in less than a quarter of an hour, while others may take longer.
- It is a good idea to leave the baby attached to the breast until it detaches spontaneously; sometimes it satisfies itself with only one breast, other times it sucks from both. that the last milk of the feeding is the richest in fat, therefore satiating, while the first - more watery and with excellent rehydrating characteristics - quenches the thirst.
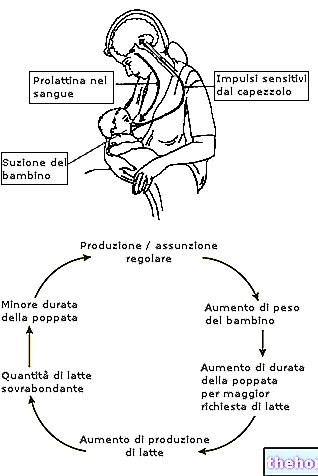
- The duration of the feeding can vary considerably from one week to the next, a phenomenon that reflects - in most cases - an adjustment to the baby's growth. Milk production is in fact regulated by demand; the more frequent and vigorous the sucking is, the more the greater the amount of milk consumed and the more abundant that produced. Some infants have "cluster feedings" (they breastfeed every hour for 2-6 hours, then sleep for a prolonged period); others, on the other hand, breastfeed every 2-3 hours both day and night.
- The state of maternal relaxation favors the flow of milk; therefore, during the feeding, the mother should sit comfortably. If, on the other hand, the newborn likes to remain attached to the breast for a long time, feeding calmly and without haste, it is advisable to adopt the position lying on his side, in order to relax the pelvic floor.
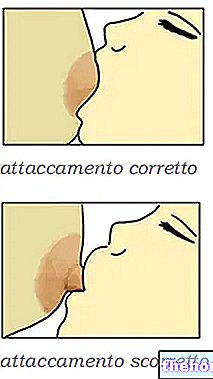
- The duration of the feed should not exceed 30 minutes; there is in fact the risk of aerophagia (ingestion of air) and neonatal gas colic, while for the mother the risk of nipple irritation increases up to the appearance of fissures, the preventive strategies of which are detailed in this article. The child who tends to remaining too long attached to the mother's breast, it also has difficulty in finding the right regularity in the alternation of feeding and resting phases.

- The mother should wash her breast before and after each feeding; scrupulous hygiene with water is sufficient, while soaps, ointments, ointments and detergent and antiseptic solutions are generally not recommended. These substances, in fact, could irritate the skin and give the nipple an unpleasant smell and taste. Special wipes are available on the market for cleansing breastfeeding breasts, obviously without surfactants, perfumes or substances that require rinsing. Your hands, of course, will need to be washed carefully before starting breastfeeding.
- If both breasts are used at each feed, it is a good idea to start alternately with the right or left breast. However, when only one breast is used at a time, for obvious reasons it is necessary to alternate it from feeding to feeding. In both cases, a safety pin pinned to the bra strap helps to remember which breast to start the next feed with.
- At the end of the feeding, the nipples should be dried and covered with a sterile compress; the child, in the meantime, will be kept in a vertical position for a few minutes, in order to favor the onset of the eventual and characteristic burp.
- On average, a newborn needs 8-12 feedings over a period of 24 hours; if after birth the baby cannot be attached, to stimulate milk production, however, it is essential to "pump" the milk at least 6-8 times in the period. of the day.
- Crying is a late sign of hunger. The newborn may manifest the need to latch onto the breast with earlier symptoms, such as opening the mouth, sucking fists, moving the eyes under the eyelids, making noises or moving the head from side to side.
- The signs that the baby is getting adequate amounts of breast milk during feedings are:
- at least 3 bowel movements per day after the 1st day
- lumpy yellow discharges from the 5th day
- at least 6 urinations per day from the 4th day, with clear or light yellow urine
- is satisfied and content after feedings
- swallowing sounds during breastfeeding
- absence of weight loss after the 3rd day
- they grow about 20-35 grams per day starting from the 5th day
- recovery of birth weight from the 10th day
- evident increase in texture, weight and size of the breasts, ed
- evident increase in the quantity and quality of milk from the 5th day
- the nipples show no signs of injury
- breastfeeding removes the sensation of fullness of the breasts
- The signs that the baby is getting inadequate amounts of breast milk during feedings are:
- the weight gain of the newborn is less than 18g per day, 125g per week or 500g per month;
- the weight at 15 days of life is lower than that recorded at birth;
- the newborn urinates less than 6 times a day, with pungent and concentrated urine (dark yellow tending to orange), and evacuates hard, dry and infrequently:
In addition to experiencing reduced weight gain, the poorly fed infant may cry often, remain too long on the breast, appear lethargic, and dissatisfied at the end of a feed, or refuse the breast.