Generality
Horner syndrome, also known as Bernard Horner syndrome, is a procession of symptoms and signs sustained by damage or malfunction of the sympathetic trunk nerves.

Figure: Person with Horner's syndrome. From the site: wikipedia.org
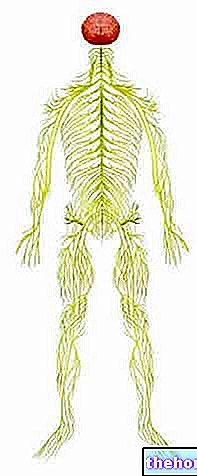
The sympathetic trunk is a set of neurons that emerge to the right and left of the spinal cord, cross the thorax and rise bilaterally up to the neck and face.
The causes of Horner's syndrome are numerous; their identification is very important in establishing the most correct therapy (causal therapy).
The most characteristic signs of Horner's syndrome are: ptosis, myosis and anhidrosis. However, anisocoria, slow dilation of the pupil and bloodshot conjunctiva are also very common.
For a correct diagnosis, the following are essential: physical examination, evaluation of clinical history, some eye tests and some diagnostic imaging tests.