Identifying the exact origin of right flank pain is critical to planning the correct therapy.

The lining that covers and protects these organs includes the skin, the intercostal muscles and the ribs (or ribs).
It should be remembered that the so-called intercostal nerves run between the coasts. Originating in the spinal cord, the intercostal nerves are peripheral nerves (that is, belonging to the peripheral nervous system), which innervate the muscles of the thoracic cage, the skin that lines the chest, and the internal tissues of the thoracic cavity.

ORGANS OF THE LOWER RIGHT SIDE
The organs of the right side, located in the lower part of the abdomen, are:
- The cecum, ie the first section of the large intestine (or large intestine);
- The vermiform appendix, that is the tubular formation that departs from the caecum and is located near the outlet of the ileum;
- The ascending colon;
- The right ovary and the right fallopian tube, exclusively in female subjects;
- The right ureter.
Similar to the case of the upper right flank, the lining that covers and protects the aforementioned anatomical structures includes skin, muscles (the abdominal muscles) and bones (left iliac crest).
gallstones: also known as gallbladder stones, they are small solid aggregates, consisting of cholesterol and calcium salts, and represent one of the most common pathologies of the biliary tract.Their presence is often associated with: abscesses, inflammation of the gallbladder, chronic diseases of the gallbladder, gallbladder polyps, gallbladder cancer or biliary tract cancer.
Gallstones are responsible for a strong painful sensation when they obstruct the bile flow; in these situations, they determine the onset of a condition known as acute cholecystitis.
The resulting pain can be dull and persistent or sharp and in waves; it can also sometimes spread to the back.
Other symptoms: nausea, vomiting, profuse sweating, jaundice, pale stools etc.
This lesion is comparable to a "crater-shaped erosion, the depth of which varies from patient to patient."
Generally, the presence of a "duodenal ulcer is linked to the" excessive production of acidic juices by the stomach or to the "infection by Helicobacter pylori.
The pain induced by the duodenal ulcer tends to be burning, dull and continuous; it tends to appear on an empty stomach (therefore before or after meals) and during the night's rest.
Other symptoms: loss of appetite, abdominal bloating, nausea, vomiting etc.
Typically, the resulting painful sensation is in the form of cramps.
Other symptoms: belching, flatulence etc.
When kidney stones are symptomatic, the resulting pain can be very acute, sometimes intolerable. Curiously, the change of position can relieve the painful sensation.
Other symptoms: vomiting, colic, dysuria, anuria, nausea, blood in the urine, etc.
The resulting pain often tends to radiate to the back as well.
Other symptoms: fever, feeling unwell, vomiting, haematuria, dysuria, etc.
The resulting pain can be sharp or it can involve a sense of squeezing.
Other symptoms: fever, cough, chest pain, phlegm, etc.
The resulting pain is very intense and usually appears 48 hours after the consumption of toxic foods.
Other symptoms: vomiting and fever.
The pain that can result from the aforementioned injuries can also be very intense, to the point that the affected person may have difficulty breathing.
Other symptoms: pain when breathing, pain when twisting the torso, pain when sneezing, etc:
The painful sensation that characterizes intercostal neuralgia can be acute and episodic, or dull and constant.
It also tends to be diffuse, meaning it affects different parts of the rib cage (not just the right side).
Other symptoms: pain when breathing, pain when twisting the torso, pain when sneezing, etc:
CAUSES OF PAIN IN THE LOWER RIGHT SIDE
Conditions that can cause right flank pain in the lower abdomen include:
- Appendicitis: is the inflammation of the vermiform appendix. Generally, it derives from an "internal obstruction of the vermiform appendix, consequent to the stagnation of undigested material (solidified fecal material, foreign body, etc.) or to the" hypertrophy of the appendicular lymphatic follicles (whose size increase very often depends on systemic infections or local).
Usually, appendicitis affects the young population, between the ages of 10 and 30.
