Symptoms
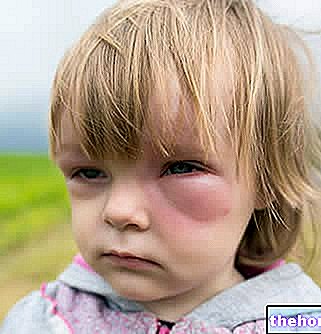
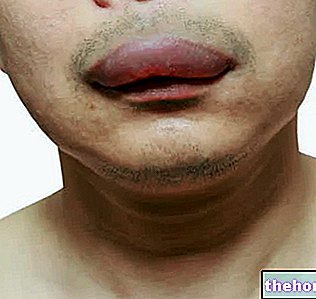
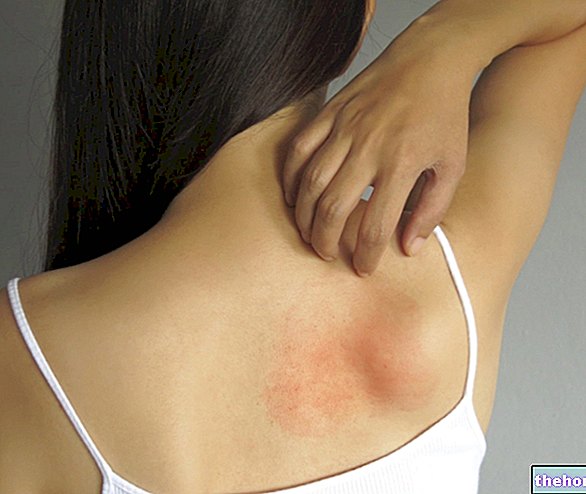
Nickel allergy is the most common cause of allergic contact dermatitis, a disease that produces skin lesions very similar to those of eczema: at first blisters form on the surface of the skin, which appears red, itchy, swollen and covered with vesicles, which can rupture and form crusts; subsequently, if contact with nickel persists over time, the skin thickens and peels, cracking and taking on a darker color.

Most likely this man does not suffer from nickel allergy ...
In this sense, only the parts of the body directly exposed to the allergen are affected and it is precisely for this reason that we speak of allergic contact dermatitis (although sometimes these symptoms can also occur in other body regions).
Over time, the typical manifestations of nickel allergy can become very uncomfortable and painful. However, their intensity within the population considered allergic (statistics speak of an incidence around 10%) is variable. according to the degree of nickel allergy.
Why Compare?
Also based on genetic factors - which justify a certain degree of familiarity with the disease - the immune system of allergic individuals reacts to nickel triggering a more or less severe reaction. The metal is in fact recognized as something foreign, like a splinter or a pathogenic microorganism, and as such is attacked through an inflammatory reaction characterized by the strong release of histamine by mast cells. This substance increases the permeability of the small blood vessels of the affected area, favoring the accumulation of liquids (vesicles), white blood cells and other substances responsible for the confinement and destruction of the damaging agent; histamine also produces severe itching locally.
Normally, after coming into contact with the skin of allergic people, nickel causes a rash within 12 to 48 hours, after which it can take two to four weeks for the rash to completely resolve.
A predisposing factor is undoubtedly sweating, which amplifies and accelerates the allergic response of the individual. The same goes for those who - for example for a particular work activity - expose the areas in contact with nickel to water and humidity.
As anticipated, family members of relatives suffering from the same problem are also at particular risk of developing an allergy.
Where is nickel found
Nickel in Objects
Nickel is a heavy metal typically found in some jewelry, zippers and jeans buttons. In non-allergic people, contact with nickel does not cause any problems, but about 10% of the population develops an allergic reaction characterized by the symptoms described above. The main offenders in this regard are earrings, rings, necklaces, straps, spectacle frames, bracelets and body-piercing jewelry; in fact, nickel is commonly present in many metal products, including gold jewelry and various alloys, contained, for example, in coins, keys, screwdrivers, buckles, bra hooks, etc. ..
Nickel in Food
However, nickel is not only found in clothing and jewelry, but also in the foods we eat every day. In people with a more severe degree of allergy, even the normal diet can trigger an unwanted allergic reaction. Unfortunately, it is not possible to indicate the nickel content of foods, since this parameter is strongly influenced by the soil in which they were grown (vegetables), by the pesticides used and by the equipment and substances used during the various steps of the production chain.
If the diet causes problems in this sense (affecting only a small percentage of people at risk), the doctor prescribes an exclusion diet, also recommending the use of cutlery, pots and other non-metallic kitchen utensils.
Normally excluded foods include chocolate, cocoa, dried fruit, legumes, tea, spinach, mushrooms, vegetable margarines, herring and oysters.
To learn more, read: Nickel in food "
Diagnosis and Treatment
See also: Medicines for the treatment of nickel allergy
The diagnosis of nickel allergy depends on the characteristics of the skin lesions and the recent contact with a possible object containing the metal. In doubtful cases, however, it is possible to resort to the so-called patch test: on the upper part of the patient's back, very small patches containing the suspected allergenic substances are applied, after which the local skin reaction is evaluated 48-72 hours later; if removing the patch containing nickel leaves a patch of inflamed skin underneath, the diagnosis of nickel allergy is positive. We remind you that in this regard, such small quantities of allergens are used as to be risk-free even in cases of strong sensitivity to the substance.
Nickel allergy, being a reaction of the immune system, is not curable. The best weapon is prevention, obviously based on avoiding contact with objects containing the metal. In the event of a particularly violent reaction, it is still possible to take medicines capable of relieving symptoms and accelerating their resolution; in this regard, the doctor may prescribe topical creams based on corticosteroids or tablets containing antihistamines to the person with a nickel allergy.