
Various factors may favor the onset of scarlet fever in adults, including, for example, advanced age, stress, contact with a person suffering from scarlet fever, poor night rest, the presence of a chronic disease ( ex: diabetes mellitus) etc.
The effects of scarlet fever in adults are the same as those of scarlet fever in children; an adult with scarlet fever, therefore, develops: a rash characterized by scarlet spots and patches, a whitish and then red patina on the tongue, sore throat, fever, headache, abdominal pain and tachycardia.
Treatment of scarlet fever in adults involves antibiotic treatment of about 10 days, associated with rest, patient isolation and symptomatic treatment.
Impossible to prevent with a vaccine, scarlet fever in adults tends to resolve positively within a week, provided that therapy is adequate and timely.

- Scarlet fever is one of the best known and most widespread exanthematous diseases; exanthematous diseases are those morbid conditions of infectious origin, which cause an exanthema (or rash), that is signs on the skin such as, for example, spots, red areas, blisters, papules and / or pustules;
- Scarlet fever mainly affects children; more specifically, it has a predilection for subjects between the ages of 3 and 10;
The marked tendency of scarlet fever to afflict the young population is explained by the presence, in the 3-10 year old human being, of an immature immune system not yet ready to deal with a bacterium such as group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. - Scarlet fever can also affect infants, adolescents and adults, although these individuals all possess, for different reasons, efficient immune defenses;
- Scarlet fever is an "infection whose transmission can occur through the inhalation of droplets of saliva emitted by an affected person when coughing, sneezing, etc." (transmission by direct contact) or through contact with objects contaminated by the infectious agent, as they passed into the hands of a sick individual (transmission by indirect contact);
- In people it affects, scarlet fever is typically responsible for: scarlet red spots or patches all over the body (it is the rash mentioned above), the formation of a white patina on the tongue and then red, peeling skin, fever, sore throat, abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat and headache;
- Getting sick with scarlet fever does not give permanent immunity, as there are many different strains (i.e. many different variants) of group A beta-haemolytic streptococcus.
What favors the appearance of Scarlet fever in Adults?
Factors such as:
- Advanced age. With aging, the human being's immune system tends to weaken and this reduces the effectiveness of the defenses against bacteria such as scarlet fever;
- An inadequate night's rest. During the night's sleep, the human body processes the proteins introduced in the diet and uses them to fight potential pathogens. Those who do not get enough sleep during the night cannot effectively use proteins for the aforementioned purpose, therefore they are more vulnerable to infections;
- The stress. Psychophysical stress can lower the immune defenses, so as to make the human being more vulnerable to infections;
- Direct contact with a person affected by scarlet fever or with objects belonging to this person.

- The presence of a chronic disease. Chronic diseases typical of adulthood such as diabetes mellitus make the human immune system weaker and less able to defend against infectious agents, such as viruses, bacteria, etc.
- The presence of an infectious disease such as AIDS. Caused by the virus known as HIV, AIDS (or Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome) is an infection that drastically affects the efficiency of the human immune system, to the point that for those who even the most banal and common pathogen (eg the cold virus) is affected by it;
- The absence of the spleen. The spleen is an organ of the immune system; therefore, in its absence compared to when it is present, the chances of developing an infection are much greater.
The absence of the spleen is often related to surgery to remove the organ in question (splenectomy), performed with the aim of treating a tumor in the spleen or a rupture of the spleen; - Chemotherapy practiced for the treatment of a tumor. Chemotherapy has several side effects, including the weakening of the immune defenses and the consequent predisposition to infections.
It should be noted that an adult could develop scarlet fever even if it does not fall under any of the aforementioned risk factors.
Contagion and Transmission
Like scarlet fever in children, scarlet fever in adults can also be transmitted through the inhalation of droplets of saliva (via aerosol) emitted by a patient or through contact with objects contaminated by the infectious agent.
in adults they are similar to the symptoms of scarlet fever in children; this means that the adult person suffering from scarlet fever has:
- A rash characterized by small dots and small spots very close to each other, of a scarlet red color and slightly in relief;
- A whitish patina on the tongue, which within a few days changes color and becomes red (raspberry tongue);