Other symptoms: general malaise, mild fever, abdominal pain inside the navel, vomiting, diarrhea, etc. - Ectopic pregnancy: is the term that doctors use to indicate a pregnancy that takes place outside the uterus (ectopic ectopic pregnancy) or in an inadequate location of the uterus (ectopic intrauterine pregnancy). Typically, it is the most common cause of right flank pain in pregnant women.
The resulting painful sensation can be acute or dull.
Other symptoms: vaginal bleeding, dizziness, pelvic pain, nausea, fainting etc. - Ovarian cyst: is a small sac filled with fluid, which forms inside or on the outer surface of the ovaries.
The resulting pain can be moderate or severe; generally, it is located in correspondence with the ovary (in this specific case, the right ovary), but it can also spread along the leg (obviously right).
Other symptoms: pelvic pain, pain during sexual intercourse, need to urinate often, dizziness, changes in the normal menstrual cycle, etc. - Constipation: is the medical term used to indicate a condition in which the emission of stool is scarce and / or infrequent.
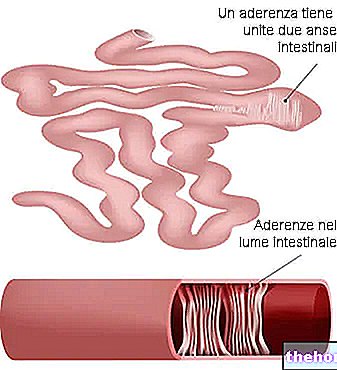
Other symptoms: hard / ribbon-like / dark stools, abdominal swelling, perception of an "obstruction in the abdominal area, etc." - Intestinal obstruction: we speak of intestinal obstruction when a section of the intestine has a blockage / obstruction, which prevents the normal progression of food along the digestive system.
Bowel obstruction is considered a medical emergency as it can lead to life-threatening complications.
The resulting pain is in the form of cramps or bite-like.
Other symptoms: dehydration, abdominal distension, abdominal swelling, bloating, constipation, vomiting, fever, etc. - Irritable bowel syndrome: is a chronic, non-inflammatory, colon disorder that alters intestinal motility.
The resulting pain is generally in the form of cramps.
Other symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal swelling, alvus alterations, etc. - Crohn's disease: it is a type of inflammatory bowel disease and has an autoimmune origin, that is, it arises from a malfunction of the immune system.
Crohn's disease can affect various parts of the colon.
The resulting pain is generally chronic.
Other symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, abdominal swelling, anorexia, asthenia, anal pain, dehydration etc. - Ulcerative colitis: it is another type of inflammatory bowel disease, the causes of which are currently unknown.
In addition to the various sections of the colon, it can also affect the rectum.
As a rule, it affects only the superficial layers of the internal intestinal walls.
Other symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, abdominal swelling, general malaise, blood in stool, night sweats etc. - Abdominal hernia: is the protrusion / protrusion of a bowel (or adjacent tissue), which normally resides in the abdominal cavity. Typically, an abdominal hernia appears following a weakening of the muscle wall that lines and contains the organs of the abdomen.
Other symptoms: bloating, constipation, vomiting, abdominal cramps etc. - Abscess of the psoas muscle: the psoas is a muscle that originates from the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and is inserted at the level of the femur. It contributes to the flexion of the thigh.
Other symptoms: lack of appetite, weight loss, bloating, night sweats etc. - Rectus abdominal muscle hematoma: may appear due to the rupture of an epigastric artery or due to a muscle tear in the rectus muscle.
Generally, the resulting pain begins suddenly and is very acute.
Other symptoms: formation of abdominal mass, fever, flushing, paleness, confusion, etc.
The recognition of the condition at the origin of the painful sensation is fundamental for therapeutic purposes: only by knowing the triggering factors can the treating physician prescribe the most appropriate therapy.
ulcerative irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, early appendicitis or mild kidney stones, doctors prescribe specific drug treatments to patients and a drastic change in eating habits (which are generally incorrect in patients).
Rarely, conditions such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis require surgeon intervention.
To know more:
- Diet and treatment for Crohn's disease
- Treatment / diet and medications for ulcerative colitis
- Treatments for constipation
- Medicines for appendicitis
To know more:
- Treatments and surgery for endometriosis
- Ectopic pregnancy therapy
- Intestinal obstruction therapy
- Surgical treatment of appendicitis
To know more:
- Medicines and treatments for pneumonia

-cos-sintomi-e-primo-soccorso.jpg)