The urine odor of a healthy and well hydrated subject is normally "sui generis" and as such free of bad fragrances. We are in fact talking about a normally aseptic liquid, which contains variable concentrations of waste substances depending on the diet, state health and hydration, and the intake of any medications.
A bad smell in the urine can therefore be a sign of pathological conditions, but not necessarily.

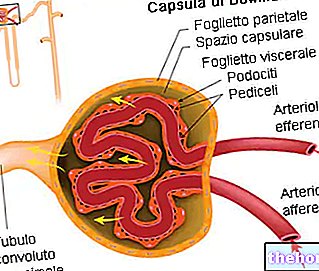
(because the solutes responsible for bad odor increase their concentration; the urine thus takes on a particularly dark color and a characteristic aroma of ammonia);
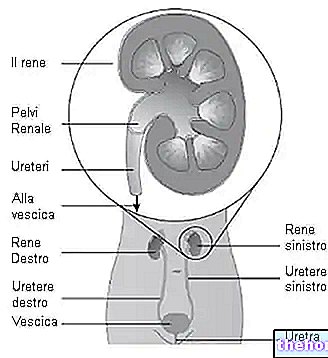
Cystitis, urinary infections, pyelonephritis (kidney infections), urethritis, prostatitis and vaginitis (in this case the problem may not be related to the urinary tract, given the anatomical proximity - to learn more see: vaginal odor);
Liver failure;
Diabetic ketoacidosis and ketonuria (also typical of prolonged fasting, accompanied by abundant urine with a sweetish odor, similar to acetone);
Rectovaginal fistula;
Phenylketonuria (rare disease present from birth);
Taking Vitamin B-6 Supplements
Metabolic disorders;
Maple syrup urine disease (rare);
Trimethylaminuria or fish odor syndrome (rare);
Some drugs can also alter the smell of urine, including some antibiotics such as amoxicillin, ampicillin, nitrofurantoin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin and trimethoprim.
The causes of bad urine odor can be investigated through a simple urinalysis and culture (to look for any bacterial infections).






.jpg)


















