Generality
In medicine, contraindications are those circumstances that make a particular therapy or a particular diagnostic procedure inadvisable; the reason for this precaution lies in the negative, or highly negative, consequences that could arise from the implementation of a particular therapy or diagnostic procedure.

What are the contraindications?
Contraindications are all those conditions that make a particular therapy or a particular diagnostic procedure inadvisable, as its implementation could result in negative consequences, if not even a (further) danger of life for the person concerned.
When it comes to contraindications, the crucial point, around which the whole discussion revolves, is the risk-benefit balance. In fact, the typical question of doctors in this regard is: is performing this therapy or diagnostic procedure more risky than the benefits that can derive from it?
There are two types of contraindications: absolute contraindications and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications
In medicine, absolute contraindications are those conditions in the presence of which the conditions for undertaking a specific medical action for diagnostic-therapeutic purposes are completely lacking.
In other words, the term absolute contraindication refers to a state of health, the presence of which categorically excludes being able to intervene with a certain treatment or carry out a certain diagnostic investigation.
Examples to understand:
- Young age represents an absolute contraindication to the administration of aspirin (acetyl-salicylic acid), as the latter, in children and adolescents under the age of 16, can be responsible for the so-called Reye's syndrome.
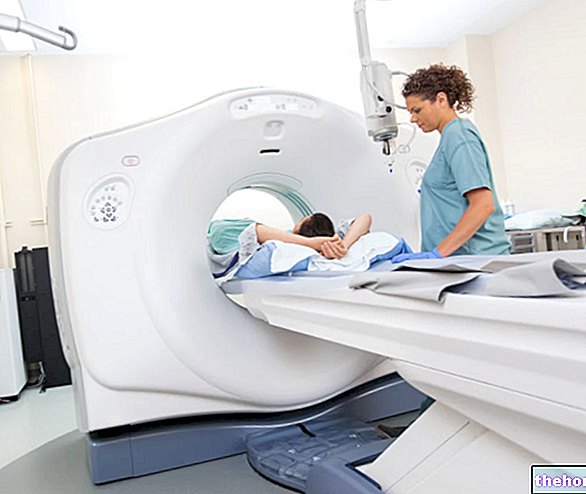
- The presence inside the human body of metal components (pacemakers, neurostimulatory devices, splinters in the eye, intracranial clips for a cerebral aneurysm, hearing aids, etc.) represents an absolute contraindication to nuclear magnetic resonance, as the latter, for effect of the magnetic fields to which it gives rise, could cause the displacement of the aforementioned metal components and alter the operation of the aforementioned devices.
- The presence of agenesis of the cochlea or of the acoustic nerve represents a contraindication to the cochlear implant, as the latter only works in the presence of the aforementioned anatomical structures of the inner ear.
TEMPORARY ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Some conditions that make a certain therapy or a certain diagnostic procedure absolutely inadvisable are temporary, either because they are treatments of a certain duration or because they are pathologies that require a certain amount of time to heal.
To refer to such circumstances, doctors coined the term of temporary absolute contraindications.
Examples to understand:
- The presence of esophageal varices is an absolute temporary contraindication to the use of the nasogastric tube, as is the presence of a stenosis of the esophagus.
In fact, with the healing of the two aforementioned medical conditions, it is possible to introduce, through the esophagus, the thin tube, which makes up the nasogastric tube, and take it to its destination. - The presence of bone fractures and a recent surgery represent two typical temporary absolute contraindications to the practice of massage therapy.
In fact, with bone welding, for the first case, and with the healing of surgical wounds, for the second case, any prohibition on the therapeutic message of the muscles, carried out with the hands, lapses. - Cervicitis and vulvovaginitis are two inflammatory conditions, which play the role of temporary absolute contraindications to colposcopy, as long as they are not completely healed.
Performing colposcopy in spite of cervicitis or vulvovaginitis is bothersome for the woman concerned and can significantly alter the outcome of the aforementioned diagnostic procedure.
Relative contraindications
In the medical field, relative contraindications take the name of those conditions in the presence of which a specific diagnostic or therapeutic procedure is inadvisable, unless there are more important circumstances, for which refraining from the aforementioned procedure is more risky than carrying it out.
In other words, the term relative contraindication indicates a state of health, the presence of which excludes a certain therapy or a certain diagnostic test, unless an "other circumstance occurs which makes it essential to carry out the aforementioned therapy or above diagnostic test.
Examples to understand:
- X-rays are contraindicated in the case of pregnancy (NB: pregnancy is the contraindication), unless a pregnant woman complains of serious ailments, the causes of which are identifiable only with an X-ray and the neglect of which could be responsible, according to the doctor , with serious consequences on the patient's health.
- The presence of metal prostheses and the presence of metal sutures in locations other than the brain represent two contraindications relating to nuclear magnetic resonance. These contraindications, in fact, lapse in the presence of reasonable reasons for not carrying out a diagnostic investigation, through magnetic resonance, could have serious repercussions and delay vital treatment.
- Heart diseases and upper respiratory tract infections (eg sinusitis) are among the contraindications relating to the hyperbaric chamber. These contraindications, in fact, cease when the supply of pure oxygen becomes vital.