See also: Insulinemic curve
Generality
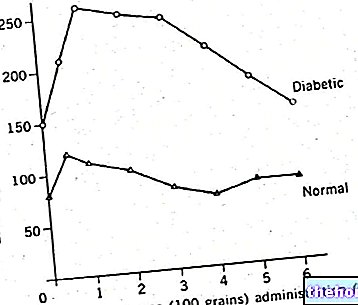
The glycemic curve is a clinical test carried out to evaluate the metabolism of carbohydrates and identify its alterations.
Also referred to as OGTT (from "English"Oral Glucose Tolerance Test”), The glycemic curve measures the concentration of sugars in the blood, before and after the oral administration of a certain quantity of sugar solution.

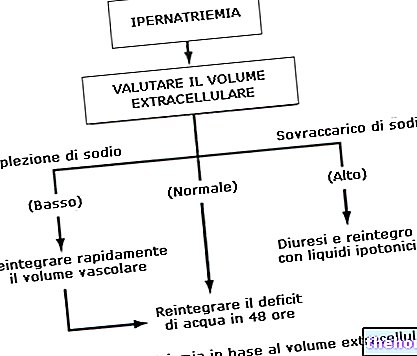
The glycemic curve is useful for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and is usually made when fasting glycaemia is repeatedly found to be between 110 and 126 mg / dl.
- In healthy people, the body produces a certain amount of insulin when glucose enters the bloodstream.
- Insulin prevents glucose from exceeding the maximum tolerated level by the body, beyond which the excess dose is stored in the liver.
- Exceeding this threshold indicates impaired glucose tolerance (IGT or "Impaired Glucose Tolerance"), Hence an" initial relative insulin deficiency that could lead to diabetes.
What's this
The glycemic curve is a test that measures blood glucose values with a sample taken in fasting mode and two hours after taking an oral glucose solution.
The blood glucose curve test is also used in pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes, a condition that is important to monitor for the health of the mother and the unborn child.
To remember
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, due to a deficit in the production or function of insulin.
Because it is measured
The glycemic curve is a test that is performed to understand if the concentration of glucose in the blood is within the normal range. Therefore, the test is useful for the screening and diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes, as well as allowing the monitoring of patients who have high (hyperglycaemia) or low (hypoglycemic) blood glucose concentrations.
The oral glucose tolerance test is often performed in pregnant women to detect the presence of gestational diabetes.












.jpg)











