Thanks to the CT scan total body It is possible to early diagnose important vascular diseases affecting coronary artery, aorta and its ramifications as well as tumors and some pathologies of the thoracic, abdominal and pelvic organs.
With a total duration of 30 minutes maximum, the CT scan total body it requires a certain preparation (in particular if the use of a contrast medium is foreseen) and, for its correct execution, it requires the patient the maximum immobility.
The risks of CT total body they are related to the dose of X-rays to which the patient is exposed during the examination and to the contrast medium (if it is intended to be used), which in some individuals is the cause of an allergic reaction.
Contraindicated in case of pregnancy, obesity and, if with contrast medium, also in the presence of diabetes and renal insufficiency, the CT scan total body provides excellent quality images, which allows for very precise diagnoses.
The equipment for the CT scan includes:
- The large donut-shaped scanning unit, called gantry. It is the source of ionizing radiation (or X-rays);
- The generator;
- The support on which to place the patient. Generally, it is a sliding bed;
- An electronic computer;
- A console command for viewing three-dimensional images;
- A system for recording the acquired data.
Sometimes, the CT scan can involve the use of a contrast medium (CT with contrast); usually based on iodine, the contrast medium allows to create, through the CT scan, extremely detailed images of: blood vessels, lymph nodes and parenchymal organs .
Although it is a normally painless examination (only in the variant with contrast it is annoying, due to the administration of the contrast medium), the CT scan is one of the minimally invasive diagnostic procedures, as the dose of ionizing radiation, to which the patient is exposed, it is considerable.
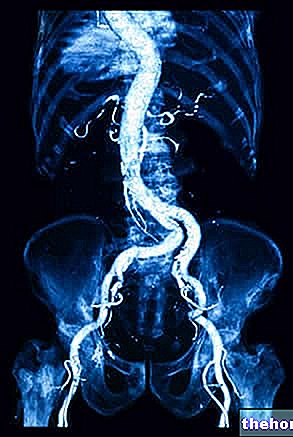
The tomography total body, therefore, it allows to acquire information about the state of health of the organs and thoracic blood vessels (eg: heart, lungs and thoracic aorta and its ramifications), abdominal (eg: stomach, pancreas, liver, intestine, abdominal lymph nodes and aorta abdominal and its ramifications) and pelvic (eg: intestine, bladder and ureters; uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, in women; prostate, in men).
The tomography total body it is a diagnostic procedure.