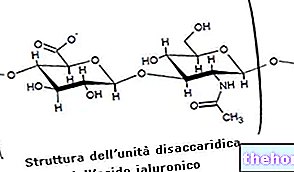
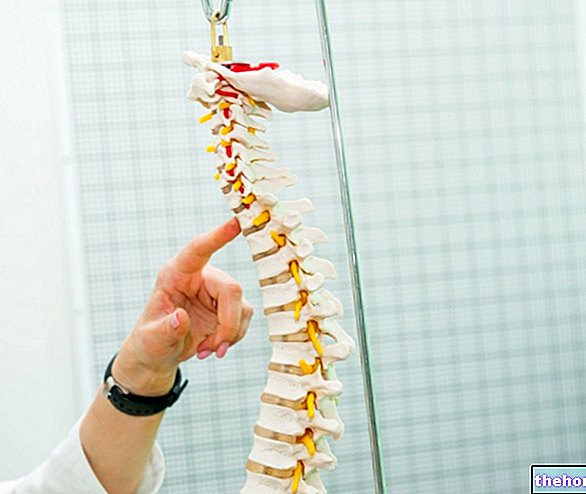
posterior) is a degenerative disease involving the joints of the spinal column.JOINTS are structures that connect or "articulate" the bones together. In this context, articular cartilage is a thin, smooth and elastic tissue that covers the end parts of the bones and allows frictionless sliding between the joint heads when they perform reciprocal movements. If the joint cartilage progressively reduces in thickness, in addition to causing chronic pain, it can limit the movement of the affected joints. Osteoarthritis does not appear suddenly, but over the years. It is, in fact, a wear and tear disease, in the sense that the joints suffer damage that, in some way, is related to the excessive use or overload of the same. Not surprisingly, osteoarthritis is often a consequence of traumatic events and processes related to aging. The degenerative process at the base of osteoarthritis is slow and progressive. Gradually, the cartilage thins, therefore also the synovial membrane and the bones involved in the joint movement can suffer damage. The bone heads are no longer protected, in fact, from the cartilage and can friction on each other. Any joint can be affected by osteoarthritis, but some are more frequently "targeted" than others. The joints most stressed by weight and activity are affected above all, therefore: spine, knees, hips, shoulders and hands.
Tags:
health-of the esophagus nutrition drugs-hypertension

This process occurs when an imbalance between functional stress and cartilage resistance occurs in a joint, favored or aggravated by local or general factors, such as concomitant diseases, age, genetic predisposition and lifestyle.
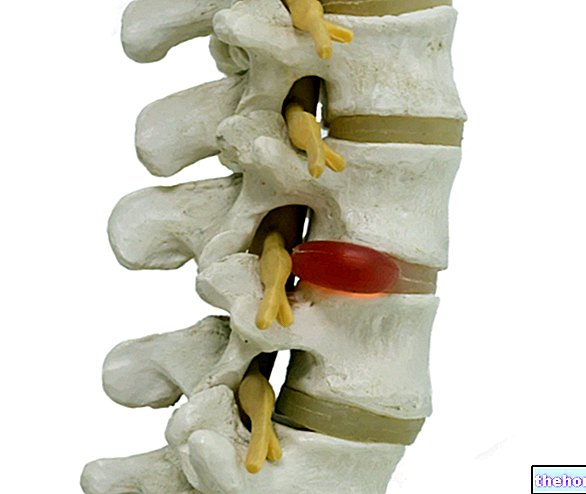
In interapophyseal arthrosis, wear and erosions typically affect the articular cartilage located between the vertebral processes. These structures undergo a slow deterioration, which causes pain and other problems, including back stiffness and limited mobility.
Unfortunately, interapophyseal arthrosis is irreversible, since the cartilage does not regenerate spontaneously. However, a series of pharmacological and surgical treatments can relieve pain and improve the functions of the affected joints.
it is a joint disease caused by a degenerative process. The latter always starts from the articular cartilages and then gradually extends to the entire joint.