- Fever at 38 ° C;
- Sore throat;
- Abdominal pain
- Tachycardia;
- Headache.
SCARLATTINA ESANTEMA: A FEW MORE DETAILS
The rash due to scarlet fever is, in patients of some age and state of health, the most characteristic symptom of the condition in question, therefore it deserves a little study.
In patients with scarlet fever, scarlet spots and patches appear first on the neck, armpits and groin area and then, within 24 hours, throughout the rest of the body, except on the nose, mouth and chin.
After a few days of scarlet fever, the rash in question leaves room for a fairly evident skin desquamation process, which represents an example of furfuraceous desquamation.
The rash produced by scarlet fever is never itchy, meaning it never itches.
Incubation times
Scarlet fever in adults has an incubation time that varies between 1 and 3 days (NB: the incubation time of an infectious disease is the time between the moment of exposure to the responsible pathogen and the moment of onset of the first symptoms ).
Scarlet fever in adults: consequences in pregnancy
Among the possible targets of scarlet fever in adults are also pregnant women.
Generally, scarlet fever in pregnant women does not pose a danger to the future unborn child; it is in fact very rare that it causes fetal malformations and is transmitted from mother to child at the time of birth.
Complications
Before the discovery of antibiotics, anyone who developed scarlet fever (including adults) was at no negligible risk of developing complications, such as meningitis, septicemia, severe sinusitis, pneumonia, encephalitis, endocarditis, rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis, which could even be fatal .
Today, thanks to a "wide availability of drugs against group A beta-haemolytic streptococcus, the aforementioned complications are fortunately rare, as is the danger of death associated with them.
Curiosity: which organs and systems can be affected by the complications of scarlet fever in adults?
- Tonsils;
- Lungs;
- Kidneys;
- Central nervous system;
- Blood;
- Heart.
Sometimes, however, it may happen that the aforementioned investigations are not very exhaustive and that the doctor needs to perform a throat swab for diagnostic confirmation.
Normally, the use of the throat swab for the confirmation of scarlet fever in adults is typical of the milder infectious forms, in which the symptoms are blurred, unclear.
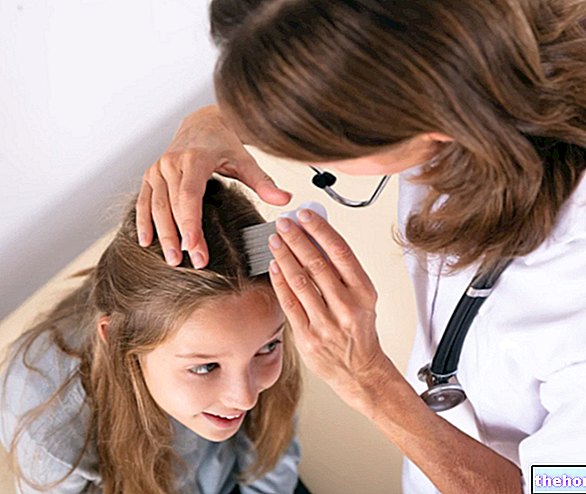
Throat Swab: What is it?
The throat swab is a diagnostic test that allows us to definitively clarify whether a certain pain in the throat is linked to a specific pathogenic microorganism or not.
Briefly, it involves rubbing the tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa using a special cotton stick, in order to take some cells to be analyzed later in the laboratory.
If the adult suffering from scarlet fever is a pregnant woman, it would be advisable for the patient to also contact the trusted gynecologist, to agree with him the details of administration (methods, dosage, etc.);
Which antibiotics are suitable for the treatment of scarlet fever in adults?

Generally, doctors treat scarlet fever in adults with oral penicillins or, if the patient has an "allergy to these drugs, with macrolides."
Symptomatic Treatment of Scarlet Fever in Adults
To relieve the symptoms of scarlet fever in adults, doctors find it extremely useful:
- The administration of an antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving drug, such as ibuprofen or paracetamol, with the aim of soothing a sore throat and reducing fever;
- Drink a lot of water, to avoid the state of dehydration that could derive from the presence of fever;
- Humidify the air in the room where the patient stays during the illness, with the aim of favoring the resolution of throat irritation;
- Consume foods of a tender or semi-solid consistency, to minimize pain in the throat resulting from swallowing food;
- Avoid exposure to irritants, such as active smoking and secondhand smoke, which have the effect of slowing the healing process.
What Can Extend Healing Times?
The healing times of scarlet fever in adults are lengthened when the patient is in a precarious state of health (eg presence of chronic immunosuppression) or when the patient neglects antibiotic treatments.













.jpg)











