Introduction
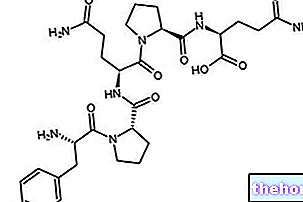
The atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP, Atrial Natriuretic Peptide, also called atriopeptin) is a peptide hormone produced by myocardial cells (myocytes) with endocrine activity, located at the atrial level. These cells contain secretory granules, where they accumulate and from which they release the atrial natriuretic peptide, which carries out a "specialized endocrine action at the cardiovascular level.
In addition to the atrial natriuretic peptide, two other related natriuretic peptides are known: the brain natriuretic peptide B (BNP), synthesized by ventricular myocardial cells and some brain neurons (so called because it was originally isolated from the pig's brain), and the natriuretic peptide C (CNP), which is of endothelial origin.
High natriuretic peptides and hypertension
Since the activity of these hormones is superimposable, we speak in the complex of natriuretic peptides. Their release is high when the muscle cells of the heart are stretched more than normal, a situation linked to the excessive presence of blood (hypervolemia), therefore to hypertensive phenomena (also resulting from the use of vasoconstrictor drugs).To compensate for the hypervolemia, natriuretic peptides - as the name suggests - cause a marked increase in diuresis and natriuresis, increasing the excretion of sodium and water through the kidney; moreover, they release the smooth muscles (vasodilating action) both at the systemic and renal level, where the action is directed above all to the arterioles afferent to the glomerulus, while it does not affect the efferent ones, which even tend to force themselves to increase glomerular filtration. These actions are mediated both by direct and indirect mechanisms, linked to the inhibitory effect on the release and / or on the action of various hormones and mediators, such as angiotensin-II, endothelin, aldosterone and vasopressin. Furthermore, natriuretic peptides act directly on the cardiovascular control center of the bulb to reduce arterial pressure, with inhibitory activity on the activation of the sympathetic system. Together, therefore, the natriuretic peptides help to reduce the venous return to the heart and with it the blood pressure values.
Other causes of high natriuretic peptides
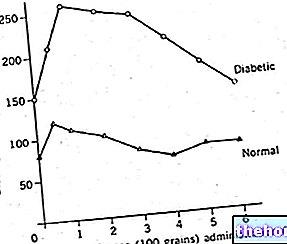
Plasma levels of natriuretic peptides increase in physiological conditions (diet rich in sodium, administration of saline solution, supine position, lifting of the legs, immersion in water up to the neck) and in pathological conditions (congestive heart failure, chronic renal failure); instead, they decrease in the opposite conditions (assuming an upright position, low-sodium diet, taking diuretics, dehydration).
Brain natriuretic peptide BNP
Released from the ventricular myocardium in response to the increased stress relieving the walls of the ventricles, typical of hypervolemia and pressure overload, the cerebral natriuretic peptide is an important marker and prognostic indicator of congestive heart failure. According to various studies, blood BNP levels predict cardiac mortality and the risk of numerous adverse cardiac events (heart disease), such as left ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular failure, acute coronary syndrome, acute myocardial infarction and sudden death from cardiac arthritis The plasma BNP assay is also useful for the therapeutic monitoring of patients suffering from congestive heart failure and other heart diseases.
Select Blood Tests Blood Tests Uric acid - uricaemia ACTH: adrenocortitotropic hormone Alanine amino transferase, ALT, SGPT Albumin Alcoholism Alphafetoprotein Alphafetoprotein in pregnancy Aldolase Amylase Ammonemia, ammonia in the blood Androstenedione Antibody-endomysial antibodies Anti-gliadicides Nucleus Helicobacter pylori antibodies Embryo carcinoal antigen - CEA Prostate specific antigen PSA Antithrombin III Haptoglobin AST - GOT or aspartate aminotransferase Azotemia Bilirubin (physiology) Direct, indirect and total bilirubin CA 125: tumor antigen 125 CA 15-3: tumor antigen 19-9 as tumor marker Calcemia Ceruloplasmin Cystatin C CK-MB - Creatine kinase MB Cholesterolemia Cholinesterase (pseudcholinesterase) Plasma concentration Creatine kinase Creatinine Creatinine Creatinine clearance Chromogranin A D-dimer Hematocrit Blood culture Hemocrome Hemoglobin Glycated hemoglobin a Blood tests Blood tests, Down syndrome screening Ferritin Rheumatoid factor Fibrin and its degradation products Fibrinogen Leukocyte formula Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin GGT - Gamma-gt Gastrinemia GCT Glycemia Red blood cells Granulocytes HE4 and Cancer at "Ova" Immunoglobulins INR Insulinemia Lactate dehydrogenase LDH Leukocytes - white blood cells Lymphocytes Lipases Tissue damage markers MCH MCHC MCV Metanephrines MPO - Myeloperoxidase Myoglobin Monocytes MPV - average platelet volume Natremia Neutrophils Homocysteine Thyroid hormones OGTT Osmocyte Plasma protein A associated with pregnancy Peptide C Pepsin and pepsinogen PCT - platelet or platelet hematocrit PDW - distribution width of platelet volumes Platelets Plateletpenia PLT - number of platelets in blood Preparation for blood tests Prist Test Total IgEk Protein C (PC) - Protein C Activated (PCA) C Reactive Protein Rast Protein Test Specific IgE Reticulocytes Renin Reuma-Test Oxygen Saturation Sideremia BAC, BAC TBG - Thyroxine Binding Globulin Prothrombin Time Partial Thromblopastin Time (PTT) Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) Testosterone Testosterone: free and bioavailable fraction Thyroglobulin Thyroxine in the blood - Total T4, free T4 Transaminases High transaminases Transglutaminase Transferrin - TIBC - TIBC - UIBC - saturation of transferrin Transtyretin Triglyceridemia Triiodothyronine in the blood - Total T3, free T3 Troponin TRH and Troponins of s thymol to TRH TSH - Thyrotropin Uremia Liver values ESR VDRL and TPHA: serological tests for syphlis Volemia Conversion of bilirubin from mg / dL to µmol / L Conversion of cholesterol and triglyceridemia from mg / dL to mmol / L Conversion of creatinine from mg / dL to µmol / L Conversion of blood glucose from mg / dL to mmol / L Conversion of testosteronemia from ng / dL - nmol / L Conversion of uricemia from mg / dL to mmol / L











.jpg)











