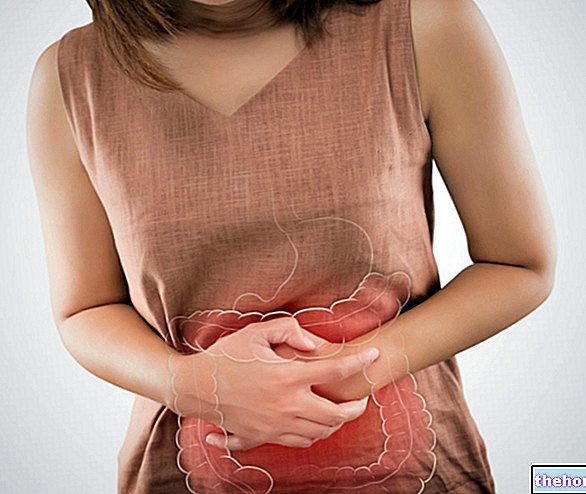
The swollen belly can be related to flatulence, abdominal pain or cramps, diarrhea and constipation, while the uncomfortable condition most frequently associated with abdominal bloating is irritable bowel syndrome.
The swollen belly is perceived as an unpleasant sensation of swelling of the abdomen, just as if the internal cavity had been inflated in a similar way to a "balloon" (sensation of air in the belly). The anatomical regions involved are: epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric and often the right and left hypochondrium.
The sensation of bloating is activated when certain volumes inside the abdomen, in particular those enclosed in the digestive tract - stomach and intestines, increase "forcibly" beyond normal. Other factors may be involved such as the menstrual cycle, fatty liver, gallstones or biliary lithiasis and certain bladder diseases; however, these are generally easy to differentiate conditions that rarely complicate the specific diagnosis.
Statistically speaking, most cases of abdominal swelling are due to benign, paraphysiological or otherwise idiopathic conditions, in the absence of any diagnosable disease or pathogenic condition. Furthermore, this perception is triggered in an extremely subjective way. Individuality is a very difficult variable to manage, especially as regards the diagnosis. In fact, cases of strong self-suggestion - typical for example of hypochondria, are not rare. On the other hand, one should not even confuse a poor specific tolerance with any abdominal swelling of psychosomatic origin, which corresponds, for emotional or behavioral issues - hyperproduction of catecholamines, aerophagia, etc. - a real but often transient abdominal distension.