In light of this, myelopathies are: spinal stenosis (which recognizes numerous causes), myelitis (which also has a wide spectrum of possible causes), spinal cord injuries resulting from trauma to the spine and vascular diseases of the spinal cord.
A myelopathy induces different symptoms, depending on what caused it (ie the causative factor) and the affected part of the spinal cord.
Myelopathies require treatment based on the causes and severity of the symptoms; however, such a therapeutic approach is only possible after a scrupulous diagnostic investigation, which also brings to light the precise causes of the pain in the spinal cord.
Brief review of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is, together with the brain, one of the two fundamental components of the central nervous system.
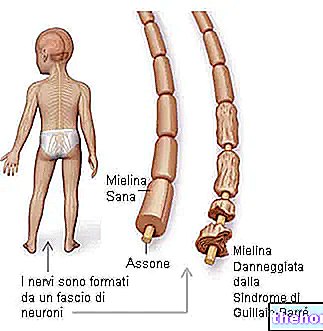
Structurally very complex, this vital nervous organ has several groups of neurons (arranged in white matter and gray matter) and 31 pairs of nerves (the so-called spinal nerves), and has the important task of sorting the incoming and outgoing signals between the different brain areas (lobes of the brain, cerebellum, etc.) and the rest of the organism.
The spinal cord takes place, in order to receive protection, inside the so-called spinal canal, that is the duct resulting from the overlapping of the vertebrae of the spinal column and their characteristic holes.

Based on this list, the picture of myelopathies appears quite simple; in fact, this is only apparently true: conditions such as spinal stenosis and myelitis, for example, are both related to a wide range of causes, which greatly complicate any discussion of myelopathies.
Meaning of the word Myelopathy
The term "myelopathy" is the result of the "union of the word" honey ", which refers to the spinal cord, and the word" patia ", which in medicine means disease.
To remember
The word "myelopathy" should not be confused with the word "myopathy"; the latter, in fact, indicates any disease or suffering of the muscles and their functionality.
of the spine. Also known as spondylosis, this condition is the result of a gradual degeneration of the spine, namely the bodies of the vertebrae (or vertebral bodies).Favored by factors such as old age, obesity and poor posture, spondylosis is the leading cause of spinal stenosis.
Spinal tumors cause vertebral stenosis, because, with their mass (which is constantly expanding), they deprive the spinal cord of the space reserved for it, causing it to compress.
According to the reliable opinion of doctors, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease.

iStock
- The "herniated disc. In medicine, the term" herniated disc "indicates the exit of the nucleus pulposus from its natural site (the intervertebral disc), in the direction of the adjacent nerve structures (adjacent tract of the spinal cord, spinal roots and spinal nerves ) or towards the nearest vertebral bodies.
The herniated disc is the cause of a myelopathy, when the nucleus pulposus invades, with its release, the space reserved for the spinal cord located in the immediate vicinity. - Congenital malformations of the spinal column. Some individuals are born with a narrower than normal spinal canal. The presence of a narrowing of the spinal canal from birth is an example of congenital spinal stenosis.
Myelitis
Myelitis is the medical condition that results from inflammation of the gray matter or white matter of the spinal cord.
Myelitis recognizes numerous causes; in fact, it can depend on viral infections (eg: poliomyelitis, AIDS, varicella virus, herpes zoster and West Nile virus), bacterial infections (eg: tuberculosis, syphilis, meningitis and Lyme disease), fungal infections (eg: Cryptococcus neoformans, Coccidioides immitis, Blastomyces dermatitidis And Histoplasma capsulatum), parasitic infections (ex: Schistosoma, Taenia solium And Trichinella spiralis), autoimmune diseases (eg: optic neuromyelitis, Sjogren's syndrome, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus) and even some vaccines (eg: hepatitis B, vaccination for measles, mumps and rubella, and vaccine for diphtheria and tetanus).
The inflammation induced by myelitis alters the functioning of the spinal cord; this is due to the damage that the aforementioned inflammation produces to the neurons of the gray and white matter of the affected spinal cord.
Spinal cord injuries of traumatic origin
Spinal cord injuries of traumatic origin are the consequence of severe trauma to the spine, which subject the latter to abnormal movements (eg: hyperflexion, hyperextension, rotation and lateral sliding) or which undermine its integrity (cause the fracture of a vertebral body, the resulting fragments of which injure the spinal cord).

Among the most frequent causes of such trauma to the spine, there are: motorcycle and car accidents, accidental falls on the back (eg falls from a horse), acts of physical violence and more (eg: gunshot wounds ) and back injuries due to contact sports (eg rugby, American football, etc.).
Vascular myelopathy
By vascular myelopathy, doctors mean a more or less severe suffering of the spinal cord, due to an "alteration of the supply of oxygenated blood to the latter" (oxygenated blood is essential for the survival of any tissue and organ in the human body, marrow including spinal cord).
The medical conditions that can induce vascular myelopathy include: atherosclerosis (with its occlusive phenomena), diabetes-induced angiopathy, hematomyelia (it is internal hemorrhage in the spinal cord), aortic dissection, polyarteritis nodosa (consists of an "inflammation of the arterial vessels with harmful effects), the aforementioned systemic lupus erythematosus, neurosyphilis and medullary ischemic phenomena (eg: medullary TIA).
When severe, vascular myelopathy can affect the blood supply to the spinal cord so deeply that it kills the spinal cord by necrosis; spinal cord necrosis as a result of vascular myelopathy is an example of a heart attack, ie the process of death of an organ or tissue resulting from a lack of oxygenated blood.
Classification of myelopathies
There are two completely different systems of classifying myelopathies: the classification system that distinguishes myelopathies into acute and chronic, and the classification system that distinguishes myelopathies into cervical (cervical myelopathy) thoracic (thoracic myelopathy) and lumbar (lumbar myelopathy).
ACUTE / CHRONIC CLASSIFICATION
The classification of myelopathies into acute and chronic uses, as a distinctive parameter, the speed with which a certain suffering of the spinal cord establishes its symptoms. In detail, all myelopathies with rapid and sudden onset are acute, while all myelopathies with gradual and progressive onset are chronic.
Examples of acute myelopathies are:
- Spinal injuries of traumatic origin;
- Vascular myelopathy connected to haemorrhagic phenomena (hematomyelia);
- Transverse myelitis (it is a particular form of myelitis),
- Spinal stenosis related to the presence of a spinal tumor.
Examples of chronic myelopathies are:
- Spinal stenosis due to the presence of spondylosis (osteoarthritis of the spine), rheumatoid arthritis or herniated disc;
- Myelitis related to multiple sclerosis;
- Myelitis due to syphilis.
CERVICAL-THORACIC-LUMBAR CLASSIFICATION
The classification of myelopathies into cervical, thoracic and lumbar uses, as a parameter of distinction, the tract of the spinal cord that is the victim of the suffering. From this it follows that:
- I am cervical all myelopathies affecting the cervical tract of the spinal cord. The cervical tract of the spinal cord is the upper section of the latter;
- I am thoracic all myelopathies affecting the thoracic tract of the spinal cord. The thoracic tract of the spinal cord is the intermediate section of the latter, starting immediately after the cervical tract;
- I am finally lumbar all myelopathies affecting the lumbar spine of the spinal cord. The lumbar section of the spinal cord is the lower section of the latter, immediately following the thoracic section.
Without going into the details of the characteristic symptomatology of each possible myelopathy, in a generic list of symptoms and signs typically observed in the presence of a spinal cord disease, the following fall by right:
- Pain in the neck, back and / or extremities (i.e. limbs);
- Sharp pains in the chest and / or abdomen;
- Sense of stiffness in the neck, back and / or extremities;
- Urinary disorders (eg: urinary incontinence and difficulty urinating, etc.) and intestinal disorders (eg: fecal incontinence and constipation);

- Flu symptoms, such as fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, widespread fatigue, loss of appetite, etc .;
- Muscle spasms and muscle fasciculations;
- Loss of reflexes
- Paralysis of the upper and / or lower limbs;
- Sense of muscle weakness in the upper and lower limbs;
- Loss of skin sensation, tenderness, tingling and / or burning sensation in the hands and / or feet (paraesthesia);
- Sense of numbness in the face;
- Posture instability and difficulty walking
- Muscle atrophy;
- Formation of fluid-filled cysts in the spinal cord (syringomyelia).
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment or if particularly severe, myelopathies are conditions that can give rise to complications; among these complications, the following are worth mentioning: the chronicity of pain, the increasingly frequent recurrence of muscle spasms, total paralysis of the upper and / or lower limbs, total loss of control of urinary and fecal function, the appearance of sexual dysfunctions ( erectile dysfunction, for the man, and anorgasmia, for the woman), the state of depression that can result from experiencing the previous complications and, finally, the onset of serious and life-threatening cardiovascular problems.
, physical examination, a thorough neurological examination, radiological tests such as myelography, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and CT of the spine, blood tests and lumbar puncture.In addition to providing a lot of information about the present condition, such a thorough diagnostic procedure allows, in uncertain cases, to exclude, step by step, pathologies with similar symptoms, but not associated with spinal cord suffering (differential diagnosis).
Why is it important to identify the causes of myelopathy?
The knowledge of the causes of myelopathy is very important, because it is on the causal factors that the planning of the most adequate therapy depends.
corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, in order to alleviate the inflammation present and mitigate the improper response of the immune system (which is the causative factor of the aforementioned inflammation);